Lecture Test 2 2010
... A. A nerve fiber is a part of a neuron, and it can also be part of a nerve. B. A nerve fiber is not a long axon, but instead it is the same thing as a nerve. C. A neuron and a nerve are the same thing. D. A neuron is the same as an axon and a nerve fiber. E. Nerves occur in the white matter of the c ...
... A. A nerve fiber is a part of a neuron, and it can also be part of a nerve. B. A nerve fiber is not a long axon, but instead it is the same thing as a nerve. C. A neuron and a nerve are the same thing. D. A neuron is the same as an axon and a nerve fiber. E. Nerves occur in the white matter of the c ...
The Nervous System
... • The spinal cord runs along the dorsal side of the body and links the brain to the rest of the body. Vertebrates have their spinal cords encased in a series of (usually) bony vertebrae that comprise the vertebral column. • The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and dendri ...
... • The spinal cord runs along the dorsal side of the body and links the brain to the rest of the body. Vertebrates have their spinal cords encased in a series of (usually) bony vertebrae that comprise the vertebral column. • The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and dendri ...
nervous system
... cell body and extend into the dendrites and axon. They serve to support the neuron (as neurofibrils) and to transport materials and organells down from the cell body to the axon (axon transport), for regeneration of damaged axons. Axon transport of certain materials also occurs in the opposite direc ...
... cell body and extend into the dendrites and axon. They serve to support the neuron (as neurofibrils) and to transport materials and organells down from the cell body to the axon (axon transport), for regeneration of damaged axons. Axon transport of certain materials also occurs in the opposite direc ...
Document
... Evolutionary Adaptation of Axon Structure • The speed of an action potential increases with the axon’s diameter • In vertebrates, axons are insulated by a myelin sheath, which causes an action potential’s speed to increase • Myelin sheaths are made by glia— oligodendrocytes in the CNS and Schwann c ...
... Evolutionary Adaptation of Axon Structure • The speed of an action potential increases with the axon’s diameter • In vertebrates, axons are insulated by a myelin sheath, which causes an action potential’s speed to increase • Myelin sheaths are made by glia— oligodendrocytes in the CNS and Schwann c ...
Text S1.
... On DW4 pattern the measured value for polarization along L1 is 52.3% (113 axons along L1 out of 216 neurons). As 113 neurons with an axon along L1 were counted at 3 DIV, as many attempted to differentiate along each direction at 1-2 DIV. Since a mean of 34.3 axons along each of the curved lines (103 ...
... On DW4 pattern the measured value for polarization along L1 is 52.3% (113 axons along L1 out of 216 neurons). As 113 neurons with an axon along L1 were counted at 3 DIV, as many attempted to differentiate along each direction at 1-2 DIV. Since a mean of 34.3 axons along each of the curved lines (103 ...
Nervous Tissue
... a. more K+ outside the cell than inside and more Na+ inside the cell than outside b. more K+ inside the cell than outside and Na+ outside the cell than inside c. more K+ and Na inside the cell than outside d. more K+ and Na outside the cell than inside BACK TO GAME ...
... a. more K+ outside the cell than inside and more Na+ inside the cell than outside b. more K+ inside the cell than outside and Na+ outside the cell than inside c. more K+ and Na inside the cell than outside d. more K+ and Na outside the cell than inside BACK TO GAME ...
Chapter 13 - Los Angeles City College
... 1. Sensory Input: Conduction of signals from sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, skin, etc.) to information processing centers (brain and spinal cord). 2. Integration: Interpretation of sensory signals and development of a response. Occurs in brain and spinal cord. 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signa ...
... 1. Sensory Input: Conduction of signals from sensory organs (eyes, ears, nose, skin, etc.) to information processing centers (brain and spinal cord). 2. Integration: Interpretation of sensory signals and development of a response. Occurs in brain and spinal cord. 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signa ...
Electrochemical Impulses
... In a resting membrane, more channels are open to K+ than Na+. Therefore, more K+ diffuses out of the cell than the amount of Na+ that is being diffused into the cell. The more rapid the diffusion of K+ outside makes the outside more positive than the inside of the cell. Therefore, the cell loses a ...
... In a resting membrane, more channels are open to K+ than Na+. Therefore, more K+ diffuses out of the cell than the amount of Na+ that is being diffused into the cell. The more rapid the diffusion of K+ outside makes the outside more positive than the inside of the cell. Therefore, the cell loses a ...
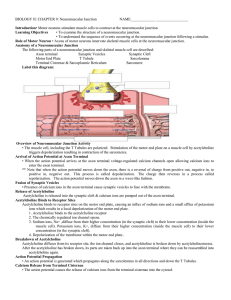
BIOLOGY II: CHAPTER 9: Neuromuscular Junction
... muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of the membrane within the motor end plate.. Breakdown of Acetylcholine Acetylcholine diffuses from its receptor site, the ion ch ...
... muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of the membrane within the motor end plate.. Breakdown of Acetylcholine Acetylcholine diffuses from its receptor site, the ion ch ...
Muscle cells generate force by shortening their length via chemical
... We make a muscle cell contract by depolarizing it, causing calcium release. How do we polarize a membrane creating membrane voltage and what is depolarization? What are the relative Na+, K+ and Ca++ concentrations on the inside/outside of the plasma membrane? Pumps maintain this difference at ATP ...
