Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... – Composed of horizontal sediment layers probably deposited by turbidity currents. – Flattest features on the Earth. ...
... – Composed of horizontal sediment layers probably deposited by turbidity currents. – Flattest features on the Earth. ...
Distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes
... Earth’s crust that determine the direction of movement. Some plates like the North American and Eurasian plates, are moving in opposite directions, away from each other. This type of movement mostly happens under the oceans. As the plates move apart, the ‘gap’ is filled by magma rising up from the m ...
... Earth’s crust that determine the direction of movement. Some plates like the North American and Eurasian plates, are moving in opposite directions, away from each other. This type of movement mostly happens under the oceans. As the plates move apart, the ‘gap’ is filled by magma rising up from the m ...
Drilling at sea: Hydrocarbon Exploration
... There are many examples of Stage 1. East African Rift Valley is the classic example. But also the Midland Valley of Scotland, the Rhine Graben, the Oslo Graben. These rifts have never got beyond stage 1. Commonly the volcanism associated with these rifts is highly alkaline and undersaturated in sili ...
... There are many examples of Stage 1. East African Rift Valley is the classic example. But also the Midland Valley of Scotland, the Rhine Graben, the Oslo Graben. These rifts have never got beyond stage 1. Commonly the volcanism associated with these rifts is highly alkaline and undersaturated in sili ...
Lecture 14 – Marine Sediments (1) The CCD is: (a) the depth at
... The sediment will be foram ooze with siliceous components; it is productive so both will be there but it is above the CCD so carbonate is preserved and there is more of it, it is far from land so little terrigenous material. If the depth is 5000 meters in the same productive area we would expect the ...
... The sediment will be foram ooze with siliceous components; it is productive so both will be there but it is above the CCD so carbonate is preserved and there is more of it, it is far from land so little terrigenous material. If the depth is 5000 meters in the same productive area we would expect the ...
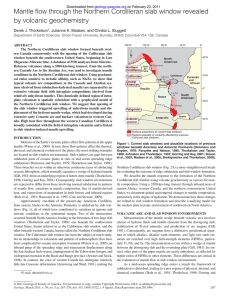
Mantle flow through the Northern Cordilleran slab window revealed
... 1996; Gorring and Kay, 2001). Consequently, slab window environments are expected to differ from those involving normal subduction in patterns of mantle flow, variations in mantle composition, flux of mantle-derived heat, and expressions of magmatism in both forearc and inboard regions (Hole et al., ...
... 1996; Gorring and Kay, 2001). Consequently, slab window environments are expected to differ from those involving normal subduction in patterns of mantle flow, variations in mantle composition, flux of mantle-derived heat, and expressions of magmatism in both forearc and inboard regions (Hole et al., ...
ES 104 Midterm Exam Study Guide 1
... Divergent boundaries – mid-ocean ridges and continental rifts The formation of new lithosphere at mid-ocean ridges – sea floor spreading Driving force at these boundaries – rising hot mantle – explains why ridges are elevated above the surrounding seafloor. Know that lithosphere gets thicker, colder ...
... Divergent boundaries – mid-ocean ridges and continental rifts The formation of new lithosphere at mid-ocean ridges – sea floor spreading Driving force at these boundaries – rising hot mantle – explains why ridges are elevated above the surrounding seafloor. Know that lithosphere gets thicker, colder ...
Plate Tectonics - El Camino College
... pile on top of it, so it becomes more and more dense with time. As the ocean floor moves away from the mid-ocean ridge (“sea-floor spreading”), it either pushes a continent (“continental drift”) or runs into another plate, leading to earthquakes. Both plates cannot occupy the same location, so the p ...
... pile on top of it, so it becomes more and more dense with time. As the ocean floor moves away from the mid-ocean ridge (“sea-floor spreading”), it either pushes a continent (“continental drift”) or runs into another plate, leading to earthquakes. Both plates cannot occupy the same location, so the p ...
Lithospheric mantle density structure of the North China Craton
... seismic and thermal data. A new seismic crustal model is applied to remove the effect of the sedimentary cover and crystalline crust from observed gravity field. An updated thermal lithosphere thickness data is used to calculate density of lithospheric mantle by removing gravity effect of lithospher ...
