Life: The Science of Biology, 9e
... undisturbed sedimentary rock (formed by the accumulation of grains on the bottom of bodies of water). • The oldest layers are at the bottom, youngest at the top. • First observed in the 17th century by ...
... undisturbed sedimentary rock (formed by the accumulation of grains on the bottom of bodies of water). • The oldest layers are at the bottom, youngest at the top. • First observed in the 17th century by ...
The Geologic Time Scale
... Each era is subdivided into periods, each of which is characterized by a somewhat less profound change in life forms as compared with the eras The periods of the Cenozoic are divided into still smaller units called epochs The epochs of other periods are not usually referred to by specific names ...
... Each era is subdivided into periods, each of which is characterized by a somewhat less profound change in life forms as compared with the eras The periods of the Cenozoic are divided into still smaller units called epochs The epochs of other periods are not usually referred to by specific names ...
Lab 2: Volcanoes, Plutons, and Igneous Rocks
... Most minerals grow approximately the same size when magmas crystallize at one depth within the Earth’s crust, and the resulting rocks have an equigranular texture. We can differentiate between two types of equigranular texture: coarse-grained and fine-grained. Because intrusive magmas cool relativel ...
... Most minerals grow approximately the same size when magmas crystallize at one depth within the Earth’s crust, and the resulting rocks have an equigranular texture. We can differentiate between two types of equigranular texture: coarse-grained and fine-grained. Because intrusive magmas cool relativel ...
Exam 2
... a. The age of relatively old igneous rocks (> 70,000 years) b. The age of relatively old fossils (> 70,000 years) c. The age of relatively young igneous rocks (< 70,000 years) d. The age of relatively young fossils (< 70,000 years) 16. In what climatic conditions is frost wedging most effective? a. ...
... a. The age of relatively old igneous rocks (> 70,000 years) b. The age of relatively old fossils (> 70,000 years) c. The age of relatively young igneous rocks (< 70,000 years) d. The age of relatively young fossils (< 70,000 years) 16. In what climatic conditions is frost wedging most effective? a. ...
Sedimentary Rock Identification
... All rocks can be subjected to metamorphic processes, so a wide variety of metamorphic rocks exist. Metamorphic rocks form when a pre-existing rock is subjected to intense heat and pressure to chemically and/or physically alter the rock into a new rock type (e.g., limestone being metamorphosed into m ...
... All rocks can be subjected to metamorphic processes, so a wide variety of metamorphic rocks exist. Metamorphic rocks form when a pre-existing rock is subjected to intense heat and pressure to chemically and/or physically alter the rock into a new rock type (e.g., limestone being metamorphosed into m ...
Remediation Sheet for Retake
... 6. The ______________________ of a rock is determined by the sizes, shapes, and positions of the minerals the rock contains. 7. ______________________metamorphic rock contains minerals that are arranged in planes or bands. 8. The most characteristic property of sedimentary rock is __________________ ...
... 6. The ______________________ of a rock is determined by the sizes, shapes, and positions of the minerals the rock contains. 7. ______________________metamorphic rock contains minerals that are arranged in planes or bands. 8. The most characteristic property of sedimentary rock is __________________ ...
This MUST be returned following next week`s exam
... 3. Are porphyritic rocks more common at continental rift zones or mid-ocean ridges? Explain your answer (3) Porphyritic rocks are rocks that have both large and small crystals. This indicates that the rock cooled at two different rates. This would be more likely at a rift zone. Since C-crust is thic ...
... 3. Are porphyritic rocks more common at continental rift zones or mid-ocean ridges? Explain your answer (3) Porphyritic rocks are rocks that have both large and small crystals. This indicates that the rock cooled at two different rates. This would be more likely at a rift zone. Since C-crust is thic ...
Rocks - OCMS Science
... Metamorphic Changes! • When rock changes into metamorphic rock, its appearance, texture, crystal structure, and mineral content change. Metamorphic rock can form out of igneous, sedimentary, or other metamorphic rock. ...
... Metamorphic Changes! • When rock changes into metamorphic rock, its appearance, texture, crystal structure, and mineral content change. Metamorphic rock can form out of igneous, sedimentary, or other metamorphic rock. ...
File
... Scientists think that Earth began as a melted mixture of many different materials. These materials underwent a physical change as they cooled and solidified. These became the first igneous rocks. Igneous rock continues to form today. Liquid rock changes from a liquid to a solid, when lava that is br ...
... Scientists think that Earth began as a melted mixture of many different materials. These materials underwent a physical change as they cooled and solidified. These became the first igneous rocks. Igneous rock continues to form today. Liquid rock changes from a liquid to a solid, when lava that is br ...
Rocks pupil notes - Lesmahagow High School
... • Learning how crystals form in igneous rock. • By the end of the lesson... • You will be able to explain why crystals in rock are different sizes. • We’ll do this by…. • Doing an experiment to cool hot liquid and examining what it looks like afterwards. ...
... • Learning how crystals form in igneous rock. • By the end of the lesson... • You will be able to explain why crystals in rock are different sizes. • We’ll do this by…. • Doing an experiment to cool hot liquid and examining what it looks like afterwards. ...
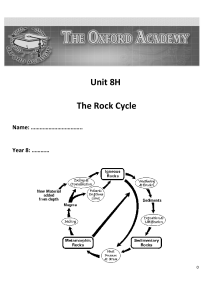
The Rock Cycle
... All rock can be heated. If it is re-melted turning back into magma, it will return to earth’s surface as igneous rock. But what happens if the temperature doesn’t melt the rock? And where does the heat come from? Inside Earth there is heat from pressure (push your hands together very hard and feel t ...
