On the Possibility of Nuclear Synthesis During Orthopositronium
... Amongst the products of reaction we focus on 3 He, since (on the one hand) it is formed directly in the neutron channel, and (on the other) it accumulates, because of the decay T → 3 He + e− + ν̃ from the tritium channel. The accumulation method with exposition time texp ∼ 0.32 years and a high-sens ...
... Amongst the products of reaction we focus on 3 He, since (on the one hand) it is formed directly in the neutron channel, and (on the other) it accumulates, because of the decay T → 3 He + e− + ν̃ from the tritium channel. The accumulation method with exposition time texp ∼ 0.32 years and a high-sens ...
Lecture 8
... •A black hole is a region of space from which nothing can escape to the outside •The boundary of a black holes is called the event horizon because no events occurring beyond the horizon can be seen from the outside. •After a star has collapsed to within a black hole, it continues to collapse to the ...
... •A black hole is a region of space from which nothing can escape to the outside •The boundary of a black holes is called the event horizon because no events occurring beyond the horizon can be seen from the outside. •After a star has collapsed to within a black hole, it continues to collapse to the ...
Name: Period: _____ Date: 8th Grade Fall Semester Exam Review
... the same column, what can you conclude about these elements? A. They have the same number of protons. B. They have the same state of matter at room temperature. C. The ratio of their protons to neutrons is the same. D. They have similar chemical properties. 21. Why are recently discovered elements a ...
... the same column, what can you conclude about these elements? A. They have the same number of protons. B. They have the same state of matter at room temperature. C. The ratio of their protons to neutrons is the same. D. They have similar chemical properties. 21. Why are recently discovered elements a ...
Theory of the Nuclear Binding Energy
... From experimental data follows that mass of alpha particle is 3727.379240(82) MeV [3]. Mass of two protons and two neutrons is 3755.67485(84) [4]. It leads to the mean binding energy per nucleon about –7.074 MeV. We can see that the theoretical result, –7.069 MeV, is very close to experimental data. ...
... From experimental data follows that mass of alpha particle is 3727.379240(82) MeV [3]. Mass of two protons and two neutrons is 3755.67485(84) [4]. It leads to the mean binding energy per nucleon about –7.074 MeV. We can see that the theoretical result, –7.069 MeV, is very close to experimental data. ...
Synoptic physics paraphrased
... providing information on their charge and momentum. As with the mass spectrometer. Cloud chambers- diffusion type. Tiny drop of alcohol condense around the ionisation trail left by the particles. Supersaturated with alcohol vapour. The path is straight because alpha particles have a relatively large ...
... providing information on their charge and momentum. As with the mass spectrometer. Cloud chambers- diffusion type. Tiny drop of alcohol condense around the ionisation trail left by the particles. Supersaturated with alcohol vapour. The path is straight because alpha particles have a relatively large ...
Advanced Level Physics - Edexcel
... (b) The electric heater runs from a 230 V supply and takes 30 hours to supply 0.55 GJ of ...
... (b) The electric heater runs from a 230 V supply and takes 30 hours to supply 0.55 GJ of ...
PDF sample
... Powerful though these electric and magnetic forces are, they are trifling compared to yet stronger forces at work within the atomic nucleus. Disrupt the effects of these strong forces and you can release nuclear power; disrupt the electric and magnetic forces and you get the more ambient effects of c ...
... Powerful though these electric and magnetic forces are, they are trifling compared to yet stronger forces at work within the atomic nucleus. Disrupt the effects of these strong forces and you can release nuclear power; disrupt the electric and magnetic forces and you get the more ambient effects of c ...
1/2 - Indico
... Standard Big-Bang model basic physics: If the recessional velocity of every galaxy remained unchanged through all time, any galaxy now receding from us was once arbitrarily close and the time that has elapsed since then is equal to the ratio of galaxy’s distance and its velocity. Since this ratio is ...
... Standard Big-Bang model basic physics: If the recessional velocity of every galaxy remained unchanged through all time, any galaxy now receding from us was once arbitrarily close and the time that has elapsed since then is equal to the ratio of galaxy’s distance and its velocity. Since this ratio is ...
NUCLEI of ATOMS Vladislav Konovalov Abstract
... 5799-97. Two debris with summary number α-particles in them, equal 46 at the end should be received. Apparently, that these debris should have minimum potential energy, i.e. to be maximum symmetrical with "magic" number of nucleons, for example, Xe(999) and Kr(99), but then the sum α-particles will ...
... 5799-97. Two debris with summary number α-particles in them, equal 46 at the end should be received. Apparently, that these debris should have minimum potential energy, i.e. to be maximum symmetrical with "magic" number of nucleons, for example, Xe(999) and Kr(99), but then the sum α-particles will ...
A Brief History of History
... Gravity is an all-pervasive force. Every object experiences gravity and every object exerts gravity on its neighbours. In the giant clouds of hydrogen and helium that filled the early universe, gravity caused some, slightly more dense parts, to pull surrounding material towards them. They grew by ‘h ...
