Limestone Scenery - Ingleborough Cave
... air, water and constantly changing temperatures, all of which attack the rocks. This attack, which causes the rocks to disintegrate (break up) or dissolve, is known as weathering. Weathering can be classified into two types - chemical weathering and physical weathering. Examples of both of these can ...
... air, water and constantly changing temperatures, all of which attack the rocks. This attack, which causes the rocks to disintegrate (break up) or dissolve, is known as weathering. Weathering can be classified into two types - chemical weathering and physical weathering. Examples of both of these can ...
Heat Unit Test - Effingham County Schools
... **20 – 30 were answered and discussed in class. Answers are on answer sheet that we made in class. 20. Which mineral is white and chips like glass? A. Calcite B. Feldspar C. Quartz D. Talc 21. Which mineral has cleavage and bubbles when acid is placed on it? A. Calcite B. Feldspar C. Quartz D. Talc ...
... **20 – 30 were answered and discussed in class. Answers are on answer sheet that we made in class. 20. Which mineral is white and chips like glass? A. Calcite B. Feldspar C. Quartz D. Talc 21. Which mineral has cleavage and bubbles when acid is placed on it? A. Calcite B. Feldspar C. Quartz D. Talc ...
Rocks Chapter 4
... grains are called sandstones. At least half the particles in a clastic rock must be sand sized in order for it to be considered a sandstone. Sandstones are very common rocks. They are formed from the sand on beaches, in riverbeds and in sand dunes. In a sandstone, the grains are cemented together by ...
... grains are called sandstones. At least half the particles in a clastic rock must be sand sized in order for it to be considered a sandstone. Sandstones are very common rocks. They are formed from the sand on beaches, in riverbeds and in sand dunes. In a sandstone, the grains are cemented together by ...
Siltstone in a Tung Chung Mazier sample. Way-up
... Plate A9 - Skarn from Site 3 showing typical textural and mineralogical heterogeneity. Note the purple fluorite. The dark green rock at bottom left is Metamudstone with faint banding. Most of the remaining skarn assemblage is calc-silicate rock. Tung Chung, Site 3; Drillcore CC-20; Box 7, 168 m ...
... Plate A9 - Skarn from Site 3 showing typical textural and mineralogical heterogeneity. Note the purple fluorite. The dark green rock at bottom left is Metamudstone with faint banding. Most of the remaining skarn assemblage is calc-silicate rock. Tung Chung, Site 3; Drillcore CC-20; Box 7, 168 m ...
Field occurrence of Plutonic Rocks
... intermediate depth intrusions. Extension: Movement of magma into fractures or voids formed by extension of the crust in response to regional tensional stress. Scale may vary from small (dikes) to large (batholiths). FORCEFUL INTRUSION : Magma forced into zones of weakness in pre-existing rocks by li ...
... intermediate depth intrusions. Extension: Movement of magma into fractures or voids formed by extension of the crust in response to regional tensional stress. Scale may vary from small (dikes) to large (batholiths). FORCEFUL INTRUSION : Magma forced into zones of weakness in pre-existing rocks by li ...
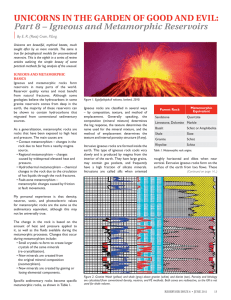
Igneous and Metamorphic Reservoirs
... Both intrusive and extrusive rocks may contain natural fractures created by contraction while cooling, and may have carried other rock fragments with them, called xenoliths. Intrusive rocks may alter the rocks above and below them by metamorphosing (baking) the rock near the intrusion. Extrusives on ...
... Both intrusive and extrusive rocks may contain natural fractures created by contraction while cooling, and may have carried other rock fragments with them, called xenoliths. Intrusive rocks may alter the rocks above and below them by metamorphosing (baking) the rock near the intrusion. Extrusives on ...
