Activity Description/Assignment
... galena, hematite, and pyrite. Texture, mineral composition, and the relationship between texture and genesis are integral parts of the igneous rock exercise. A cross section containing typical igneous rock bodies has questions to help students focus on the geological context of the rocks they are id ...
... galena, hematite, and pyrite. Texture, mineral composition, and the relationship between texture and genesis are integral parts of the igneous rock exercise. A cross section containing typical igneous rock bodies has questions to help students focus on the geological context of the rocks they are id ...
rocks and minerals webquest
... old mine that has been vacant for years. They plan to search the newly found territory, and hope to discover new rocks and minerals that can be added to their collection. The only problem is, that the mine is too big for them to search alone, and they are asking for your help. Are your prepared to g ...
... old mine that has been vacant for years. They plan to search the newly found territory, and hope to discover new rocks and minerals that can be added to their collection. The only problem is, that the mine is too big for them to search alone, and they are asking for your help. Are your prepared to g ...
Rock Study extras
... Biotite: a typically brown to black rock-forming mineral present in at least some percentage in most igneous and both regional and contact metamorphic rocks Feldspar: the major constituent of many igneous and metamorphic rocks; they form at medium to high temperature and at some depth; Ralph Waldo E ...
... Biotite: a typically brown to black rock-forming mineral present in at least some percentage in most igneous and both regional and contact metamorphic rocks Feldspar: the major constituent of many igneous and metamorphic rocks; they form at medium to high temperature and at some depth; Ralph Waldo E ...
Rocks and Minerals Lesson 5
... because they are often a combination of minerals and other materials. He recommends that we start with investigating the rocks we made in class. The geologist would like us to prepare a report of the minerals found in the rocks we created and describe the properties we observe. To assist in our rock ...
... because they are often a combination of minerals and other materials. He recommends that we start with investigating the rocks we made in class. The geologist would like us to prepare a report of the minerals found in the rocks we created and describe the properties we observe. To assist in our rock ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... the result of the application of heat, pressure and directed stress, or some combination of these effects applied to preexisting rock of any type. The process by which metamorphic rocks are produced is called metamorphism. ...
... the result of the application of heat, pressure and directed stress, or some combination of these effects applied to preexisting rock of any type. The process by which metamorphic rocks are produced is called metamorphism. ...
kindernews
... learning the importance of rocks and minerals. Rocks are used in thousands of ways. Without rocks, there would be no bricks, cement, glass, or coal. Rocks make up much of our planet and are mined to provide many of Sally explores a friend’s rock collection the things around us, from cars to computer ...
... learning the importance of rocks and minerals. Rocks are used in thousands of ways. Without rocks, there would be no bricks, cement, glass, or coal. Rocks make up much of our planet and are mined to provide many of Sally explores a friend’s rock collection the things around us, from cars to computer ...
Coasts Revision PowerPoint 1
... the energy to pick up sand particles and pebbles and hurl them at the cliff face. This ‘sand blasting’ effect is thought to be the most rapid process of coastal erosion in the UK. • Attrition: rocks and pebbles are constantly colliding with each other as they are moved by waves. This action reduces ...
... the energy to pick up sand particles and pebbles and hurl them at the cliff face. This ‘sand blasting’ effect is thought to be the most rapid process of coastal erosion in the UK. • Attrition: rocks and pebbles are constantly colliding with each other as they are moved by waves. This action reduces ...
ES BW 1/3/2017 Name_________________________
... pressure c. Minerals evaporating out of liquid solution d. The cooling of molten rock 4. When determining the exact age of a rock or fossil it is known as what? a. Relative Dating b. Absolute Dating c. Carbon Dating d. Fossil Dating 5. When determining the age of a rock in relation to rock around it ...
... pressure c. Minerals evaporating out of liquid solution d. The cooling of molten rock 4. When determining the exact age of a rock or fossil it is known as what? a. Relative Dating b. Absolute Dating c. Carbon Dating d. Fossil Dating 5. When determining the age of a rock in relation to rock around it ...
скачати
... top of each other one after another, each layer was deposited at a later time than the one before it. The youngest layer is on the top, and the oldest layer is on the bottom. This principle was founded by the Danish anatomist Nicolas Steno, who noted that during floods, streams spread across their f ...