... We make a muscle cell contract by depolarizing it, causing calcium release. How do we polarize a membrane creating membrane voltage and what is depolarization? What are the relative Na+, K+ and Ca++ concentrations on the inside/outside of the plasma membrane? Pumps maintain this difference at ATP ...
File
... Synapses serve to connect neurons, enabling neurons to communicate by passing signals between them. Neurons control these functions by passing signals across the synapse from one neuron to the next. These signals dictate whether the receiving neuron is activated. The summaries of the diagrams should ...
... Synapses serve to connect neurons, enabling neurons to communicate by passing signals between them. Neurons control these functions by passing signals across the synapse from one neuron to the next. These signals dictate whether the receiving neuron is activated. The summaries of the diagrams should ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = nerves that extend from the brain (cranial nerves) and spinal cord (spinal nerves). ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) = nerves that extend from the brain (cranial nerves) and spinal cord (spinal nerves). ...
Peripheral Neuropathy
... muscles. Many nerves are mixed nerves carrying sensorimotor impulses. Peripheral neuropathy may be experienced as numbness, tingling or burning sensations, pain which may be intense but will eventually reduce to numbness, or muscular weakness. To understand peripheral neuropathy it helps to understa ...
... muscles. Many nerves are mixed nerves carrying sensorimotor impulses. Peripheral neuropathy may be experienced as numbness, tingling or burning sensations, pain which may be intense but will eventually reduce to numbness, or muscular weakness. To understand peripheral neuropathy it helps to understa ...
F214 Oct MOCK - Mrs Miller`s Blog
... sodium channels open and sodium ions move into neurone; potential difference rises from –70mV to 30mV; at Y: potassium channels open and potassium ions move out of neurone; potential difference falls from 30mV to –76mV; AVP;; e.g. ...
... sodium channels open and sodium ions move into neurone; potential difference rises from –70mV to 30mV; at Y: potassium channels open and potassium ions move out of neurone; potential difference falls from 30mV to –76mV; AVP;; e.g. ...
The Two Messenger Services of the Brain
... In fact you can expect feeling to return at a rate of about 1 millimeter a day!!!) ...
... In fact you can expect feeling to return at a rate of about 1 millimeter a day!!!) ...
Chapter 13
... – Portions of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons are found here – Dorsal root of spinal nerves contains sensory fibers entering the gray matter – Ventral root of a spinal nerve contains motor fibers exiting the gray matter ...
... – Portions of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons are found here – Dorsal root of spinal nerves contains sensory fibers entering the gray matter – Ventral root of a spinal nerve contains motor fibers exiting the gray matter ...
Sample Pathway Questions
... thoracic/lumbar regions of the spinal cord. The axon of the neuron passes out the ventral root of the spinal nerve and into the white ramus of the sympathetic chain. In the sympathetic chain ganglion, it will synapse with the cell body of the ganglionic neuron. The axon of the ganglionic neuron will ...
... thoracic/lumbar regions of the spinal cord. The axon of the neuron passes out the ventral root of the spinal nerve and into the white ramus of the sympathetic chain. In the sympathetic chain ganglion, it will synapse with the cell body of the ganglionic neuron. The axon of the ganglionic neuron will ...
The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activity
... Autonomic ganglion are motor ganglia containing the cell bodies of motor neurons They are sites of synapse and information transmission from pre to postganglionic neurons The presence of intrinsic ganglionic cells, analogous to interneurons, suggests that certain intergrative functions may occur the ...
... Autonomic ganglion are motor ganglia containing the cell bodies of motor neurons They are sites of synapse and information transmission from pre to postganglionic neurons The presence of intrinsic ganglionic cells, analogous to interneurons, suggests that certain intergrative functions may occur the ...
The Nervous System
... Axon: carry electrical signals (messages) out of the cells, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons via Axon/Terminals • Myelin: insulates & protects Axons w/a fatty substance ...
... Axon: carry electrical signals (messages) out of the cells, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons via Axon/Terminals • Myelin: insulates & protects Axons w/a fatty substance ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... Consequently, a potential difference (PD) exists across this resting cell membrane. Definition: Potential Difference (PD) = the difference in electrical charge between 2 points (i.e. across a cell membrane). ...
... Consequently, a potential difference (PD) exists across this resting cell membrane. Definition: Potential Difference (PD) = the difference in electrical charge between 2 points (i.e. across a cell membrane). ...
Restoring axonal localization and transport of transmembrane
... of the hippocampus (Milde et al., 2015). This brings us back to the current study. Andrews et al. (2016) showed developing motor and sensory neurons have the ability to traffic growth-promoting integrins within the axonal compartment but only sensory neurons of the PNS, specifically neurons of the D ...
... of the hippocampus (Milde et al., 2015). This brings us back to the current study. Andrews et al. (2016) showed developing motor and sensory neurons have the ability to traffic growth-promoting integrins within the axonal compartment but only sensory neurons of the PNS, specifically neurons of the D ...
Chapter 11
... In PNS – a little bit of regeneration – neurilemma plays a role in fiber regeneration In CNS - none ...
... In PNS – a little bit of regeneration – neurilemma plays a role in fiber regeneration In CNS - none ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.