3.4 How are the rock classes Rocks and Rock
... entombed trees bear evidence that a rock-forming process is ongoing... The rock around the spring itself appears to be made of layered crystalline material with sponge-like holes. ...
... entombed trees bear evidence that a rock-forming process is ongoing... The rock around the spring itself appears to be made of layered crystalline material with sponge-like holes. ...
Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks Earth Science Rock
... minerals, organic material, or fossil fragments. The wide range of textures common in sedimentary rocks is separated into clastic, chemical, and bioclastic (biochemical) groups. Clastic rocks Clastic textures are composed of cemented inorganic particles (clasts) that typically range in size from 1/2 ...
... minerals, organic material, or fossil fragments. The wide range of textures common in sedimentary rocks is separated into clastic, chemical, and bioclastic (biochemical) groups. Clastic rocks Clastic textures are composed of cemented inorganic particles (clasts) that typically range in size from 1/2 ...
Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks
... minerals, organic material, or fossil fragments. The wide range of textures common in sedimentary rocks is separated into clastic, chemical, and bioclastic (biochemical) groups. Clastic rocks Clastic textures are composed of cemented inorganic particles (clasts) that typically range in size from 1/2 ...
... minerals, organic material, or fossil fragments. The wide range of textures common in sedimentary rocks is separated into clastic, chemical, and bioclastic (biochemical) groups. Clastic rocks Clastic textures are composed of cemented inorganic particles (clasts) that typically range in size from 1/2 ...
Rocks - Cloudfront.net
... Rocks may last a long time but they do change. Even tough igneous rocks may be broken down to smaller particles. We call this process weathering. Small particles may be moved to new areas. We call this transportation. ...
... Rocks may last a long time but they do change. Even tough igneous rocks may be broken down to smaller particles. We call this process weathering. Small particles may be moved to new areas. We call this transportation. ...
File - CBSE FRIENDS OCEAN
... effect like that of glitter. It arises from minute, preferentially oriented mineral platelets within the material. These platelets are so numerous that they also influence the material's body colour. In aventurine quartz, chrome-bearing fuchsite makes for a green stone and various iron oxides make f ...
... effect like that of glitter. It arises from minute, preferentially oriented mineral platelets within the material. These platelets are so numerous that they also influence the material's body colour. In aventurine quartz, chrome-bearing fuchsite makes for a green stone and various iron oxides make f ...
Igneous Rocks
... 4. After observing the rocks, write down some questions you have in your notebook. Share these questions with the class. 5. Put all of your materials back on the ...
... 4. After observing the rocks, write down some questions you have in your notebook. Share these questions with the class. 5. Put all of your materials back on the ...
FIELD OCCURRENCE OF PLUTONIC IGNEOUS ROCKS I. Basic
... or intermediate depth intrusions. Extension: Movement of magma into fractures or voids formed by extension of the crust in response to regional tensional stress. Scale may vary from small (dikes) to large (batholiths). FORCEFUL INTRUSION : Magma forced into zones of weakness in preexisting rocks by ...
... or intermediate depth intrusions. Extension: Movement of magma into fractures or voids formed by extension of the crust in response to regional tensional stress. Scale may vary from small (dikes) to large (batholiths). FORCEFUL INTRUSION : Magma forced into zones of weakness in preexisting rocks by ...
IgPetLab6
... Plutonic (intrusive) rocks crystallize more slowly than volcanic rocks. As a result, they are typically coarser-grained and more equigranular than volcanic rocks, with the actual grain-size reflecting an interplay between cooling rate, and therefore the depth of crystallization, volatile content and ...
... Plutonic (intrusive) rocks crystallize more slowly than volcanic rocks. As a result, they are typically coarser-grained and more equigranular than volcanic rocks, with the actual grain-size reflecting an interplay between cooling rate, and therefore the depth of crystallization, volatile content and ...
Processess - Historic Cemeteries Conservation Trust
... Repeated heating and cooling of rocks can cause cracks to form. During the day the part of the stone facing the sun heats up more quickly than the side facing the shade, and expands. At night the sunny side of the stone cools and contracts. The continual expansion and contraction eventually cau ...
