What is the theory of plate tectonics?
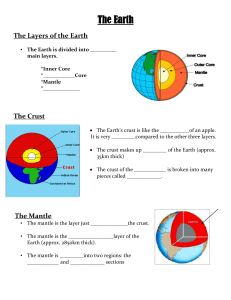
... core – the layer at the centre of the Earth. This layer is divided into two sections: the liquid, outer core and the solid, inner core. ...
... core – the layer at the centre of the Earth. This layer is divided into two sections: the liquid, outer core and the solid, inner core. ...
Landform
... A tide is the rise and fall in the level of the ocean. Tides are caused by the pull of gravity of the sun and the moon on Earth’s waters. Since the moon is closer to Earth than the sun, it has a greater effect on tides. There are 2 high tides and 2 low tides each day. The highest tides occur about e ...
... A tide is the rise and fall in the level of the ocean. Tides are caused by the pull of gravity of the sun and the moon on Earth’s waters. Since the moon is closer to Earth than the sun, it has a greater effect on tides. There are 2 high tides and 2 low tides each day. The highest tides occur about e ...
The Earth The Layers of the Earth • The Earth is divided into ______
... 1. Jigsaw effect-the continents ______ together like a jigsaw puzzle, especially South America and Africa. ...
... 1. Jigsaw effect-the continents ______ together like a jigsaw puzzle, especially South America and Africa. ...
U and Th in Earth Reservoirs
... • Is 5.4 Ga different from 6.3 Ga ? – (and whom do you believe?) – If you vary the primordial ratios by ±20% (a reasonable uncertainty) you get: • T(235U/238U) = 6.1 - 6.5 Ga • T(232Th/238U) = 3.5 - 7.2 Ga ...
... • Is 5.4 Ga different from 6.3 Ga ? – (and whom do you believe?) – If you vary the primordial ratios by ±20% (a reasonable uncertainty) you get: • T(235U/238U) = 6.1 - 6.5 Ga • T(232Th/238U) = 3.5 - 7.2 Ga ...
SHS Core Earth Science CG
... 1. geologic processes that occur on the surface of the Earth such as weathering, erosion, mass wasting, and sedimentation (include the role of ocean basins in the formation of sedimentary rocks) 2. geologic processes that occur within the Earth ...
... 1. geologic processes that occur on the surface of the Earth such as weathering, erosion, mass wasting, and sedimentation (include the role of ocean basins in the formation of sedimentary rocks) 2. geologic processes that occur within the Earth ...
The importance of the Earth`s biosphere in stabilizing the large
... photosynthetic life plays an important role in the energy budget of Earth [4], leading to alterations of chemical reservoirs [1,3]. Since the surface is recycled into its interior at subduction zones, a direct connection to the Earth’s interior is given [5,7], and it has been speculated [6] that the ...
... photosynthetic life plays an important role in the energy budget of Earth [4], leading to alterations of chemical reservoirs [1,3]. Since the surface is recycled into its interior at subduction zones, a direct connection to the Earth’s interior is given [5,7], and it has been speculated [6] that the ...
Plate Tectonics-1-1
... shape planet Earth. They study the processes that create Earth’s features and search for clues about Earth’s history. ...
... shape planet Earth. They study the processes that create Earth’s features and search for clues about Earth’s history. ...
Geodynamics
... studies of the Earth's interior within the framework of the community-based initiative known as Cooperative Studies of the Earth's Deep Interior (CSEDI). Funding will support basic research on the character and dynamics of the Earth's mantle and core, their influence on the evolution of the Earth as ...
... studies of the Earth's interior within the framework of the community-based initiative known as Cooperative Studies of the Earth's Deep Interior (CSEDI). Funding will support basic research on the character and dynamics of the Earth's mantle and core, their influence on the evolution of the Earth as ...
Geology: The Earth and Its Changes
... Offer reasons for their findings and consider reasons suggested by others. ...
... Offer reasons for their findings and consider reasons suggested by others. ...
Unit 5 – Structure of the Earth
... 7. The outer core is a liquid inner layer Mostly liquid iron Thought to be the source of the earth’s magnetic field. ...
... 7. The outer core is a liquid inner layer Mostly liquid iron Thought to be the source of the earth’s magnetic field. ...
Earth as a System - Bakersfield College
... Formulating a Hypothesis (predictions as to why) • Explaining how and why it works (after factfinding), “educated guessing” Testing the Hypothesis (experimenting) • performing experimentations that test the accuracy of the hypothesis ...
... Formulating a Hypothesis (predictions as to why) • Explaining how and why it works (after factfinding), “educated guessing” Testing the Hypothesis (experimenting) • performing experimentations that test the accuracy of the hypothesis ...
What is wind?
... • Earth rotates, causing winds to be deflected, or curved. • The apparent curving of the path of a moving object from an otherwise straight path due to Earth’s rotation is called the Coriolis effect. ...
... • Earth rotates, causing winds to be deflected, or curved. • The apparent curving of the path of a moving object from an otherwise straight path due to Earth’s rotation is called the Coriolis effect. ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 12
... b. Broad, flat structures made up of layer upon layer of lava c. Hawaiian volcanoes are examples ...