... seismic and thermal data. A new seismic crustal model is applied to remove the effect of the sedimentary cover and crystalline crust from observed gravity field. An updated thermal lithosphere thickness data is used to calculate density of lithospheric mantle by removing gravity effect of lithospher ...
Earth`s Crust - Student Handouts - PITA
... earthquakes. This rubbing and scraping is called ___. 37) Together, the lithosphere, asthenosphere and mesosphere make up the layer called the ___. 41) When two plates collide, ocean crust will sink back into the mantle, slightly pulling down the edge of the other plate, creating a V-shaped valley w ...
... earthquakes. This rubbing and scraping is called ___. 37) Together, the lithosphere, asthenosphere and mesosphere make up the layer called the ___. 41) When two plates collide, ocean crust will sink back into the mantle, slightly pulling down the edge of the other plate, creating a V-shaped valley w ...
PDF File - Tulane University
... depleted relative to MORBs. Second, the elements Nb, Ta, and Ti show negative anomalies (depletion) relative to elements like Ba, K, La, and Ce. We'll discuss the implications of each of these points below: 1. Lack of HREE depletion. When oceanic crust is subducted it traverses a path of increasing ...
... depleted relative to MORBs. Second, the elements Nb, Ta, and Ti show negative anomalies (depletion) relative to elements like Ba, K, La, and Ce. We'll discuss the implications of each of these points below: 1. Lack of HREE depletion. When oceanic crust is subducted it traverses a path of increasing ...
Earth Communication
... move slowly and change in size. Intense geologic activity, like earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries where plates move away from each other, past each other or toward one another. There are eight large plates and four smaller plates that make up the outer shell of the Earth like a puz ...
... move slowly and change in size. Intense geologic activity, like earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries where plates move away from each other, past each other or toward one another. There are eight large plates and four smaller plates that make up the outer shell of the Earth like a puz ...
Earth Communication
... move slowly and change in size. Intense geologic activity, like earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries where plates move away from each other, past each other or toward one another. There are eight large plates and four smaller plates that make up the outer shell of the Earth like a puz ...
... move slowly and change in size. Intense geologic activity, like earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries where plates move away from each other, past each other or toward one another. There are eight large plates and four smaller plates that make up the outer shell of the Earth like a puz ...
Introduction to the special issue on “Subduction Zones”
... enters a subduction zone, the positive buoyancy of the continental crust will resist subduction, leading to a slow-down, and ultimately to the end of subduction (e.g., McKenzie, 1969). Continental collision is accompanied by severe crustal and lithospheric deformation, mountain building, slab breako ...
... enters a subduction zone, the positive buoyancy of the continental crust will resist subduction, leading to a slow-down, and ultimately to the end of subduction (e.g., McKenzie, 1969). Continental collision is accompanied by severe crustal and lithospheric deformation, mountain building, slab breako ...
Constraints on flux rates and mantle dynamics beneath island arcs
... convective overturn within the mantle wedge1,2 and may also localize the sheeted downwellings of upper-mantle convection3. The surface expressions of subduction are the curved chains of active volcanoes that form island arcs, and the magmatic flux in these volcanoes is an important component of new ...
... convective overturn within the mantle wedge1,2 and may also localize the sheeted downwellings of upper-mantle convection3. The surface expressions of subduction are the curved chains of active volcanoes that form island arcs, and the magmatic flux in these volcanoes is an important component of new ...
Introduction: Tracking Past Plate Motions (2)
... When the sinking of a subducting plate is faster than the forward motion of the overriding plate, the margin of the overriding plate can be subjected to tensional (pulling) stress. If the overriding plate is oceanic or if the extension of a continental margin has progressed to an extreme state, an ...
... When the sinking of a subducting plate is faster than the forward motion of the overriding plate, the margin of the overriding plate can be subjected to tensional (pulling) stress. If the overriding plate is oceanic or if the extension of a continental margin has progressed to an extreme state, an ...
The American Cordillera: Part III, The North American Taphrogen
... Miocene. The Numic retreat rate is much slower during this period suggesting that perhaps it has detached from the deeper portion of the subducted Farallon slab. The Piman slab retreats more rapidly from 3025 Ma and pulls off the southwesterly edge of the main Laramide flat slab segment (the segment ...
... Miocene. The Numic retreat rate is much slower during this period suggesting that perhaps it has detached from the deeper portion of the subducted Farallon slab. The Piman slab retreats more rapidly from 3025 Ma and pulls off the southwesterly edge of the main Laramide flat slab segment (the segment ...
