What Is Weathering?
... What Is Mechanical Weathering? • Ice Wedging occurs when water seeps into cracks in rock & freezes…the rock expands and finally breaks • This type of weathering causes potholes in the road ...
... What Is Mechanical Weathering? • Ice Wedging occurs when water seeps into cracks in rock & freezes…the rock expands and finally breaks • This type of weathering causes potholes in the road ...
minerals - WorkBank247.com
... of colors and may show cross-bedding or other depositional features. With an increase in the presence of clay, sandstones grade into the shales 62. CONGLOMERATE Gravels turned into solid rock are called conglomerates. This rock contains the largest sedimentary particles which may range up to the siz ...
... of colors and may show cross-bedding or other depositional features. With an increase in the presence of clay, sandstones grade into the shales 62. CONGLOMERATE Gravels turned into solid rock are called conglomerates. This rock contains the largest sedimentary particles which may range up to the siz ...
Metamorphic Textures
... alignment of sheet silicate minerals and/or compositional and mineralogical layering in the rock. Most foliation is caused by the preferred orientation of phylosilicates, like clay minerals, micas, and chlorite. Preferred orientation develops as a result of nonhydrostatic or differential stress acti ...
... alignment of sheet silicate minerals and/or compositional and mineralogical layering in the rock. Most foliation is caused by the preferred orientation of phylosilicates, like clay minerals, micas, and chlorite. Preferred orientation develops as a result of nonhydrostatic or differential stress acti ...
Fluid evolution within Eastern Rhodopian sedimentary rock
... clay minerals, and pyrite-hematite assemblages in a ductile-brittle transition zone, below the detachment. However, at one of the prospects, i.e. Surnak, this transition zone is displaced to deeper crustal levels, within the metamorphic basement rocks, and the later rock units are also mineralized, ...
... clay minerals, and pyrite-hematite assemblages in a ductile-brittle transition zone, below the detachment. However, at one of the prospects, i.e. Surnak, this transition zone is displaced to deeper crustal levels, within the metamorphic basement rocks, and the later rock units are also mineralized, ...
Granitization of the Basic Volcanic Rocks in the Contact Aureole of
... of SiO2, Al2O3, Na2O, K2O, Rb, Ba, Zr, Nb, and Cl into the replaced rocks and removal of FeO, MgO, CaO, and some trace elements (Cr, Co, Ti, Y, and S) (Fig. 3). Thus, the study of altered rocks of the Vakhtalkinskaya Sequence in the contact aureole of the Yurchikskii gabbronorite massif indicates th ...
... of SiO2, Al2O3, Na2O, K2O, Rb, Ba, Zr, Nb, and Cl into the replaced rocks and removal of FeO, MgO, CaO, and some trace elements (Cr, Co, Ti, Y, and S) (Fig. 3). Thus, the study of altered rocks of the Vakhtalkinskaya Sequence in the contact aureole of the Yurchikskii gabbronorite massif indicates th ...
What is the rock cycle? - River Dell Regional School District
... which sediment is moved from one place to another. • Water, wind, ice, and gravity can erode sediments, which are eventually deposited in bodies of water and other low-lying areas. • Sediment comes to rest by a process called deposition. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company ...
... which sediment is moved from one place to another. • Water, wind, ice, and gravity can erode sediments, which are eventually deposited in bodies of water and other low-lying areas. • Sediment comes to rest by a process called deposition. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company ...
12.4 Case Study: Geological Classification
... • Metamorphic, if the rock was formed under conditions of high temperature and pressure; and • Sedimentary, if the rock was formed from the laying down of deposits of sediment. Igneous rocks include basalt, granite, and obsidian. Metamorphic rocks include marble, quartzite, and slate. Sedimentary ro ...
... • Metamorphic, if the rock was formed under conditions of high temperature and pressure; and • Sedimentary, if the rock was formed from the laying down of deposits of sediment. Igneous rocks include basalt, granite, and obsidian. Metamorphic rocks include marble, quartzite, and slate. Sedimentary ro ...
Unit II - SP College
... remains of those animals and plants which contain lime in abundance e.g Calk and Limestone. Foraminifera, Corals, Crinoids and Crustacea are the animal classes most concerned in limestone formation. 2. Carbonaceous Rocks; these rocks are dominated by carbon content and represent the remains of veget ...
