Earth`s Systems and Resources Test 1
... altitude to the Himalayas of today. This would still be the case if not for the process of A) erosion. C) volcanism. B) folding. ...
... altitude to the Himalayas of today. This would still be the case if not for the process of A) erosion. C) volcanism. B) folding. ...
Document
... 4. The process in which water, wind, ice, and heat break down rock is called ______________________ 5. One reason that weathering is important is because it breaks rock down into fragments, or ______________________, from which sedimentary rocks are made. 6. The process by which sediment is removed ...
... 4. The process in which water, wind, ice, and heat break down rock is called ______________________ 5. One reason that weathering is important is because it breaks rock down into fragments, or ______________________, from which sedimentary rocks are made. 6. The process by which sediment is removed ...
Geomorphology - WordPress.com
... the features of this era are absent due to erosion and other Earth movements. The oldest rocks of the continents and remnant features which today exist in the form of lower, rounded hills (shields) in the interior of the continents must have been formed during this era. Most of the rocks of this era ...
... the features of this era are absent due to erosion and other Earth movements. The oldest rocks of the continents and remnant features which today exist in the form of lower, rounded hills (shields) in the interior of the continents must have been formed during this era. Most of the rocks of this era ...
1 Final Exam, Earth 50 Fall 2006
... 6. In what part of the modern ocean would you find the oldest bottom water? Please briefly explain your reasoning. The Pacific—Pacific water is at the end of the transit of deep waters from their sites of formation in the Atlantic. 7. During construction of the Aswan High Dam across the Nile River, ...
... 6. In what part of the modern ocean would you find the oldest bottom water? Please briefly explain your reasoning. The Pacific—Pacific water is at the end of the transit of deep waters from their sites of formation in the Atlantic. 7. During construction of the Aswan High Dam across the Nile River, ...
5.2 Relative Time
... 1. Fill in each blank with the appropriate word. The placing of geologic events in sequence from oldest to youngest is termed a) _____________ age dating. This technique uses several common-sense principles. A sequence of sedimentary rocks that is vertical was not formed that way, but was deposited ...
... 1. Fill in each blank with the appropriate word. The placing of geologic events in sequence from oldest to youngest is termed a) _____________ age dating. This technique uses several common-sense principles. A sequence of sedimentary rocks that is vertical was not formed that way, but was deposited ...
Unit 12 vocabulary
... and stick together and turn into rock. 2) Compaction: A process whereby sediments pack, crush, and settle under the action of gravity and pressure from overlying layers. 3) Sedimentary Rock: Rock made of layers of compressed organic and inorganic sediments. 4) Metamorphic Rock: Rock deep within Eart ...
... and stick together and turn into rock. 2) Compaction: A process whereby sediments pack, crush, and settle under the action of gravity and pressure from overlying layers. 3) Sedimentary Rock: Rock made of layers of compressed organic and inorganic sediments. 4) Metamorphic Rock: Rock deep within Eart ...
WORKSHEET 2nd SS LESSON FOUR
... Relief: surface shape, due to differences in height among natural structures on land. Rust: iron oxide, a reddish-brown compound formed when iron is exposed to air and moisture. Seam: underground layer of a mineral or element. 2ND COURSE Cement: substance like glue that bond particles together to ma ...
... Relief: surface shape, due to differences in height among natural structures on land. Rust: iron oxide, a reddish-brown compound formed when iron is exposed to air and moisture. Seam: underground layer of a mineral or element. 2ND COURSE Cement: substance like glue that bond particles together to ma ...
Rocks ISM 22 2014 - AlmaMiddleSchoolScience
... Broken pieces of rocks called CLASTS Chemical precipitates ( dissolved solids come out of solution) Organic fragments – shells, decayed plant matter – this is called BIOCLASTIC ...
... Broken pieces of rocks called CLASTS Chemical precipitates ( dissolved solids come out of solution) Organic fragments – shells, decayed plant matter – this is called BIOCLASTIC ...