... All rock can be heated. If it is re-melted turning back into magma, it will return to earth’s surface as igneous rock. But what happens if the temperature doesn’t melt the rock? And where does the heat come from? Inside Earth there is heat from pressure (push your hands together very hard and feel t ...
The Geologic Time Scale
... Each era is subdivided into periods, each of which is characterized by a somewhat less profound change in life forms as compared with the eras The periods of the Cenozoic are divided into still smaller units called epochs The epochs of other periods are not usually referred to by specific names ...
... Each era is subdivided into periods, each of which is characterized by a somewhat less profound change in life forms as compared with the eras The periods of the Cenozoic are divided into still smaller units called epochs The epochs of other periods are not usually referred to by specific names ...
Sedimentary Rock with DR 2.2
... 14. The more quickly an igneous rock cools and solidifies the ___smaller_______ the grain. 15. Where will igneous rock that has cooled most quickly be found? ___________exterior of the ...
... 14. The more quickly an igneous rock cools and solidifies the ___smaller_______ the grain. 15. Where will igneous rock that has cooled most quickly be found? ___________exterior of the ...
NAME --------------------------------------------------------------
... 3.(a)Differatiate a mineral and arock -a mineral is any naturally occurring crystalline inorganic substance with definite chemical composition and physical properties that form part of the earth;s crust,while -a rock is any naturally occurring aggregate of mineral particles of the earth;s crust. (b) ...
... 3.(a)Differatiate a mineral and arock -a mineral is any naturally occurring crystalline inorganic substance with definite chemical composition and physical properties that form part of the earth;s crust,while -a rock is any naturally occurring aggregate of mineral particles of the earth;s crust. (b) ...
stAIR Project
... the earth. It takes temperatures between 600 and 1,300 degrees Celsius (1,100 and 2,400 degrees Fahrenheit) to melt a rock, turning it into a substance called magma (molten rock). ...
... the earth. It takes temperatures between 600 and 1,300 degrees Celsius (1,100 and 2,400 degrees Fahrenheit) to melt a rock, turning it into a substance called magma (molten rock). ...
8H booklet - Oxfordscience
... rock), shale (sedimentary rock) or slate (metamorphic rock). Gneiss Rocks: Gneiss rocks are metamorphic rocks. These rocks have been granite (igneous rock). Grains in the rock flattened through tremendous heat and pressure. Conglomerate Rocks: Conglomerate rocks are sedimentary rocks. They are made ...
... rock), shale (sedimentary rock) or slate (metamorphic rock). Gneiss Rocks: Gneiss rocks are metamorphic rocks. These rocks have been granite (igneous rock). Grains in the rock flattened through tremendous heat and pressure. Conglomerate Rocks: Conglomerate rocks are sedimentary rocks. They are made ...
Air, Land , and Water
... mixture of gases, including nitrogen and oxygen with small amounts of water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other trace gases. ...
... mixture of gases, including nitrogen and oxygen with small amounts of water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other trace gases. ...
Type of Rock
... Metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks are changed by heat and pressure. Rocks formed by metamorphism (to change) look very different from the original rock. Most metamorphism occurs as either regional or contact metamorphism. Contact metamorphism occurs when magma intrudes (forces its way into) ...
... Metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks are changed by heat and pressure. Rocks formed by metamorphism (to change) look very different from the original rock. Most metamorphism occurs as either regional or contact metamorphism. Contact metamorphism occurs when magma intrudes (forces its way into) ...
Relative Time and Correlation
... A. ____________________________ 1.Sedimentary rock layers, or strata, were originally deposited as relatively horizontal sheets of sediment. 2.Strata that do not retain their original horizontality have been displaced by movements of Earth’s crust. ...
... A. ____________________________ 1.Sedimentary rock layers, or strata, were originally deposited as relatively horizontal sheets of sediment. 2.Strata that do not retain their original horizontality have been displaced by movements of Earth’s crust. ...
JBES-Vol5No6-p338-344 - International network for natural
... collision of sialic masses. Many types of granite, however, may post date the thickening event by tens of millions of years. 2) Because the crust is solid in its normal state, some thermal disturbance is required to form granitoids. 3) Most workers are of the opinion that the majority of granitoids ...
... collision of sialic masses. Many types of granite, however, may post date the thickening event by tens of millions of years. 2) Because the crust is solid in its normal state, some thermal disturbance is required to form granitoids. 3) Most workers are of the opinion that the majority of granitoids ...
Chapter 6.1
... The siltstone has low porosity, so the oil will not flow though it. The company would have to drill though the siltstone to reach the oil-containing shale. If the layer of siltstone is too thick, the company might not be able to drill deep enough to reach the oil. ...
... The siltstone has low porosity, so the oil will not flow though it. The company would have to drill though the siltstone to reach the oil-containing shale. If the layer of siltstone is too thick, the company might not be able to drill deep enough to reach the oil. ...
Earth Sciences 089G MIDTERM EXAMINATION MARKING KEY Part
... Significance Minerals with the same composition but different crystal forms. The product of stress-induced orientation of mineral grains in regional metamorphic rocks. Process primarily responsible for the destruction of original rock textures during metamorphism. Local zone of alteration of country ...
... Significance Minerals with the same composition but different crystal forms. The product of stress-induced orientation of mineral grains in regional metamorphic rocks. Process primarily responsible for the destruction of original rock textures during metamorphism. Local zone of alteration of country ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.