... top of each other one after another, each layer was deposited at a later time than the one before it. The youngest layer is on the top, and the oldest layer is on the bottom. This principle was founded by the Danish anatomist Nicolas Steno, who noted that during floods, streams spread across their f ...
Many geologists study rocks and minerals, as rocks
... Rocks are classified according to how they are formed. There are 3 types. They can be igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic. Igneous rocks are hard rocks possessing variably colored crystals. There are two types of igneous rocks: Intrusive igneous rocks, which are formed from magma (molten rock) that ...
... Rocks are classified according to how they are formed. There are 3 types. They can be igneous, sedimentary or metamorphic. Igneous rocks are hard rocks possessing variably colored crystals. There are two types of igneous rocks: Intrusive igneous rocks, which are formed from magma (molten rock) that ...
prompt questionnaire for teachers
... 1. Gives shape to the island of Ireland. 2. An accurate history book. 3. From 2000 million years ago to the present. 4. Can reveal Ireland's history. 5. First maps made of these 150 years ago. (Rocks) ...
... 1. Gives shape to the island of Ireland. 2. An accurate history book. 3. From 2000 million years ago to the present. 4. Can reveal Ireland's history. 5. First maps made of these 150 years ago. (Rocks) ...
Dunbar Geology Walk - Edinburgh Geological Society
... more rainfall and permanent rivers. Sediment accumulating under water is less likely to contain oxidised iron, and so the rocks are more variable in colour, often cream or grey. Much of the Carboniferous sedimentary rock formed in river deltas and it often contains plant fossils and coal layers. As ...
... more rainfall and permanent rivers. Sediment accumulating under water is less likely to contain oxidised iron, and so the rocks are more variable in colour, often cream or grey. Much of the Carboniferous sedimentary rock formed in river deltas and it often contains plant fossils and coal layers. As ...
The Rock Cycle - Holy Angels School
... • In some cases, the rock gets hot enough to melt and form magma, or molten rock. • If the magma reaches Earth’s surface, it is called lava. • The magma and lava eventually cool to form new rock. What are the classes of rocks? • Igneous rock forms when magma cools and hardens. It forms on or beneath ...
... • In some cases, the rock gets hot enough to melt and form magma, or molten rock. • If the magma reaches Earth’s surface, it is called lava. • The magma and lava eventually cool to form new rock. What are the classes of rocks? • Igneous rock forms when magma cools and hardens. It forms on or beneath ...
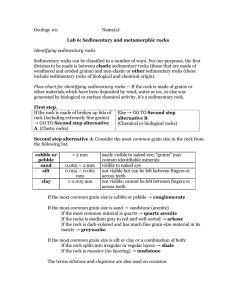
Lab 6
... Metamorphic rocks have been subjected to sufficient heat and/or pressure to melt some of their constituent minerals, but not all of them. As a result of this selective mobilization of chemicals, only certain chemical reactions can occur, and so a whole new set of metamorphic minerals are crystallize ...
... Metamorphic rocks have been subjected to sufficient heat and/or pressure to melt some of their constituent minerals, but not all of them. As a result of this selective mobilization of chemicals, only certain chemical reactions can occur, and so a whole new set of metamorphic minerals are crystallize ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... Unconformities Conformable contact: The boundary between adjacent beds or units does not represent substantial gap in time A succession of beds of nearly the same age that represent ...
... Unconformities Conformable contact: The boundary between adjacent beds or units does not represent substantial gap in time A succession of beds of nearly the same age that represent ...
Geology of the, Maltese Islands
... Igneous rocks – rocks formed from lava/magma. They are composed of crystals and other minerals e.g. granite Sedimentary rocks (gebel bijogeniku)– rocks formed from sediments and bodies of dead organisms which settle on each other when dead (Limestone, Sandstone). Geomorphic rocks – rocks baked by th ...
... Igneous rocks – rocks formed from lava/magma. They are composed of crystals and other minerals e.g. granite Sedimentary rocks (gebel bijogeniku)– rocks formed from sediments and bodies of dead organisms which settle on each other when dead (Limestone, Sandstone). Geomorphic rocks – rocks baked by th ...
