Digest #: 3535 TITLE WHAT IS EARTH SCIENCE?
... What are the four branches that make up earth sciences? Who is known as the founder of modern astronomy? What does VLA stand for? What is it used for? What is the big bang theory? What role does the sun play in sustaining life on earth? How does the moon affect the oceans’ tides? How do meteorites h ...
... What are the four branches that make up earth sciences? Who is known as the founder of modern astronomy? What does VLA stand for? What is it used for? What is the big bang theory? What role does the sun play in sustaining life on earth? How does the moon affect the oceans’ tides? How do meteorites h ...
Inside the Earth
... • 2240 km thick (1400 mi) • 6093 C (11,000 ˚ F) • Movement is source of Earth’s magnetic field ...
... • 2240 km thick (1400 mi) • 6093 C (11,000 ˚ F) • Movement is source of Earth’s magnetic field ...
The Five Themes of Geography
... move from one location to another? Human Environment Interaction – How do people relate to the physical world? ...
... move from one location to another? Human Environment Interaction – How do people relate to the physical world? ...
The Earth - Humble ISD
... Continental Drift – __________________ first presented the theory. He claimed that in Earth’s early existence there was only one body of land, ______________. That supercontinent then slowly split and separated into the continents we see today. _____________Boundary – Where plates move apart or spre ...
... Continental Drift – __________________ first presented the theory. He claimed that in Earth’s early existence there was only one body of land, ______________. That supercontinent then slowly split and separated into the continents we see today. _____________Boundary – Where plates move apart or spre ...
Date: Block
... S6E5.e: Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the Earth’s surface. S6E5.f: Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics) on geological features including oceans. I. Deformation A. Stress: the amount of force per unit area on a given mat ...
... S6E5.e: Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the Earth’s surface. S6E5.f: Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics) on geological features including oceans. I. Deformation A. Stress: the amount of force per unit area on a given mat ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Introduction to Earthquakes EASA
... The study of earthquakes and seismic waves that move through and around the earth is called __________________________________. ...
... The study of earthquakes and seismic waves that move through and around the earth is called __________________________________. ...
Plate Tectonics
... 10. hypothesis that the continents have moved slowly to their current locations 11. boundary between two plates that are moving apart 12. sections of Earth's crust and upper mantle 13. largest layer of Earth's surface, composed mostly of silicon, oxygen, magnesium, and iron 14. outermost layer of Ea ...
... 10. hypothesis that the continents have moved slowly to their current locations 11. boundary between two plates that are moving apart 12. sections of Earth's crust and upper mantle 13. largest layer of Earth's surface, composed mostly of silicon, oxygen, magnesium, and iron 14. outermost layer of Ea ...
Document
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
01 - Mayfield City Schools
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
directed reading inside earth
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
... 3. Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. List the three layers of the Earth, based on their chemical compositio ...
Components of Earth
... Movement of Energy in the Atmosphere • Air is constantly moving • Troposphere – currents of lighter air warmed by the Earth’s surface rise into the atmosphere – The currents of heavier air (cooler) sink towards the ground. ...
... Movement of Energy in the Atmosphere • Air is constantly moving • Troposphere – currents of lighter air warmed by the Earth’s surface rise into the atmosphere – The currents of heavier air (cooler) sink towards the ground. ...
Long and Short-term Changes in Climate
... Terms and Concepts: plate tectonics, continental drift, ice age, interglacial period, Milankovitch Cycles ...
... Terms and Concepts: plate tectonics, continental drift, ice age, interglacial period, Milankovitch Cycles ...
Ch25 History of Life on Earth
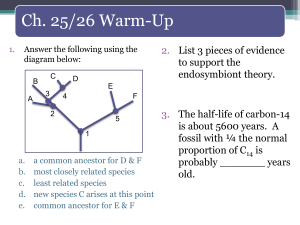
... least related species new species C arises at this point common ancestor for E & F ...
... least related species new species C arises at this point common ancestor for E & F ...
Name__________________________________ pd________ Use the links to help you answer the questions.
... 15. You have learned that the core is very hot, and that the mantle has convection currents which transfer core heat to the crust. Use this website: Http://www.agiweb.org/education/aapg/curricula/9-12.html Read the first bullet in “Energy in the Earth System” and list the 3 sources (external & inter ...
