Semester 1 Review - Lemon Bay High School
... 51. What type of tidal patterns exists on the west coast of the United States, which receives two high tides and two low tides of varying heights per day? 52. Tidal height is compared to what reference level? 53. Most of the world's ocean coasts have a(n) _____ tidal pattern. 54. Where was the first ...
... 51. What type of tidal patterns exists on the west coast of the United States, which receives two high tides and two low tides of varying heights per day? 52. Tidal height is compared to what reference level? 53. Most of the world's ocean coasts have a(n) _____ tidal pattern. 54. Where was the first ...
Plate Tectonics - Paul J. Goodenough
... 1. Less dense magma flows sideways dragging the seafloor along. 2. As the seafloor spread apart, magma flows up through cracks in at the ridge forming new rock. B. Evidence 1. Drilling: Ocean floor rock samples show that the age of the rock gets older the further the rock is from the mid-ocean ridge ...
... 1. Less dense magma flows sideways dragging the seafloor along. 2. As the seafloor spread apart, magma flows up through cracks in at the ridge forming new rock. B. Evidence 1. Drilling: Ocean floor rock samples show that the age of the rock gets older the further the rock is from the mid-ocean ridge ...
Convection and Density
... Causes of Plate Motion • Heat from the Earth’s core causes materials in the lower asthenosphere to become less dense and rise up. • When the materials come in contact with the lithosphere they start to cool down and become denser again. • As the cooled magma falls and new heated magma rises, it act ...
... Causes of Plate Motion • Heat from the Earth’s core causes materials in the lower asthenosphere to become less dense and rise up. • When the materials come in contact with the lithosphere they start to cool down and become denser again. • As the cooled magma falls and new heated magma rises, it act ...
What happens in an earthquake?
... • Now describe in a paragraph what happens when an earthquake occurs… EXTENSION - Make sure you use the following words: Tension Focus Epicentre Seismic waves Friction ...
... • Now describe in a paragraph what happens when an earthquake occurs… EXTENSION - Make sure you use the following words: Tension Focus Epicentre Seismic waves Friction ...
Lecture 10 Plate Tectonics i
... latitude (north or south of equator) • Radiometric dates of ocean floor basalts, plus distance from ridge, gives paleolatitude for last 200 million years ...
... latitude (north or south of equator) • Radiometric dates of ocean floor basalts, plus distance from ridge, gives paleolatitude for last 200 million years ...
Chapter 4
... between two tectonic plates that are pulling away from each other. As tectonic plates pull apart, stress between the plates causes a series of faults to form along the rift zone. ...
... between two tectonic plates that are pulling away from each other. As tectonic plates pull apart, stress between the plates causes a series of faults to form along the rift zone. ...
Ch 8 Earth Science PPT
... most widely used measurement for earthquakes because it is the only magnitude scale that estimates the energy released by earthquakes. ...
... most widely used measurement for earthquakes because it is the only magnitude scale that estimates the energy released by earthquakes. ...
History in Geography
... (Just to note) • Magnetism caused by presence of magnetic minerals in the rocks • Scientists were not surprised to learn that seafloor rocks contain the magnetic mineral magnetite ...
... (Just to note) • Magnetism caused by presence of magnetic minerals in the rocks • Scientists were not surprised to learn that seafloor rocks contain the magnetic mineral magnetite ...
Earth_Yesterday_Today_and_Tomorrow
... The Earth has a very long history (4.6 billion years). Scientists learn about major events in the history of the earth by using rocks, rock layers, and fossils. The fossils in some layers of rock can be used to determine the relative age of different rock layers(its age compared to other rocks). Law ...
... The Earth has a very long history (4.6 billion years). Scientists learn about major events in the history of the earth by using rocks, rock layers, and fossils. The fossils in some layers of rock can be used to determine the relative age of different rock layers(its age compared to other rocks). Law ...
Earth, Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
... The Earth has a very long history (4.6 billion years). Scientists learn about major events in the history of the earth by using rocks, rock layers, and fossils. The fossils in some layers of rock can be used to determine the relative age of different rock layers(its age compared to other rocks). Law ...
... The Earth has a very long history (4.6 billion years). Scientists learn about major events in the history of the earth by using rocks, rock layers, and fossils. The fossils in some layers of rock can be used to determine the relative age of different rock layers(its age compared to other rocks). Law ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR MID-TERM EXAM KEY In which type of rock are
... What does the picture below illustrate (show): Fault ...
... What does the picture below illustrate (show): Fault ...
Venus - Sdbv
... retrograde (backwards) which causes 2 solar days per year, yet the greenhouse effect keeps the entire planet at about 800oF. ...
... retrograde (backwards) which causes 2 solar days per year, yet the greenhouse effect keeps the entire planet at about 800oF. ...
Review for Earthquakes Test
... 1. What does magnitude measure? _________________________________________________________________ 2. What scale is traditionally used to measure magnitude? _______________________________________________ 3. Each increase in magnitude number represents a _____________ increase in energy released. 4. ...
... 1. What does magnitude measure? _________________________________________________________________ 2. What scale is traditionally used to measure magnitude? _______________________________________________ 3. Each increase in magnitude number represents a _____________ increase in energy released. 4. ...
Plate Tectonics
... break up about 200 million years ago. • Continents "drifted" to their present positions. ...
... break up about 200 million years ago. • Continents "drifted" to their present positions. ...
Earth Science
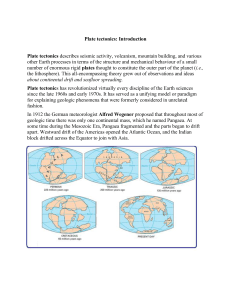
... shapes of the continents, the similarity of life forms and land forms in corresponding parts of Africa and South America, and the increasing separation of Greenland and Europe. Even with the evidence and the realization that the earth was old enough for this to have occurred; very few contemporary s ...
... shapes of the continents, the similarity of life forms and land forms in corresponding parts of Africa and South America, and the increasing separation of Greenland and Europe. Even with the evidence and the realization that the earth was old enough for this to have occurred; very few contemporary s ...
Stress and Strain - El Molino High School
... • Secondary waves, called S-waves, are named with respect to their arrival times. • They are slower than P-waves, so they are the second set of waves to be felt. S-waves have a motion that causes rocks to move perpendicular to the direction of the waves. ...
... • Secondary waves, called S-waves, are named with respect to their arrival times. • They are slower than P-waves, so they are the second set of waves to be felt. S-waves have a motion that causes rocks to move perpendicular to the direction of the waves. ...
Iron Hill Museum Middle School Geology Program Teachers: This
... 1. All processes that affect rocks and minerals are a result of energy from the Sun or Earth’s interior. 2. Rocks cycle from one kind to another due to processes that are aided by the hydrosphere, atmosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. 3. Humans depend on rocks and minerals for many purposes. These r ...
... 1. All processes that affect rocks and minerals are a result of energy from the Sun or Earth’s interior. 2. Rocks cycle from one kind to another due to processes that are aided by the hydrosphere, atmosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. 3. Humans depend on rocks and minerals for many purposes. These r ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.