... Repeated heating and cooling of rocks can cause cracks to form. During the day the part of the stone facing the sun heats up more quickly than the side facing the shade, and expands. At night the sunny side of the stone cools and contracts. The continual expansion and contraction eventually cau ...
Igneous Rocks
... In many igneous rocks, large mineral crystals "float" in a fine-grained groundmass. The large grains are called phenocrysts, and a rock with phenocrysts is called a porphyry; that is, it has a porphyritic texture. Phenocrysts are minerals that solidified earlier than the rest of the rock, and they a ...
... In many igneous rocks, large mineral crystals "float" in a fine-grained groundmass. The large grains are called phenocrysts, and a rock with phenocrysts is called a porphyry; that is, it has a porphyritic texture. Phenocrysts are minerals that solidified earlier than the rest of the rock, and they a ...
Erosion
... • As the velocity decreases, there is a loss of carrying power and larger, heavier, denser particles settle out first. ...
... • As the velocity decreases, there is a loss of carrying power and larger, heavier, denser particles settle out first. ...
Clastic sedimentary rocks 0305731
... sedimentary rocks by a process termed lithification which is just part of a broader process termed diagenesis.. Lithification may result from compaction of clay minerals due to increasing burial depth. Also, it could be caused by cementation due to introduction of solutions rich with dissolved eleme ...
... sedimentary rocks by a process termed lithification which is just part of a broader process termed diagenesis.. Lithification may result from compaction of clay minerals due to increasing burial depth. Also, it could be caused by cementation due to introduction of solutions rich with dissolved eleme ...
Glossary of Terms Related to Prospecting and Exploration
... the volcano. The caldera can then be filled with sediments and volcanics and intruded by younger intrusions. More than one caldera can form in any one area as volcanism continues. Such calderas are called "nested". ...
... the volcano. The caldera can then be filled with sediments and volcanics and intruded by younger intrusions. More than one caldera can form in any one area as volcanism continues. Such calderas are called "nested". ...
GEOL_2_mid_term_I
... B) The mineral grains have glassy textures. C) The rock consists of broken, volcanic-rock and mineral fragments. D) The rock is crystalline; mineral grains are of distinctly different sizes. (13) 1 pt. Extrusive igneous rocks are typically finer grained than intrusive igneous rocks. Why? A) Intrusiv ...
... B) The mineral grains have glassy textures. C) The rock consists of broken, volcanic-rock and mineral fragments. D) The rock is crystalline; mineral grains are of distinctly different sizes. (13) 1 pt. Extrusive igneous rocks are typically finer grained than intrusive igneous rocks. Why? A) Intrusiv ...
Petroleum Geology www.AssignmentPoint.com Petroleum geology
... Bulk rock volume, or the gross rock volume of rock above any hydrocarbonwater contact, is determined by mapping and correlating sedimentary packages. The net-to-gross ratio, typically estimated from analogues and wireline logs, is used to calculate the proportion of the sedimentary packages that con ...
... Bulk rock volume, or the gross rock volume of rock above any hydrocarbonwater contact, is determined by mapping and correlating sedimentary packages. The net-to-gross ratio, typically estimated from analogues and wireline logs, is used to calculate the proportion of the sedimentary packages that con ...
Rock Types and Stratigraphy
... parts of the deposit. The term ignimbrite is used to describe these rocks. If ignimbrites are deposited on a steep slope, they begin to flow, and they resemble lava flows. Ignimbrites are associated with nuées ardentes (Fig. 1.6). Lavas are emitted from volcanoes at temperatures only slightly above ...
... parts of the deposit. The term ignimbrite is used to describe these rocks. If ignimbrites are deposited on a steep slope, they begin to flow, and they resemble lava flows. Ignimbrites are associated with nuées ardentes (Fig. 1.6). Lavas are emitted from volcanoes at temperatures only slightly above ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.