Cenozoic plate tectonic reconstructions of SE Asia
... situated in a backarc setting, and the width of the basin may be due to subduction beneath the PSP at both its south and NE edges, causing geochemical and tectonic complexity since both Pacific and Indian plates were being subducted. The new palaeomagnetic data from east Indonesia give a greater con ...
... situated in a backarc setting, and the width of the basin may be due to subduction beneath the PSP at both its south and NE edges, causing geochemical and tectonic complexity since both Pacific and Indian plates were being subducted. The new palaeomagnetic data from east Indonesia give a greater con ...
An Alternative EARTH - Geological Society of America
... basement are preserved, strata commonly begin, not with mafic volcanic rocks, but with thin micaceous quartzite (Fig. 2), derived from basement that was above sea level nearby, and/or with thin chert and banded iron formation (Bleeker, 2002). Above this, lower parts of supracrustal successions are t ...
... basement are preserved, strata commonly begin, not with mafic volcanic rocks, but with thin micaceous quartzite (Fig. 2), derived from basement that was above sea level nearby, and/or with thin chert and banded iron formation (Bleeker, 2002). Above this, lower parts of supracrustal successions are t ...
Word file - FSU GK-12 Contact Information
... 7. So if our two pieces of clay are oceanic crust, and where they meet is a spreading center, how would these plates move? Away from each other Show me with your clay. 8. If they move away from each other, what happens at the ridge? New mantle material rises and attaches to the edge of the plate. Wh ...
... 7. So if our two pieces of clay are oceanic crust, and where they meet is a spreading center, how would these plates move? Away from each other Show me with your clay. 8. If they move away from each other, what happens at the ridge? New mantle material rises and attaches to the edge of the plate. Wh ...
Invitation and - FSU GK-12 Contact Information
... 7. So if our two pieces of clay are oceanic crust, and where they meet is a spreading center, how would these plates move? Away from each other Show me with your clay. 8. If they move away from each other, what happens at the ridge? New mantle material rises and attaches to the edge of the plate. Wh ...
... 7. So if our two pieces of clay are oceanic crust, and where they meet is a spreading center, how would these plates move? Away from each other Show me with your clay. 8. If they move away from each other, what happens at the ridge? New mantle material rises and attaches to the edge of the plate. Wh ...
Download PDF-format paper copies
... Grand (D) and Li and Romanowicz (C). GEMLAB2 (B) is similar to GEMLAB1, but without the strong phase transitions. Root-mean-square spectral amplitude is contoured as a function of nondimensional mantle depth (surface at the top, CMB at the bottom) and spherical harmonic degree (0 to 12). Each panel ...
... Grand (D) and Li and Romanowicz (C). GEMLAB2 (B) is similar to GEMLAB1, but without the strong phase transitions. Root-mean-square spectral amplitude is contoured as a function of nondimensional mantle depth (surface at the top, CMB at the bottom) and spherical harmonic degree (0 to 12). Each panel ...
oceanic crust
... • The dust particles collided together, clumping into larger and larger (and larger and larger…) particles • Tremendous amounts of heat were released from decaying radioactive elements deep within the newly-assembled planet, and from gravitational compression and nearly constant asteroid impacts ...
... • The dust particles collided together, clumping into larger and larger (and larger and larger…) particles • Tremendous amounts of heat were released from decaying radioactive elements deep within the newly-assembled planet, and from gravitational compression and nearly constant asteroid impacts ...
CHAPTER 3
... - Early mariners, and even scientists, had no idea how deep the oceans are or how rugged their bathymetry is. - In about 85 B.C. Posidonius, a Greek geographer, used a large rock tied to a rope to measure a depth of 2 km (1.2 mi) in the Mediterranean Sea. - Soundings, or measures of the depth of the ...
... - Early mariners, and even scientists, had no idea how deep the oceans are or how rugged their bathymetry is. - In about 85 B.C. Posidonius, a Greek geographer, used a large rock tied to a rope to measure a depth of 2 km (1.2 mi) in the Mediterranean Sea. - Soundings, or measures of the depth of the ...
Oceanic trench
The oceanic trenches are hemispheric-scale long but narrow topographic depressions of the sea floor. They are also the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few mm to over ten cm per year. A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.