Mineralogy, geochemistry and origin of Chaharfarsakh intrusive and
... and dacite are main extrusive rocks in Chaharfarsakh bodies and composed of plagioclase, hornblende, quartz, biotite minerals with porphyritic texture. Chaharfarsakh granitoid have subalkaline, meta to peralominouse nature, I type granitoids and show tendancy to contamination continental crust.Tecto ...
... and dacite are main extrusive rocks in Chaharfarsakh bodies and composed of plagioclase, hornblende, quartz, biotite minerals with porphyritic texture. Chaharfarsakh granitoid have subalkaline, meta to peralominouse nature, I type granitoids and show tendancy to contamination continental crust.Tecto ...
Save - PDAC
... Sedimentary rocks form at the Earth’s surface – no great heat or pressure here! They are made of weathered and eroded pieces of preexisting rocks which ended up being dropped or deposited by wind, water or ice. When these sediments were buried by more layers of sand, gravel or mud, the fragments wer ...
... Sedimentary rocks form at the Earth’s surface – no great heat or pressure here! They are made of weathered and eroded pieces of preexisting rocks which ended up being dropped or deposited by wind, water or ice. When these sediments were buried by more layers of sand, gravel or mud, the fragments wer ...
Most fossils form from organisms buried in sediments soon after they
... Where do most fossils form? Plants and animals that lived in or near water were preserved more often than other organisms. Why do we usually only find the bones, shells, teeth, seeds and woody stems of an organism fossilized? In many cases, the soft flesh of dead organisms was eaten by animals befor ...
... Where do most fossils form? Plants and animals that lived in or near water were preserved more often than other organisms. Why do we usually only find the bones, shells, teeth, seeds and woody stems of an organism fossilized? In many cases, the soft flesh of dead organisms was eaten by animals befor ...
rock cycle
... Bowen’s Reaction Series • Bowen’s reaction series the simplified pattern that illustrates the order in which minerals crystallize from cooling magma according to their chemical composition and melting point • The pattern of mineral formation from magma depends on the chemical composition of the magm ...
... Bowen’s Reaction Series • Bowen’s reaction series the simplified pattern that illustrates the order in which minerals crystallize from cooling magma according to their chemical composition and melting point • The pattern of mineral formation from magma depends on the chemical composition of the magm ...
rock cycle
... Bowen’s Reaction Series • Bowen’s reaction series the simplified pattern that illustrates the order in which minerals crystallize from cooling magma according to their chemical composition and melting point • The pattern of mineral formation from magma depends on the chemical composition of the magm ...
... Bowen’s Reaction Series • Bowen’s reaction series the simplified pattern that illustrates the order in which minerals crystallize from cooling magma according to their chemical composition and melting point • The pattern of mineral formation from magma depends on the chemical composition of the magm ...
Absolute vs. Relative Dating of Rocks
... Scientists use a method called radioactive decay to determine the absolute age of a rock. Rocks contain thousands of particles called isotopes that decay (fall apart) over time. As they decay, they turn from one isotope to another. For example: ...
... Scientists use a method called radioactive decay to determine the absolute age of a rock. Rocks contain thousands of particles called isotopes that decay (fall apart) over time. As they decay, they turn from one isotope to another. For example: ...
Assignment Checklist Pet Rock Project Unit Ti
... clues to your rock’s origin. Be sure to tell if it was broken off a ledge, or just loose on the ground. Was it near a stream? Was in found in a ditch. Where did the ditch begin and end? What is the physical appearance of your rock? Color, texture or layering, mass, volume, density How was your rock ...
... clues to your rock’s origin. Be sure to tell if it was broken off a ledge, or just loose on the ground. Was it near a stream? Was in found in a ditch. Where did the ditch begin and end? What is the physical appearance of your rock? Color, texture or layering, mass, volume, density How was your rock ...
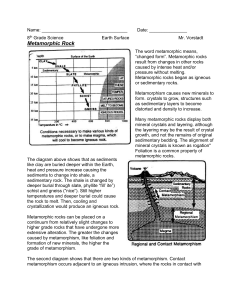
Name: Date: 8th Grade Science Earth Surface Mr. Vorstadt
... the intrusion have been baked. But, when a large mass of rock is buried deep within the Earth, heat and pressure can cause widespread regional metamorphism. Most of the rocks of Westchester probably began as a mixture of sedimentary and igneous rocks, including sandstone, shale, limestone and basal ...
... the intrusion have been baked. But, when a large mass of rock is buried deep within the Earth, heat and pressure can cause widespread regional metamorphism. Most of the rocks of Westchester probably began as a mixture of sedimentary and igneous rocks, including sandstone, shale, limestone and basal ...
Rocks WebQuest!
... little pieces become cemented together. There are other types of sedimentary rocks whose particles do not come from broken rock fragments. Chemical sedimentary rocks are made of mineral crystals such as halite and gypsum formed by chemical processes. The sediment particles of organic sedimentary roc ...
... little pieces become cemented together. There are other types of sedimentary rocks whose particles do not come from broken rock fragments. Chemical sedimentary rocks are made of mineral crystals such as halite and gypsum formed by chemical processes. The sediment particles of organic sedimentary roc ...
Section
... 3. A solid material made up of one or more minerals or other substances, including the remains of once-living things is called ___. Rock forming ___ minerals. ...