Earth Sciences 089G MIDTERM EXAMINATION MARKING KEY Part
... (1) and therefore solidify earlier in the magma cooling process (1). Felsic rocks (Granite-Rhyolite) predominantly contain felsic minerals (quartz, K feldspar, micas, Na plag.) (2), which crystallize at lower magma temperatures (1), and therefore, at later phases of magma cooling (1). 3. Describe th ...
... (1) and therefore solidify earlier in the magma cooling process (1). Felsic rocks (Granite-Rhyolite) predominantly contain felsic minerals (quartz, K feldspar, micas, Na plag.) (2), which crystallize at lower magma temperatures (1), and therefore, at later phases of magma cooling (1). 3. Describe th ...
MSWord file
... (1) and therefore solidify earlier in the magma cooling process (1). Felsic rocks (Granite-Rhyolite) predominantly contain felsic minerals (quartz, K feldspar, micas, Na plag.) (2), which crystallize at lower magma temperatures (1), and therefore, at later phases of magma cooling (1). 3. Describe th ...
... (1) and therefore solidify earlier in the magma cooling process (1). Felsic rocks (Granite-Rhyolite) predominantly contain felsic minerals (quartz, K feldspar, micas, Na plag.) (2), which crystallize at lower magma temperatures (1), and therefore, at later phases of magma cooling (1). 3. Describe th ...
ExamView - Untitled.tst - Newark Catholic High School
... 2. Minerals can form when differences in density force magma upward into warmer layers of Earth’s interior. _________________________ ...
... 2. Minerals can form when differences in density force magma upward into warmer layers of Earth’s interior. _________________________ ...
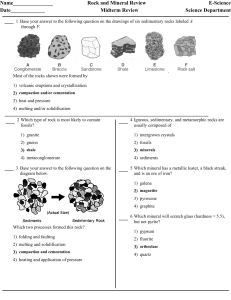
Rocks and Minerals Midterm Rev
... 7 The profile below shows the average diameter of sediment that was sorted and deposited in specific areas A, B, C, and D by a stream entering an ocean. ...
... 7 The profile below shows the average diameter of sediment that was sorted and deposited in specific areas A, B, C, and D by a stream entering an ocean. ...
Geologic Principles and Relative Dating
... a. ________________________________________________________ to the ages of other rock or events in the geological sequence b. Saying “ ________________________________________________” shows its age relative to a known. c. This means that geologists can say which layers are older than which and thus ...
... a. ________________________________________________________ to the ages of other rock or events in the geological sequence b. Saying “ ________________________________________________” shows its age relative to a known. c. This means that geologists can say which layers are older than which and thus ...
Earth Science SOL Review Sheet #1
... from the action of groundwater in areas of easily soluble rocks characterized by caves, underground drainage, and sinkholes permeability – the rate at which a fluid can move through a material physical weathering – natural processes that takes big rocks and turn them into small rocks or sediments (r ...
... from the action of groundwater in areas of easily soluble rocks characterized by caves, underground drainage, and sinkholes permeability – the rate at which a fluid can move through a material physical weathering – natural processes that takes big rocks and turn them into small rocks or sediments (r ...
Rocks!
... We sometimes call rocks pebbles, boulders, stones, crystals or gemstones. A boulder is a large rock A pebble is a small rock that has been rounded by wind or water. Stones are larger than pebbles. Crystals and gemstones are rocks made of just one mineral. E.g a diamond is made of carbon. ...
... We sometimes call rocks pebbles, boulders, stones, crystals or gemstones. A boulder is a large rock A pebble is a small rock that has been rounded by wind or water. Stones are larger than pebbles. Crystals and gemstones are rocks made of just one mineral. E.g a diamond is made of carbon. ...
study-guide-for-test-on-rocks
... ____________24. When molten material, such as an igneous intrusion comes in contact with solid rock. This is from high temperatures and moderate to low pressure. Temperatures decrease with distance from the intrusion, therefore the metamorphic change also decrease with distance. ...
