Bagian 2 termodinamika
... and propels itself without the use of coal or oil in the following way. It pumps in warm sea water, extracts heat from that sea water, concentrates the extracted heat in its boilers, and discharges the cooled seawater back into the ocean. The discharged water may be ice if enough heat has been taken ...
... and propels itself without the use of coal or oil in the following way. It pumps in warm sea water, extracts heat from that sea water, concentrates the extracted heat in its boilers, and discharges the cooled seawater back into the ocean. The discharged water may be ice if enough heat has been taken ...
Thermal mass - City of Hobart
... The sun’s light falls upon the earth at varying angles depending upon the time of year. As illustrated below, summer sun is ’high’, winter sun is ‘low’. This offers opportunities to control the amount of solar gain, e.g moderate summer heat/gain and maximise winter heat/gain. ...
... The sun’s light falls upon the earth at varying angles depending upon the time of year. As illustrated below, summer sun is ’high’, winter sun is ‘low’. This offers opportunities to control the amount of solar gain, e.g moderate summer heat/gain and maximise winter heat/gain. ...
Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and Latent Heat In addition
... Question: If not the sun, then where does the atmosphere get its energy from? Answer: Most of the atmosphere's energy comes from from the Earth below It works kind of like the following..... ...
... Question: If not the sun, then where does the atmosphere get its energy from? Answer: Most of the atmosphere's energy comes from from the Earth below It works kind of like the following..... ...
lecture21
... in the reverse direction. The first law places no restriction on direction. A process will not occur unless it satisfies both the first and second laws of thermodynamics. Second law not only identifies the direction of process, it also asserts that energy has quality as well as quantity. Thermal Res ...
... in the reverse direction. The first law places no restriction on direction. A process will not occur unless it satisfies both the first and second laws of thermodynamics. Second law not only identifies the direction of process, it also asserts that energy has quality as well as quantity. Thermal Res ...
Summary of Heat Transfer
... Phenomenon: Thermal radiation The radiation energy transfer is through energy-carrying electromagnetic waves that are emitted by atoms and molecules due to change in their energy content. It means: does not depend on an intermediate material. The rate of thermal energy emitted by a surface depends ...
... Phenomenon: Thermal radiation The radiation energy transfer is through energy-carrying electromagnetic waves that are emitted by atoms and molecules due to change in their energy content. It means: does not depend on an intermediate material. The rate of thermal energy emitted by a surface depends ...
Heat
... calorie The amount of heat required to increase the temperature of 1 gram of water from 4C to 5C. Notice this is a lower case word. Calorie with a capital “C” is used when refering to food. It equals 1000 calories (lower case “c”), or 1 ...
... calorie The amount of heat required to increase the temperature of 1 gram of water from 4C to 5C. Notice this is a lower case word. Calorie with a capital “C” is used when refering to food. It equals 1000 calories (lower case “c”), or 1 ...
Reversible and irreversible Processes
... infinitesimal small change in some property of the system. “Gedankenexperiment” to picture a reversible process: ...
... infinitesimal small change in some property of the system. “Gedankenexperiment” to picture a reversible process: ...
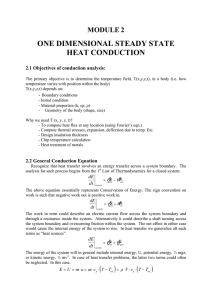
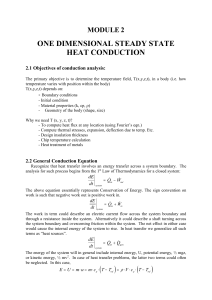
one dimensional steady state heat conduction
... With constant k, the above equation may be integrated twice to obtain the general solution: T ( x ) C1 x C 2 where C1 and C2 are constants of integration. To obtain the constants of integration, we apply the boundary conditions at x = 0 and x = L, in which case T (0) Ts ,1 ...
... With constant k, the above equation may be integrated twice to obtain the general solution: T ( x ) C1 x C 2 where C1 and C2 are constants of integration. To obtain the constants of integration, we apply the boundary conditions at x = 0 and x = L, in which case T (0) Ts ,1 ...
Document
... 15. How much heat energy is required to heat a 14.75 g sample of ice at -23˚C to steam at 121˚C? Cice = 2.06 J/g˚C Csteam = 2.02 J/g˚C ΔHfus = 6.02 kJ/mol ΔHvap = 40.7 kJ/mol ...
... 15. How much heat energy is required to heat a 14.75 g sample of ice at -23˚C to steam at 121˚C? Cice = 2.06 J/g˚C Csteam = 2.02 J/g˚C ΔHfus = 6.02 kJ/mol ΔHvap = 40.7 kJ/mol ...
Heat sink

A heat sink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device into a coolant fluid in motion. Then-transferred heat leaves the device with the fluid in motion, therefore allowing the regulation of the device temperature at physically feasible levels. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool central processing units or graphics processors. Heat sinks are used with high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the basic device is insufficient to moderate its temperature.A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die temperature of the integrated circuit. Thermal adhesive or thermal grease improve the heat sink's performance by filling air gaps between the heat sink and the heat spreader on the device.