Lesson 2-1 Guided Reading
... information. Charts arrange numbers and other data in rows and columns. To read a chart, look at the labels at the top of each column and on the left side. They explain what the chart is showing. There are different types of graphs. Bar graphs use wide lines to show data. They are useful for compari ...
... information. Charts arrange numbers and other data in rows and columns. To read a chart, look at the labels at the top of each column and on the left side. They explain what the chart is showing. There are different types of graphs. Bar graphs use wide lines to show data. They are useful for compari ...
Dynamic Earth Interactive: Plate Tectonics Grade 8 Earth Science
... 19. In California, there is a transform boundary between the North American Plate and what other plate? ...
... 19. In California, there is a transform boundary between the North American Plate and what other plate? ...
Study Guide - Answers
... Suppose both a primary and secondary wave start together and travel for 5 minutes, which wave will travel farther? ...
... Suppose both a primary and secondary wave start together and travel for 5 minutes, which wave will travel farther? ...
Layers of the Earth
... The asthenosphere is the layer of Earth that lies at a depth 100–250 km beneath Earth's surface. The asthenosphere gets its name from the Greek word for weak, asthenis, because of the relatively fragile nature of the materials of which it is made. It lies in the upper portion of Earth's structure tr ...
... The asthenosphere is the layer of Earth that lies at a depth 100–250 km beneath Earth's surface. The asthenosphere gets its name from the Greek word for weak, asthenis, because of the relatively fragile nature of the materials of which it is made. It lies in the upper portion of Earth's structure tr ...
Teacher Guide - Sally Ride EarthKAM
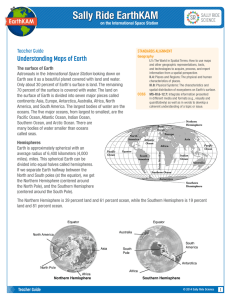
... Latitude measures how far north or south a point lies from the equator. The equator is at 0 degrees (0°) latitude, and it divides Earth into its northern and southern hemispheres. It is the starting point for measuring distances in degrees north or south of the equator. Values for latitude range fro ...
... Latitude measures how far north or south a point lies from the equator. The equator is at 0 degrees (0°) latitude, and it divides Earth into its northern and southern hemispheres. It is the starting point for measuring distances in degrees north or south of the equator. Values for latitude range fro ...
UNIT C - apel slice
... In some places, snowfall is high and temperature is low. Sometimes more snow falls in winter than melts in summer. The snow piles up year after year. As it thickens, it turns to ice. If the mass of ice starts to move downhill, it becomes a glacier. A glacier (GLAY•sher) is a large, moving mass of ic ...
... In some places, snowfall is high and temperature is low. Sometimes more snow falls in winter than melts in summer. The snow piles up year after year. As it thickens, it turns to ice. If the mass of ice starts to move downhill, it becomes a glacier. A glacier (GLAY•sher) is a large, moving mass of ic ...
Layers of the Earth PBL
... scale model of Earth’s interior, with an accompanying educational narrative script for their “From Crust to Core” tour exhibit. All requirements for the “From Crust to Core” competition are detailed in the accompanying application form. ...
... scale model of Earth’s interior, with an accompanying educational narrative script for their “From Crust to Core” tour exhibit. All requirements for the “From Crust to Core” competition are detailed in the accompanying application form. ...
Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1, The Geosphere Day 1
... • Plants need sunlight to produce their food, and almost every other organism gets its food from plants and algae. • Most of the algae float at the surface of the ocean and is known as phytoplankton. Energy Flow in the Biosphere • The energy used by organisms must be obtained in the biosphere and mu ...
... • Plants need sunlight to produce their food, and almost every other organism gets its food from plants and algae. • Most of the algae float at the surface of the ocean and is known as phytoplankton. Energy Flow in the Biosphere • The energy used by organisms must be obtained in the biosphere and mu ...
12.710: Introduction to Marine Geology and Geophysics Solutions to
... accretion to earlier than the life of 129I in the solar system (determined by our ability to resolve small differences in Xe isotopes – e.g. if that limit is 5 half-lives of 129I, accretion must have occurred within the first 82 Ma of the solar system. In this case we can resolve this to maybe ~50Ma ...
... accretion to earlier than the life of 129I in the solar system (determined by our ability to resolve small differences in Xe isotopes – e.g. if that limit is 5 half-lives of 129I, accretion must have occurred within the first 82 Ma of the solar system. In this case we can resolve this to maybe ~50Ma ...
Chapter 8 - reynolds study center
... 18. The oceanic crust is mainly intrusive/extrusive rock rich in the minerals _______________, _______________, and _______________. The continental crust is mainly intrusive/extrusive rock rich in the minerals _______________ and _______________. The oceanic crust is more/less dense (circle correc ...
... 18. The oceanic crust is mainly intrusive/extrusive rock rich in the minerals _______________, _______________, and _______________. The continental crust is mainly intrusive/extrusive rock rich in the minerals _______________ and _______________. The oceanic crust is more/less dense (circle correc ...
8.1 Earth has several layers
... • Tectonic plates rest on the asthenosphere (layer of soft, hot rock) • Convection currents within Earth helps to move the plates • convection—the transfer of heat by the movement of a material • convection current—a motion that transfers heat energy to a material • Moves very slowly, a few centimet ...
... • Tectonic plates rest on the asthenosphere (layer of soft, hot rock) • Convection currents within Earth helps to move the plates • convection—the transfer of heat by the movement of a material • convection current—a motion that transfers heat energy to a material • Moves very slowly, a few centimet ...
ppt
... materials sank to the center and the lighter materials rose to the top. Because of this, the crust is made of the lightest materials (rock- basalts and granites) and the core consists of heavy metals (nickel and iron). ...