... b. Broad, flat structures made up of layer upon layer of lava c. Hawaiian volcanoes are examples ...
Earth History 870:035
... (some limitations) • Although physical laws may be constant through time, rates sometimes vary! – e.g., Earth’s rotation is slowing down ...
... (some limitations) • Although physical laws may be constant through time, rates sometimes vary! – e.g., Earth’s rotation is slowing down ...
Get out your pieces for Tectonicland Have your HOMEWORK out
... Answer these questions in your notebook: ...
... Answer these questions in your notebook: ...
Chapter 5 Earth and Its Moon
... Tides tend to exert a “drag” force on Earth, slowing its rotation. This will continue until Earth rotates synchronously with the Moon, so that the same side of Earth always points toward the Moon. ...
... Tides tend to exert a “drag” force on Earth, slowing its rotation. This will continue until Earth rotates synchronously with the Moon, so that the same side of Earth always points toward the Moon. ...
Historical Geology
... • Solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago – by condensation and gravitational collapse – of a rotating interstellar cloud ...
... • Solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago – by condensation and gravitational collapse – of a rotating interstellar cloud ...
sxES_G6_RNG_ch04-A_070-073.fm
... 19. Wegener’s idea that the continents slowly moved over Earth’s surface became known as 20. Circle the letter of each sentence that supports Wegener’s hypothesis. a. Some continents match up like jigsaw puzzle pieces. b. Different rock structures are found on different continents. c. Fossils of tro ...
... 19. Wegener’s idea that the continents slowly moved over Earth’s surface became known as 20. Circle the letter of each sentence that supports Wegener’s hypothesis. a. Some continents match up like jigsaw puzzle pieces. b. Different rock structures are found on different continents. c. Fossils of tro ...
Usually rocks are formed by heat, pressure, or both. Which of these
... C. Creating mountains and trenches on land and in the oceans D. Rearranging the order of the Earth’s ...
... C. Creating mountains and trenches on land and in the oceans D. Rearranging the order of the Earth’s ...
ASTR 1110H – Fall 2004
... The Earth’s atmosphere is transparent to visible (and some UV) radiation from the Sun. This radiation strikes the surface of the Earth, heating it. The Earth then reradiates that heat as infrared radiation, but the Earth’s atmosphere is opaque to those wavelengths, so the heat is retained. 18. Venus ...
... The Earth’s atmosphere is transparent to visible (and some UV) radiation from the Sun. This radiation strikes the surface of the Earth, heating it. The Earth then reradiates that heat as infrared radiation, but the Earth’s atmosphere is opaque to those wavelengths, so the heat is retained. 18. Venus ...
7 Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements:
... 7th Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements: Learning Target: I will be able to create & develop a Movie with Live Movie Maker by utilizing the knowledge I have been practicing over the last two weeks. I will explore and compile facts about an Earth Science topic that I am starting to study in ...
... 7th Grade Earth Science Movie Maker Requirements: Learning Target: I will be able to create & develop a Movie with Live Movie Maker by utilizing the knowledge I have been practicing over the last two weeks. I will explore and compile facts about an Earth Science topic that I am starting to study in ...
Earth`s Structure Worksheet
... 3. Outer Core – The outer core is the only liquid layer of the Earth – a sea of mostly iron and nickel. It is roughly 1800 – 3200 miles below the surface and about 1400 miles thick. Temperatures reach 6,000° C. ...
... 3. Outer Core – The outer core is the only liquid layer of the Earth – a sea of mostly iron and nickel. It is roughly 1800 – 3200 miles below the surface and about 1400 miles thick. Temperatures reach 6,000° C. ...
Label and Describe the Earth Diagram
... Read the definitions then use the information to color code, label and describe IN YOUR OWN WORDS each section of the diagram below. Definitions: crust – (green) the rigid, rocky outer surface of the Earth, composed mostly of basalt and granite. The crust is the thinnest of all layers. It is thicker ...
... Read the definitions then use the information to color code, label and describe IN YOUR OWN WORDS each section of the diagram below. Definitions: crust – (green) the rigid, rocky outer surface of the Earth, composed mostly of basalt and granite. The crust is the thinnest of all layers. It is thicker ...
Spherical Earth

The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to around the 6th century BC, when it was mentioned in ancient Greek philosophy, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC, when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given. The paradigm was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's expedition's circumnavigation (1519−1522).The concept of a spherical Earth displaced earlier beliefs in a flat Earth: In early Mesopotamian mythology, the world was portrayed as a flat disk floating in the ocean and surrounded by a spherical sky, and this forms the premise for early world maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus. Other speculations on the shape of Earth include a seven-layered ziggurat or cosmic mountain, alluded to in the Avesta and ancient Persian writings (see seven climes).The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 18th century (Maupertuis).In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to be of the order of 1/300 (Delambre, Everest). The modern value as determined by the US DoD World Geodetic System since the 1960s is close to 1/298.25.