Unit C – The Changing Earth(pages 292 – 401)
... 3. Like its name suggests, a lava lamp is a good model of Earth’s convection currents. The semi-liquid material inside the lamp could represent the mantle. The heat source at the lamp’s base could represent heat from the Earth’s core. A bubble starts at the bottom of the lamp, slowly rises, and then ...
... 3. Like its name suggests, a lava lamp is a good model of Earth’s convection currents. The semi-liquid material inside the lamp could represent the mantle. The heat source at the lamp’s base could represent heat from the Earth’s core. A bubble starts at the bottom of the lamp, slowly rises, and then ...
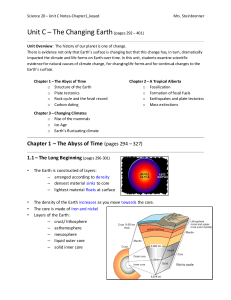
The Layers of the Earth
... 1. The students will be able to identify and describe the layers of the solid Earth (including Lithosphere, the hot convecting mantle, the dense metallic liquid, and solid core). 2. The students will be able to use a self-evaluation scale to rate themselves during the lesson. ...
... 1. The students will be able to identify and describe the layers of the solid Earth (including Lithosphere, the hot convecting mantle, the dense metallic liquid, and solid core). 2. The students will be able to use a self-evaluation scale to rate themselves during the lesson. ...
What is Geology?
... Mid-Ocean Ridges: a connected system of undersea volcanoes that roam over the Earth like the raised string on a baseball. It is a continuous 40,000-mile seam that encircles Earth and bisects the oceans. A mid-ocean ridge represents an area where, in accordance with plate tectonic theory, tectonic ...
... Mid-Ocean Ridges: a connected system of undersea volcanoes that roam over the Earth like the raised string on a baseball. It is a continuous 40,000-mile seam that encircles Earth and bisects the oceans. A mid-ocean ridge represents an area where, in accordance with plate tectonic theory, tectonic ...
A new method to invert seismic waveforms for 3
... primarily of iron. The temperature and chemical composition within D" vary rapidly as the distance to the core-mantle boundary (CMB) decreases. Data on material and energy flux in D" can provide important information for understanding the Earth's dynamics and evolution, but the three dimensional (3- ...
... primarily of iron. The temperature and chemical composition within D" vary rapidly as the distance to the core-mantle boundary (CMB) decreases. Data on material and energy flux in D" can provide important information for understanding the Earth's dynamics and evolution, but the three dimensional (3- ...
Document
... • Coal can be found underneath the cold and dry Antarctic ice cap, though coal can only form in warm and wet conditions. • Glossopteris, a fern, was found on the continents of South America, Africa, India, and Australia. • Mesosaurus, an early freshwater reptile, fossils are both found in Africa and ...
... • Coal can be found underneath the cold and dry Antarctic ice cap, though coal can only form in warm and wet conditions. • Glossopteris, a fern, was found on the continents of South America, Africa, India, and Australia. • Mesosaurus, an early freshwater reptile, fossils are both found in Africa and ...
Crust - Cobb Learning
... Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
... Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
continent, continental drift, seafloor, ocean floor, tectonic
... E.SE.06.51 Explain plate tectonic movement and that the lithospheric plates move centimeters each year. Instructional Clarifications 1. Explain is to clearly describe by means of illustrations (drawing), demonstrations, written reports, or verbally the movement of lithospheric plates. 2. The Earth’s ...
... E.SE.06.51 Explain plate tectonic movement and that the lithospheric plates move centimeters each year. Instructional Clarifications 1. Explain is to clearly describe by means of illustrations (drawing), demonstrations, written reports, or verbally the movement of lithospheric plates. 2. The Earth’s ...
Script - FOG - City College of San Francisco
... layers – were formed. Let’s look closer at the core. It’s made mostly of iron and is separated into two physically distinct layers. They are compositionally quite similar – mostly made of iron. However, physically, we have a small solid inner core at the very center of the earth, where, though tempe ...