... Gravity is an all-pervasive force. Every object experiences gravity and every object exerts gravity on its neighbours. In the giant clouds of hydrogen and helium that filled the early universe, gravity caused some, slightly more dense parts, to pull surrounding material towards them. They grew by ‘h ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
... resonance” when it is irradiated with RF photons having energy equal to the energy difference between the spin states. ¾ A photon with the right amount of energy can be absorbed and cause the spinning proton to flip. ...
... resonance” when it is irradiated with RF photons having energy equal to the energy difference between the spin states. ¾ A photon with the right amount of energy can be absorbed and cause the spinning proton to flip. ...
File - Prairie Science
... Nova and Supernovas: Some white dwarf stars are part of a binary star system. If a white dwarf is around a red giant, the gravity of the very dense white dwarf may capture loosely held gases from the red giant. As the gases accumulate, the pressure builds up and may lead to an explosion called a n ...
... Nova and Supernovas: Some white dwarf stars are part of a binary star system. If a white dwarf is around a red giant, the gravity of the very dense white dwarf may capture loosely held gases from the red giant. As the gases accumulate, the pressure builds up and may lead to an explosion called a n ...
Wednesday, November 5 - Otterbein University
... the point where we could answer this question • Needed to develop very advanced physics: quantum mechanics and nuclear physics • Virtually the only process that can do it is nuclear fusion ...
... the point where we could answer this question • Needed to develop very advanced physics: quantum mechanics and nuclear physics • Virtually the only process that can do it is nuclear fusion ...
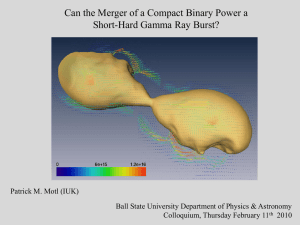
motl_bsu_021210
... horizon*, to escape from the event horizon you must have a velocity equal to the speed of light (impossible for any material body). The region inside the event horizon is fundamentally isolated (causally disconnected) from the outside Universe From a certain point of view, astrophysical black holes ...
... horizon*, to escape from the event horizon you must have a velocity equal to the speed of light (impossible for any material body). The region inside the event horizon is fundamentally isolated (causally disconnected) from the outside Universe From a certain point of view, astrophysical black holes ...
Subatomic particle processes within neutron stars
... approximately have a number of 1057 neutrons and therefore we would in fact deal with a huge nucleus having a mass number of A~1057 that is held together by gravity and supported by neutron degeneracy pressure. It is estimated that the radius of such a star would lie somewhere between the incredibly ...
... approximately have a number of 1057 neutrons and therefore we would in fact deal with a huge nucleus having a mass number of A~1057 that is held together by gravity and supported by neutron degeneracy pressure. It is estimated that the radius of such a star would lie somewhere between the incredibly ...
Nuclear drip line

In nuclear physics, the boundaries for nuclear particle-stability are called drip lines. Atomic nuclei contain both protons and neutrons—the number of protons defines the identity of that element (ie, carbon always has 6 protons), but the number of neutrons within that element may vary (carbon-12 and its isotope carbon-13, for example). The number of isotopes each element may have is visually represented by plotting boxes, each of which represents a unique nuclear species, on a graph with the number of neutrons increasing on the abscissa (X axis) and number of protons increasing along the ordinate (Y axis). The resulting chart is commonly referred to as the table of nuclides, and is to nuclear physics what the periodic table of the elements is to chemistry.An arbitrary combination of protons and neutrons does not necessarily yield a stable nucleus. One can think of moving up and/or to the right across the nuclear chart by adding one type of nucleon (i.e. a proton or neutron, both called nucleons) to a given nucleus. However, adding nucleons one at a time to a given nucleus will eventually lead to a newly formed nucleus that immediately decays by emitting a proton (or neutron). Colloquially speaking, the nucleon has 'leaked' or 'dripped' out of the nucleus, hence giving rise to the term ""drip line"". Drip lines are defined for protons, neutrons, and alpha particles, and these all play important roles in nuclear physics. The nucleon drip lines are at the extreme of the proton-to-neutron ratio: at p:n ratios at or beyond the driplines, no stable nuclei can exist. The location of the neutron drip line is not well known for most of the nuclear chart, whereas the proton and alpha driplines have been measured for a wide range of elements. The nucleons drip out of such unstable nuclei for the same reason that water drips from a leaking faucet: in the water case, there is a lower potential available that is great enough to overcome surface tension and so produces a droplet; in the case of nuclei, the emission of a particle from a nucleus, against the strong nuclear force, leaves the total potential of the nucleus and the emitted particle in a lower state. Because nucleons are quantized, only integer values are plotted on the table of isotopes; this indicates that the drip line is not linear but instead looks like a step function up close.