... ____________24. When molten material, such as an igneous intrusion comes in contact with solid rock. This is from high temperatures and moderate to low pressure. Temperatures decrease with distance from the intrusion, therefore the metamorphic change also decrease with distance. ...
Carbonate rocks
... Carbonates accumulate in warm, clear, shallow marine water • Within about 40° of the equator • Rarely in areas where there is a significant input of terrigenous material • Mostly at depths of less than a few tens of metres, but in some cases in deeper water (up to 4000 m max.) ...
... Carbonates accumulate in warm, clear, shallow marine water • Within about 40° of the equator • Rarely in areas where there is a significant input of terrigenous material • Mostly at depths of less than a few tens of metres, but in some cases in deeper water (up to 4000 m max.) ...
The Rock Cycle
... action by wind or water but can include heat, pressure, and ice! This doesn’t involve rock movement…the rock sits there and these things happen to it. Erosion, on the other hand, involves the movement of rocks. ...
... action by wind or water but can include heat, pressure, and ice! This doesn’t involve rock movement…the rock sits there and these things happen to it. Erosion, on the other hand, involves the movement of rocks. ...
Caverns, Sinkholes and Karst groundwater
... As water moves through soil and other organic materials, the water combines with carbon dioxide to form carbonic acid. This weak acid chemically weathers the rock that the acid passes through by breaking down and dissolving the minerals in the rock. ...
... As water moves through soil and other organic materials, the water combines with carbon dioxide to form carbonic acid. This weak acid chemically weathers the rock that the acid passes through by breaking down and dissolving the minerals in the rock. ...
The Physical Regions of Canada
... tropical climate and it was covered by water, plants, and animals. Over time, these deposits were compressed in layers of sedimentary rock to form rich deposits of fossil fuels and evaporites. ...
... tropical climate and it was covered by water, plants, and animals. Over time, these deposits were compressed in layers of sedimentary rock to form rich deposits of fossil fuels and evaporites. ...
Page 1 of 4 FOSS California Pebbles, Sand and Silt Module
... Museum: A building in which collections of scientific, historical or artistic value are studied and exhibited. Nutrient: Something that living things need to grow and stay healthy. Particle: A piece of rock. Pebble: a rock that is smaller than a cobble, but bigger than gravel. Pointed: Having sharp ...
... Museum: A building in which collections of scientific, historical or artistic value are studied and exhibited. Nutrient: Something that living things need to grow and stay healthy. Particle: A piece of rock. Pebble: a rock that is smaller than a cobble, but bigger than gravel. Pointed: Having sharp ...
Unit 3 Test - Problem
... Dora wrote down some observations of four rock samples she was studying. Based on her observations, which of the following rock samples is most likely a sedimentary rock? A. ...
... Dora wrote down some observations of four rock samples she was studying. Based on her observations, which of the following rock samples is most likely a sedimentary rock? A. ...
Metamorphic Rock - Frost Middle School
... heat is not enough to melt the parent rock Recrystallization • Heat and/or pressure can cause the bonds in the ...
... heat is not enough to melt the parent rock Recrystallization • Heat and/or pressure can cause the bonds in the ...
Earth’s Resources - District Five Schools of Spartanburg
... rocks. Some rocks, like granite, are made of several minerals. Some rocks, like limestone, are made mostly of one mineral. A rock’s color gives clues about the minerals that make it up. ...
... rocks. Some rocks, like granite, are made of several minerals. Some rocks, like limestone, are made mostly of one mineral. A rock’s color gives clues about the minerals that make it up. ...
Chapter 5 Conglomerate and sandstone
... Chapter 11 Carbonate rocks Make sure that you understand the differences between the three main carbonate minerals aragonite, calcite and dolomite. Many organisms make their shells out of aragonite, but most of that aragonite is eventually transformed into calcite. the mineral dolomite is not typica ...
... Chapter 11 Carbonate rocks Make sure that you understand the differences between the three main carbonate minerals aragonite, calcite and dolomite. Many organisms make their shells out of aragonite, but most of that aragonite is eventually transformed into calcite. the mineral dolomite is not typica ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.