... layers – were formed. Let’s look closer at the core. It’s made mostly of iron and is separated into two physically distinct layers. They are compositionally quite similar – mostly made of iron. However, physically, we have a small solid inner core at the very center of the earth, where, though tempe ...
plate tectonics
... Earth has been losing heat since it formed, billions of years ago. But it’s producing almost as much heat as it’s losing. The process by which Earth makes heat is called radioactive decay. It involves the disintegration of natural radioactive elements inside Earth – like uranium, for example. Uraniu ...
... Earth has been losing heat since it formed, billions of years ago. But it’s producing almost as much heat as it’s losing. The process by which Earth makes heat is called radioactive decay. It involves the disintegration of natural radioactive elements inside Earth – like uranium, for example. Uraniu ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources
... information about the relative position, density, and composition of Earth’s layers (crust, mantle and core). Therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be for students to obtain and communicate information from a variety of sources (informational texts, primary and secondary sources, models ...
... information about the relative position, density, and composition of Earth’s layers (crust, mantle and core). Therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be for students to obtain and communicate information from a variety of sources (informational texts, primary and secondary sources, models ...
esga3094 - 4J Blog Server
... Destructive plate margins called are where one oceanic plate is forced down into the mantle beneath a second plate. Where two plates move together, ...
... Destructive plate margins called are where one oceanic plate is forced down into the mantle beneath a second plate. Where two plates move together, ...
Mining Matters II - The Earth`s Crust Une mine de renseignements II
... were removed and the continents were put together. There are other matching outlines where Canada would piece together with Greenland if the Atlantic Ocean did not separate them. Is it possible that at one time the continents were actually a single land mass with no oceans between them? Alfred Wegen ...
... were removed and the continents were put together. There are other matching outlines where Canada would piece together with Greenland if the Atlantic Ocean did not separate them. Is it possible that at one time the continents were actually a single land mass with no oceans between them? Alfred Wegen ...
Rapid Changes in Earth`s Surface
... Earth’s surface is constantly changing. Wind, water, and ice break down large rocks and move sediments on the surface. It usually takes years for weathering, erosion, and deposition to cause noticeable changes. Some events, though, change Earth’s surface much more quickly. These include volcanic eru ...
... Earth’s surface is constantly changing. Wind, water, and ice break down large rocks and move sediments on the surface. It usually takes years for weathering, erosion, and deposition to cause noticeable changes. Some events, though, change Earth’s surface much more quickly. These include volcanic eru ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources - Lexington County School District
... 2) the geologic activities at plate boundaries, and 3) the changes in landform areas over geologic time. The focus of assessment should be for students to use evidence from 1) the motion of lithospheric plates 2) geologic activities at plate boundaries and 3) changes in landform area over geologic t ...
... 2) the geologic activities at plate boundaries, and 3) the changes in landform areas over geologic time. The focus of assessment should be for students to use evidence from 1) the motion of lithospheric plates 2) geologic activities at plate boundaries and 3) changes in landform area over geologic t ...
ANSWER KEY Lesson One: Layers of the Earth Vocabulary Station
... apple, the Earth’s crust is very thin compared to the mantle and the core. 3. The “meat” of the apple represents the mantle. The mantle is the largest of the Earth’s layers and is made up of molten rock which is similar to very hot asphalt. 4. The core of the apple represents the outer and inner cor ...
... apple, the Earth’s crust is very thin compared to the mantle and the core. 3. The “meat” of the apple represents the mantle. The mantle is the largest of the Earth’s layers and is made up of molten rock which is similar to very hot asphalt. 4. The core of the apple represents the outer and inner cor ...
Sample
... gravitationally through collisions out of a nebula of gas and dust as the solar system formed. Earth’s overall interior structure is a series of spherical shells. These layers formed after accretion of a relatively homogeneous planet was completed when the heat generated by collisions during accreti ...