... materials sank to the center and the lighter materials rose to the top. Because of this, the crust is made of the lightest materials (rock- basalts and granites) and the core consists of heavy metals (nickel and iron). ...
Earthquake Waves - davis.k12.ut.us
... • Faults are areas where two volumes of rock have been shifted relative to each other • Faults are produced by the movement of the tectonic plates on the Earth’s surface ...
... • Faults are areas where two volumes of rock have been shifted relative to each other • Faults are produced by the movement of the tectonic plates on the Earth’s surface ...
PLATE TECTONICS - Cockeysville Middle
... • The Earth’s surface is broken up into 15 lithospheric plates. • These plates are composed of the top part of the mantle and the crust. • There are oceanic plates (more dense) and continental plates (less dense). • These plates “float” on the asthenosphere, the plastic-like flowing part of the mant ...
... • The Earth’s surface is broken up into 15 lithospheric plates. • These plates are composed of the top part of the mantle and the crust. • There are oceanic plates (more dense) and continental plates (less dense). • These plates “float” on the asthenosphere, the plastic-like flowing part of the mant ...
What is earthquake…
... strength of the rocks, break and "snap" to a new position. In the process of breaking, vibrations called "seismic waves" are generated. These waves travel outward from the source of the earthquake along the surface and through the Earth at varying speeds depending on the material through which they ...
... strength of the rocks, break and "snap" to a new position. In the process of breaking, vibrations called "seismic waves" are generated. These waves travel outward from the source of the earthquake along the surface and through the Earth at varying speeds depending on the material through which they ...
Earth`s Composition and Structure
... 2. Earth has a stratified atmosphere, mainly composed of nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) 3. Earth is made of a variety of minerals, glasses, melts, fluids and volatiles, all left behind during birth of the solar system 4. The Earth has layers: a thin silicate crust, a thick iron- & magnesium silicate ...
... 2. Earth has a stratified atmosphere, mainly composed of nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2) 3. Earth is made of a variety of minerals, glasses, melts, fluids and volatiles, all left behind during birth of the solar system 4. The Earth has layers: a thin silicate crust, a thick iron- & magnesium silicate ...
The Earths interior structure - Lecture 1
... layer with even faster v With no change in properties, no refractions, no reflections ...
... layer with even faster v With no change in properties, no refractions, no reflections ...
Benchmark Test Study Guide October 2013 Standard: The student
... 3. What is the epicenter of an earthquake and where is it located? The epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus; energy that reaches the surface is greatest at this point. 4. How do scientists use the time between the arrival of the P waves and S waves to help determine the ...
... 3. What is the epicenter of an earthquake and where is it located? The epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus; energy that reaches the surface is greatest at this point. 4. How do scientists use the time between the arrival of the P waves and S waves to help determine the ...
Layers of Earth Notes On-Level
... LAYERS OF THE EARTH • GEOLOGY – STUDY OF PLANET EARTH • INCLUDING SURFACE & INTERIOR • GEOLOGISTS – A PERSON WHO STUDIES INSIDE THE EARTH, TEMP, PRESSURE, HOW THEY AFFECT THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH. ...
... LAYERS OF THE EARTH • GEOLOGY – STUDY OF PLANET EARTH • INCLUDING SURFACE & INTERIOR • GEOLOGISTS – A PERSON WHO STUDIES INSIDE THE EARTH, TEMP, PRESSURE, HOW THEY AFFECT THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH. ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... • The Earth is divided into four main layers. Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core ...
... • The Earth is divided into four main layers. Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core ...
Journey to the Center of Earth
... Layer that we live on (Lithosphere) 5-25 miles thick Consists of cooled rock Thinnest layer of the earth There are 2 kinds of Crust: Continental (thicker) and Oceanic (thinner) ...
... Layer that we live on (Lithosphere) 5-25 miles thick Consists of cooled rock Thinnest layer of the earth There are 2 kinds of Crust: Continental (thicker) and Oceanic (thinner) ...
Objective: Describe the composition and structure of Earth.
... • Evidence from deep probes and seismic waves, reconstructions of historical changes in Earth’s surface and its magnetic field, and an understanding of physical and chemical processes lead to a model of Earth with a hot but solid inner core, a liquid outer core, a solid mantle and crust. Motions of ...
... • Evidence from deep probes and seismic waves, reconstructions of historical changes in Earth’s surface and its magnetic field, and an understanding of physical and chemical processes lead to a model of Earth with a hot but solid inner core, a liquid outer core, a solid mantle and crust. Motions of ...
Coordinate Systems and Projections Part I
... •Sphere can be used for small-scale maps (< 1:5,000,000) •Spheroid gives better accuracy for large-scale maps (>1:1,000,000 ...
... •Sphere can be used for small-scale maps (< 1:5,000,000) •Spheroid gives better accuracy for large-scale maps (>1:1,000,000 ...
Spherical Earth

The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to around the 6th century BC, when it was mentioned in ancient Greek philosophy, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC, when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given. The paradigm was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's expedition's circumnavigation (1519−1522).The concept of a spherical Earth displaced earlier beliefs in a flat Earth: In early Mesopotamian mythology, the world was portrayed as a flat disk floating in the ocean and surrounded by a spherical sky, and this forms the premise for early world maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus. Other speculations on the shape of Earth include a seven-layered ziggurat or cosmic mountain, alluded to in the Avesta and ancient Persian writings (see seven climes).The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 18th century (Maupertuis).In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to be of the order of 1/300 (Delambre, Everest). The modern value as determined by the US DoD World Geodetic System since the 1960s is close to 1/298.25.