... remains of those animals and plants which contain lime in abundance e.g Calk and Limestone. Foraminifera, Corals, Crinoids and Crustacea are the animal classes most concerned in limestone formation. 2. Carbonaceous Rocks; these rocks are dominated by carbon content and represent the remains of veget ...
Lab 6 - Description
... parallel to the front pinacoid. Typically found in mafic rocks such as gabbro. Often occurs in lamellae or folded masses. ...
... parallel to the front pinacoid. Typically found in mafic rocks such as gabbro. Often occurs in lamellae or folded masses. ...
Lab 6 - Description
... parallel to the front pinacoid. Typically found in mafic rocks such as gabbro. Often occurs in lamellae or folded masses. ...
... parallel to the front pinacoid. Typically found in mafic rocks such as gabbro. Often occurs in lamellae or folded masses. ...
Interactive Animation: Relative Geologic Dating
... GeoTutor: Constructing an Order of Sequence of Geologic Events Geologic Time Scale Geologists have divided the whole of history into units of increasing magnitude. This is called the geologic time scale. The entire time scale was originally based on relative dating, since radiometric dating was no ...
... GeoTutor: Constructing an Order of Sequence of Geologic Events Geologic Time Scale Geologists have divided the whole of history into units of increasing magnitude. This is called the geologic time scale. The entire time scale was originally based on relative dating, since radiometric dating was no ...
Rocks and How They Form
... They have a crystal structure which means they have a specific orderly arrangement of atoms. Minerals can be made of one or more elements. Minerals are formed by the cooling of magma and evaporation of water containing dissolved mineral, and they can change into different minerals with heat, pressur ...
... They have a crystal structure which means they have a specific orderly arrangement of atoms. Minerals can be made of one or more elements. Minerals are formed by the cooling of magma and evaporation of water containing dissolved mineral, and they can change into different minerals with heat, pressur ...
Rocks 3 - My Teacher Pages
... Textures of Igneous Rocks, continued Other Igneous Rock Textures • When highly viscous magma cools very rapidly, few crystals will grow. When the magma contains a small amount of dissolved gases, a glassy texture will result. When the magma contains a large percentage of dissolved gases, the gases a ...
... Textures of Igneous Rocks, continued Other Igneous Rock Textures • When highly viscous magma cools very rapidly, few crystals will grow. When the magma contains a small amount of dissolved gases, a glassy texture will result. When the magma contains a large percentage of dissolved gases, the gases a ...
SUBMIT_1
... strata traps and migration pathway formed by Hercynian unconformity, and rift basins had excellent Upper Cretaceous marine source rocks and good hydrocarbon preservation with little tectonic activity . Meanwhile, in the salt-containing passive margin basins and delta basins of West Africa, thick st ...
... strata traps and migration pathway formed by Hercynian unconformity, and rift basins had excellent Upper Cretaceous marine source rocks and good hydrocarbon preservation with little tectonic activity . Meanwhile, in the salt-containing passive margin basins and delta basins of West Africa, thick st ...
lab 6: common minerals in igneous rocks
... Pyroxenes fall into two groups based on their composition and resulting optical properties: the monoclinic clinopyroxenes and the orthorhombic orthopyroxenes. Clinopyroxenes contain Ca, and in igneous rocks can be thought of as (Ca,Mg,Fe)2Si2O6, with small amounts of Al, Mn and Na substituting for ...
... Pyroxenes fall into two groups based on their composition and resulting optical properties: the monoclinic clinopyroxenes and the orthorhombic orthopyroxenes. Clinopyroxenes contain Ca, and in igneous rocks can be thought of as (Ca,Mg,Fe)2Si2O6, with small amounts of Al, Mn and Na substituting for ...
Minerals - SchoolRack
... – Inorganic—not made by life processes – Element or compound with a definite chemical composition – Orderly arrangement of atoms; all minerals are crystalline solids ...
... – Inorganic—not made by life processes – Element or compound with a definite chemical composition – Orderly arrangement of atoms; all minerals are crystalline solids ...
Metamorphic Rocks - geoscirocks home page
... 1) Metamorphic rocks form by recrystallization and/or neocrystallization of preexisting rock (parent rock) in the solid state. 2) Most cases of metamorphism occur at or near tectonic plate boundaries. 3) Agents of metamorphism include heat, pressure, reactive fluids, and stress. 4) Two metamorphic p ...