Sedimentary Rocks - Mr. Volpe`s Earth Science Emporium
... c. Dissolved minerals crystallize in water or water evaporates and mineral crystals form ...
... c. Dissolved minerals crystallize in water or water evaporates and mineral crystals form ...
Earths Crust review questions
... mostly of Basalt, forming strange octagonal shapes. What type of rock is Basalt? _________________________________________________ 58. Bonus: The “Canadian Shield” is a part of the Earth’s crust that is 2 Billion years old. What type of rock is it made of? ___________________________________________ ...
... mostly of Basalt, forming strange octagonal shapes. What type of rock is Basalt? _________________________________________________ 58. Bonus: The “Canadian Shield” is a part of the Earth’s crust that is 2 Billion years old. What type of rock is it made of? ___________________________________________ ...
relative age dating summary
... Principle of Original Lateral Continuity – Sedimentary rock layers, and lava flows, extend laterally in all directions until they thin to their termination (pinch out) or reach the edges of their basins of deposition. Principle of Unconformities – An unconformity is a rock surface that represents a ...
... Principle of Original Lateral Continuity – Sedimentary rock layers, and lava flows, extend laterally in all directions until they thin to their termination (pinch out) or reach the edges of their basins of deposition. Principle of Unconformities – An unconformity is a rock surface that represents a ...
Rock Classification
... Aim: Into what three groups are rocks classified? Why are they grouped this way? GEO-TOUR #2—Limestone & Coal Limestone is a rock composed of the remains of marine animals (such as shells and other hard parts.) Coal is a rock composed of the remains of LONG ago (like over 300 million years ago!) pla ...
... Aim: Into what three groups are rocks classified? Why are they grouped this way? GEO-TOUR #2—Limestone & Coal Limestone is a rock composed of the remains of marine animals (such as shells and other hard parts.) Coal is a rock composed of the remains of LONG ago (like over 300 million years ago!) pla ...
classifying rocks - Dublin City Schools
... Magma-molten material inside the earth Lava- magma that reaches the surface. Anytime magma cools whether inside the Earth or as lava, minerals crystallize. The size of the crystals depend on the rate of cooling. Cools slow- large crystals Cools fast- small crystals ...
... Magma-molten material inside the earth Lava- magma that reaches the surface. Anytime magma cools whether inside the Earth or as lava, minerals crystallize. The size of the crystals depend on the rate of cooling. Cools slow- large crystals Cools fast- small crystals ...
Earth`s History Lesson 3: Absolute Dating
... • When they form, minerals in igneous rocks often contain only a parent isotope and none of the daughter isotope. • This makes the isotope percentage more accurate and easier to interpret. What are some radiometric dating methods? • Scientists use many different isotopes for radiometric dating. • Th ...
... • When they form, minerals in igneous rocks often contain only a parent isotope and none of the daughter isotope. • This makes the isotope percentage more accurate and easier to interpret. What are some radiometric dating methods? • Scientists use many different isotopes for radiometric dating. • Th ...
Chapter 5 Answer Keys
... 22. discontinuous reaction series 23. continuous reaction series 24. calcium 25. sodium 26. When magma cools rapidly, the calcium-rich cores are unable to react completely with the magma, resulting in a zoned crystal with sodium-rich outer layers and calciumrich cores. 27. At the end of magma crysta ...
... 22. discontinuous reaction series 23. continuous reaction series 24. calcium 25. sodium 26. When magma cools rapidly, the calcium-rich cores are unable to react completely with the magma, resulting in a zoned crystal with sodium-rich outer layers and calciumrich cores. 27. At the end of magma crysta ...
igneous rocks - Faculty Perry, Oklahoma
... Igneous comes from the Latin word ignis, meaning “fire”. Igneous rock is any rock that forms from cooled magma or lava. Extrusive igneous rocks are formed from lava that erupted at the Earth’s surface. Basalt, pumice and obsidian are common extrusive rocks. Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when ma ...
... Igneous comes from the Latin word ignis, meaning “fire”. Igneous rock is any rock that forms from cooled magma or lava. Extrusive igneous rocks are formed from lava that erupted at the Earth’s surface. Basalt, pumice and obsidian are common extrusive rocks. Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when ma ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.