... gravitationally through collisions out of a nebula of gas and dust as the solar system formed. Earth’s overall interior structure is a series of spherical shells. These layers formed after accretion of a relatively homogeneous planet was completed when the heat generated by collisions during accreti ...
mantle - Uplift Mighty Prep
... 1. How do we know what the inside of the Earth is made of? 2. What are the three basic layers of the Earth. 3. What layer do we live on? 4. What part makes up the bulk of the Earth’s mass? ...
... 1. How do we know what the inside of the Earth is made of? 2. What are the three basic layers of the Earth. 3. What layer do we live on? 4. What part makes up the bulk of the Earth’s mass? ...
Earth Space EOC Study Guide
... where the Earth is actually tilted toward the Sun and away from the Sun. Label which position would be summer and winter in the Northern Hemisphere. (Page 777) 48. Describe two ways to demonstrate the Earth is rotating around the Sun. (Page 775) 49. Draw the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, an ...
... where the Earth is actually tilted toward the Sun and away from the Sun. Label which position would be summer and winter in the Northern Hemisphere. (Page 777) 48. Describe two ways to demonstrate the Earth is rotating around the Sun. (Page 775) 49. Draw the relative positions of the Earth, Moon, an ...
Skinner Chapter 4
... Read each question carefully before answering. Work at a steady pace, and you should have ample time to finish. _____________________________________________ 1. Rocks deep inside the Earth are so hot that it is possible for them to flow like sticky liquids. 2. Radiation is the process by which heat ...
... Read each question carefully before answering. Work at a steady pace, and you should have ample time to finish. _____________________________________________ 1. Rocks deep inside the Earth are so hot that it is possible for them to flow like sticky liquids. 2. Radiation is the process by which heat ...
Earth`s plates
... The lithosphere is broken up into pieces called tectonic plates They float on the mantle Different sizes and shapes ...
... The lithosphere is broken up into pieces called tectonic plates They float on the mantle Different sizes and shapes ...
Exam Block #1
... geology are of practical value to people. Natural disasters are simply natural processes when people live where these processes occur. Earth is now gaining about 100 million people each year. Resources, such as water, soil, metals, non-metals, and energy (oil, gas, coal, geothermal) all come f ...
... geology are of practical value to people. Natural disasters are simply natural processes when people live where these processes occur. Earth is now gaining about 100 million people each year. Resources, such as water, soil, metals, non-metals, and energy (oil, gas, coal, geothermal) all come f ...
Earth`s Interior
... (2) S-Wave Shadow Zone • Larger than the P-wave shadow zone • Direct S-Waves are not recorded in the entire region more than 103o from the epicenter • Indicates that S-waves do not pass through the core at all ...
... (2) S-Wave Shadow Zone • Larger than the P-wave shadow zone • Direct S-Waves are not recorded in the entire region more than 103o from the epicenter • Indicates that S-waves do not pass through the core at all ...
Name_________________________ Earth`s
... The outer layer of the earth is called the __________________. It is made up of tectonic ________________. Just underneath the crust is the _____________________ and right in the middle of the earth is the _____________. Colliding plates produce _______________________ and _____________________ at t ...
... The outer layer of the earth is called the __________________. It is made up of tectonic ________________. Just underneath the crust is the _____________________ and right in the middle of the earth is the _____________. Colliding plates produce _______________________ and _____________________ at t ...
Spherical Earth

The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to around the 6th century BC, when it was mentioned in ancient Greek philosophy, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC, when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given. The paradigm was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's expedition's circumnavigation (1519−1522).The concept of a spherical Earth displaced earlier beliefs in a flat Earth: In early Mesopotamian mythology, the world was portrayed as a flat disk floating in the ocean and surrounded by a spherical sky, and this forms the premise for early world maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus. Other speculations on the shape of Earth include a seven-layered ziggurat or cosmic mountain, alluded to in the Avesta and ancient Persian writings (see seven climes).The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 18th century (Maupertuis).In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to be of the order of 1/300 (Delambre, Everest). The modern value as determined by the US DoD World Geodetic System since the 1960s is close to 1/298.25.