... 1) Metamorphic rocks form by recrystallization and/or neocrystallization of preexisting rock (parent rock) in the solid state. 2) Most cases of metamorphism occur at or near tectonic plate boundaries. 3) Agents of metamorphism include heat, pressure, reactive fluids, and stress. 4) Two metamorphic p ...
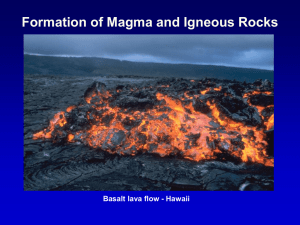
Formation of Magma and Igneous Rocks Basalt
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely SiO2 (~45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, Ca ...
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely SiO2 (~45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, Ca ...
How to Describe an Igneous Rock Lab, University of Aberdeen
... Essential minerals are those which are necessary to the naming of the rock, but may only be present in minor quantities e.g. a crinanite must contain a small amount of analcite. Accessory minerals are those which are present in very small amounts (< 1% by volume), and can normally be ignored when na ...
... Essential minerals are those which are necessary to the naming of the rock, but may only be present in minor quantities e.g. a crinanite must contain a small amount of analcite. Accessory minerals are those which are present in very small amounts (< 1% by volume), and can normally be ignored when na ...
Year 8 Activity Pack sample - UNIT 8HB
... Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when magma cools down underground. They are named because the magma has ‘intruded’ into rocks that were already present. Most intrusive igneous rocks have large crystals, but not always! The diagram shows three different ways in which magma can be intruded. Large v ...
... Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when magma cools down underground. They are named because the magma has ‘intruded’ into rocks that were already present. Most intrusive igneous rocks have large crystals, but not always! The diagram shows three different ways in which magma can be intruded. Large v ...
What is a Mineral
... Silicon and oxygen are the main components of the Earth’s crust (90%) and both elements make up all silicate minerals. Examples: Feldspar – makes up about 50% of the Earth’s crust and is the main component of most of the rocks on the Earth’s surface. Biotite Mica – are shiny and soft, and they s ...
... Silicon and oxygen are the main components of the Earth’s crust (90%) and both elements make up all silicate minerals. Examples: Feldspar – makes up about 50% of the Earth’s crust and is the main component of most of the rocks on the Earth’s surface. Biotite Mica – are shiny and soft, and they s ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... • Metamorphism progresses from low to high grades • Rocks remain solid during metamorphism ...
... • Metamorphism progresses from low to high grades • Rocks remain solid during metamorphism ...
Chapter 7 - Heritage Collegiate
... Regional metamorphism - this type of metamorphism occurs during mountain building and in subduction zones when rocks are subjected to intense stress and high temperatures. This type of metamorphism creates slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss, and quartzite. Pressure is the main cause of metamorphism her ...
... Regional metamorphism - this type of metamorphism occurs during mountain building and in subduction zones when rocks are subjected to intense stress and high temperatures. This type of metamorphism creates slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss, and quartzite. Pressure is the main cause of metamorphism her ...
Be – Beryllium 79
... isotope (9Be). Beryllium is a lithophile element and occurs in the Earth’s crust at concentrations ranging from 1 to 3 mg kg-1 (Ryan 1999). The small size of the Be2+ ion (35 pm) implies that Be behaves incompatibly during early magmatic fractionation. This, and the instability of Be complexes at hi ...
... isotope (9Be). Beryllium is a lithophile element and occurs in the Earth’s crust at concentrations ranging from 1 to 3 mg kg-1 (Ryan 1999). The small size of the Be2+ ion (35 pm) implies that Be behaves incompatibly during early magmatic fractionation. This, and the instability of Be complexes at hi ...
Geology Practice Test (12-2-15) Name: Date: 1. Which bedrock
... by tectonic movements onto the edges of continents, where they often become part of mountains. These displaced oceanic lithosphere segments are called ophiolites. They provide an opportunity to study the composition of oceanic lithosphere and are a key feature in recognizing past tectonic plate conv ...
... by tectonic movements onto the edges of continents, where they often become part of mountains. These displaced oceanic lithosphere segments are called ophiolites. They provide an opportunity to study the composition of oceanic lithosphere and are a key feature in recognizing past tectonic plate conv ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.