... 15. You have learned that the core is very hot, and that the mantle has convection currents which transfer core heat to the crust. Use this website: Http://www.agiweb.org/education/aapg/curricula/9-12.html Read the first bullet in “Energy in the Earth System” and list the 3 sources (external & inter ...
Unit 7 Earth`s Resources
... Overarching Concept: 9.7 - Elements on Earth move among reservoirs in the solid earth, oceans, atmosphere and organisms as part of biogeochemical cycles. Elements on Earth exist in essentially fixed amounts and are located in various chemical reservoirs. The cyclical movement of matter between r ...
... Overarching Concept: 9.7 - Elements on Earth move among reservoirs in the solid earth, oceans, atmosphere and organisms as part of biogeochemical cycles. Elements on Earth exist in essentially fixed amounts and are located in various chemical reservoirs. The cyclical movement of matter between r ...
Earth`s Spheres The biosphere is the region of the earth
... skin on an apple. The bulk of living organisms actually live within a smaller fraction of the biosphere, from about 500 meters below the ocean's surface to about 6 kilometers above sea level. Dynamic interactions occur between the biotic region (biosphere) and the abiotic regions (atmosphere, lithos ...
... skin on an apple. The bulk of living organisms actually live within a smaller fraction of the biosphere, from about 500 meters below the ocean's surface to about 6 kilometers above sea level. Dynamic interactions occur between the biotic region (biosphere) and the abiotic regions (atmosphere, lithos ...
la teoria della deriva dei continenti e della tettonica a zolle
... MORGAN & MCKENZIE. This theory explains the phenomena that are involved in the Earth’s crust changes such as the seismic activity, the orogeny, the presence of the volcanos on the territory and the formation of the oceanics trenches. ...
... MORGAN & MCKENZIE. This theory explains the phenomena that are involved in the Earth’s crust changes such as the seismic activity, the orogeny, the presence of the volcanos on the territory and the formation of the oceanics trenches. ...
Presentation
... The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball sm ...
... The Earth is composed of four different layers. The crust is the layer that you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The mantle is much hotter and has the ability to flow. The outer core and inner core are even hotter with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ball sm ...
layers of earth hw2
... 8. Make a statement about the relationship between depth under the Earth and pressure. (Ex: As you go deeper into the Earth…) ...
... 8. Make a statement about the relationship between depth under the Earth and pressure. (Ex: As you go deeper into the Earth…) ...
The Deep Ocean Exploration Institute T Investigating Earth’s dynamic processes
... thermal vents revolutionized our conheats iron to a temperature just below its cepts of where and how life can exist. An melting point to bend and shape a horseabundance of life flourishes in conditions shoe.) Solid rocks within Earth’s mantle we had considered too extreme, supcan flow, with hot buo ...
... thermal vents revolutionized our conheats iron to a temperature just below its cepts of where and how life can exist. An melting point to bend and shape a horseabundance of life flourishes in conditions shoe.) Solid rocks within Earth’s mantle we had considered too extreme, supcan flow, with hot buo ...
Earthquake Vocabulary Part 2
... A measure of the damage done by an earthquake. Determined on the basis of the earthquake’s effect on people, structures, and the natural environment. ...
... A measure of the damage done by an earthquake. Determined on the basis of the earthquake’s effect on people, structures, and the natural environment. ...
Spherical Earth

The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to around the 6th century BC, when it was mentioned in ancient Greek philosophy, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC, when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given. The paradigm was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's expedition's circumnavigation (1519−1522).The concept of a spherical Earth displaced earlier beliefs in a flat Earth: In early Mesopotamian mythology, the world was portrayed as a flat disk floating in the ocean and surrounded by a spherical sky, and this forms the premise for early world maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus. Other speculations on the shape of Earth include a seven-layered ziggurat or cosmic mountain, alluded to in the Avesta and ancient Persian writings (see seven climes).The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 18th century (Maupertuis).In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to be of the order of 1/300 (Delambre, Everest). The modern value as determined by the US DoD World Geodetic System since the 1960s is close to 1/298.25.