... 3. A solid material made up of one or more minerals or other substances, including the remains of once-living things is called ___. Rock forming ___ minerals. ...
Metamorphic reading
... of form.” This describes how some rocks take on a whole new look when they are under great temperatures and pressures. Not only do the resulting new rocks look different, they have recrystallized and might be chemically changed too. New metamorphic rocks can form from any existing type of rock – ign ...
... of form.” This describes how some rocks take on a whole new look when they are under great temperatures and pressures. Not only do the resulting new rocks look different, they have recrystallized and might be chemically changed too. New metamorphic rocks can form from any existing type of rock – ign ...
study guide part 2
... 1. What are the parts of animals most likely to be preserved? -Hard parts such as bones, shells, or teeth 2. What is the isotope scientist use to find out how old a fossil is ? -Carbon-14 or C-14 3. Law of Superposition states -the oldest rocks are at the bottom, and youngest rocks are near the surf ...
... 1. What are the parts of animals most likely to be preserved? -Hard parts such as bones, shells, or teeth 2. What is the isotope scientist use to find out how old a fossil is ? -Carbon-14 or C-14 3. Law of Superposition states -the oldest rocks are at the bottom, and youngest rocks are near the surf ...
Multiple Choice 3. ______ is a major dissolved volatile constituent in
... b. pressure c. chemical action d. all of these 32. ____________ is a strong, parallel alignment of different mineral bands in a metamorphic rock. a. Rock cleavage b. Foliation c. Stress streaking d. Marbleizing 34. The common rock produced by the metamorphism of limestone is __________. a. marble b. ...
... b. pressure c. chemical action d. all of these 32. ____________ is a strong, parallel alignment of different mineral bands in a metamorphic rock. a. Rock cleavage b. Foliation c. Stress streaking d. Marbleizing 34. The common rock produced by the metamorphism of limestone is __________. a. marble b. ...
The Rock Cycle PPT
... change into a ___________ metamorphic ______. rock In some cases, the rock gets hot enough to melt into _________. magma The magma eventually cools to form rock igneous __________ ______. ...
... change into a ___________ metamorphic ______. rock In some cases, the rock gets hot enough to melt into _________. magma The magma eventually cools to form rock igneous __________ ______. ...
Lab 5
... 19. In what depositional environment did rock R25 form (see diagram above)? Hint: these kinds of rocks are called evaporites. Explain how they form. ...
... 19. In what depositional environment did rock R25 form (see diagram above)? Hint: these kinds of rocks are called evaporites. Explain how they form. ...
homework-igneous-rock-5.1-5.2
... ___________________________4. Magma is often a slushy mix of molten rock, gases and mineral crystals. ___________________________5. Silica is the most abundant compound found in magma. ___________________________6. Magmas are classified as basaltic, andesitic, or rhyolitic. _________________________ ...
... ___________________________4. Magma is often a slushy mix of molten rock, gases and mineral crystals. ___________________________5. Silica is the most abundant compound found in magma. ___________________________6. Magmas are classified as basaltic, andesitic, or rhyolitic. _________________________ ...
Pertemuan 4 - Sri Atmaja P. Rosyidi
... usually mechanically weak and can be ripped and grid roller. They are not widely used in rock making as typically prone to abrasion and erosion and moisture sensitive and of suspect durability. ...
... usually mechanically weak and can be ripped and grid roller. They are not widely used in rock making as typically prone to abrasion and erosion and moisture sensitive and of suspect durability. ...
Fossils
... Fossils are the remains or traces of prehistoric life. Fossils have been used to divide geologic time into eons, eras, periods, and epochs. ...
... Fossils are the remains or traces of prehistoric life. Fossils have been used to divide geologic time into eons, eras, periods, and epochs. ...
Earth Materials
... • composition, which tells you what minerals are in it, and therefore what magma it came from, and; • the texture, which indicates whether the rock cooled quickly or slowly (extrusive or ...
... • composition, which tells you what minerals are in it, and therefore what magma it came from, and; • the texture, which indicates whether the rock cooled quickly or slowly (extrusive or ...
Lab6Siliciclastic14
... Few modern sediments or sandstones, including marine turbidites, contain significant fine-grained matrix. The question is thus are all greywackes produced by diagenesis of lithic arenite protoliths, or was there something different about the transport and depositional mechanism of greywackes in the ...
... Few modern sediments or sandstones, including marine turbidites, contain significant fine-grained matrix. The question is thus are all greywackes produced by diagenesis of lithic arenite protoliths, or was there something different about the transport and depositional mechanism of greywackes in the ...
Glaciers
... Wind can change the shape of land • Wind easily picks up and carries beach and desert sand • Wind is more likely to cause erosion during a dry period • Sediments that wind carries also weather th ...
... Wind can change the shape of land • Wind easily picks up and carries beach and desert sand • Wind is more likely to cause erosion during a dry period • Sediments that wind carries also weather th ...
Are you Ready to Rock
... The name Metamorphic comes from the Greek to "change form” •Metamorphic rock is formed by applying great pressure and temperature to existing rock converting it into a new distinct type of rock. •Igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and even other metamorphic rocks and be modified into metamorphic rock ...
... The name Metamorphic comes from the Greek to "change form” •Metamorphic rock is formed by applying great pressure and temperature to existing rock converting it into a new distinct type of rock. •Igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and even other metamorphic rocks and be modified into metamorphic rock ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.