Master`s Thesis - Chalmers Publication Library
... than 360 million people in the world [1]. Communication, social and economic problems are only some aspects of this impairment. Receiving acoustic stimulation through the auditory system and converting it to auditory sensation will result in hearing. The acoustic stimuli received by the ears is conv ...
... than 360 million people in the world [1]. Communication, social and economic problems are only some aspects of this impairment. Receiving acoustic stimulation through the auditory system and converting it to auditory sensation will result in hearing. The acoustic stimuli received by the ears is conv ...
Otoacoustic Emissions in Young Children with Autism
... system asymmetry and suggested that this asymmetry indirectly reflects more central auditory processing alterations [16, 17]. However, MOC functions were found to be normal in Asperger syndrome, which is part of the autistic spectrum and shows auditory sensitivity reactions similar to those observed ...
... system asymmetry and suggested that this asymmetry indirectly reflects more central auditory processing alterations [16, 17]. However, MOC functions were found to be normal in Asperger syndrome, which is part of the autistic spectrum and shows auditory sensitivity reactions similar to those observed ...
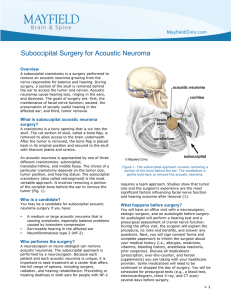
Suboccipital Surgery for Acoustic Neuroma
... the dura. The dura is opened and folded back to expose the brain. Retractors are used to gently hold back the cerebellum, allowing the surgeon to see the acoustic neuroma and the nerves (Fig. 3). Step 4: debulk the tumor Depending on the size, acoustic neuromas can be attached to the facial nerve, t ...
... the dura. The dura is opened and folded back to expose the brain. Retractors are used to gently hold back the cerebellum, allowing the surgeon to see the acoustic neuroma and the nerves (Fig. 3). Step 4: debulk the tumor Depending on the size, acoustic neuromas can be attached to the facial nerve, t ...
Cochlear Implant - Capital Blue Cross
... sounds that are louder than 90 dB HL [hearing level] at frequencies of 2 and 4 kHz without acoustic hearing aids. Adequate benefit from acoustic hearing aids is defined for this guidance as: for adults, a score of 50% or greater on Bamford-Kowal-Bench (BKB) sentence testing at a sound intensity of 7 ...
... sounds that are louder than 90 dB HL [hearing level] at frequencies of 2 and 4 kHz without acoustic hearing aids. Adequate benefit from acoustic hearing aids is defined for this guidance as: for adults, a score of 50% or greater on Bamford-Kowal-Bench (BKB) sentence testing at a sound intensity of 7 ...
Dichotic Word Recognition in Young and Older Adults
... in which one auditory stimulus is presented to the right ear and a second, different stimulus is presented simultaneously to the left ear. The difficulty of the dichotic listening task is dependent upon the type of stimuli presented to the two ears. At one end of the dichotic difficulty continuum, b ...
... in which one auditory stimulus is presented to the right ear and a second, different stimulus is presented simultaneously to the left ear. The difficulty of the dichotic listening task is dependent upon the type of stimuli presented to the two ears. At one end of the dichotic difficulty continuum, b ...
OSHA Occupational Noise - San Diego State University
... • If threshold shift from occ. noise exp. – Employee fitted with hearing protectors, trained in use and care, required to use them. – Employee refitted with better attenuation hearing protectors and retrained in hearing protector use – Refer employee to eval/exam if add. testing necessary or if medi ...
... • If threshold shift from occ. noise exp. – Employee fitted with hearing protectors, trained in use and care, required to use them. – Employee refitted with better attenuation hearing protectors and retrained in hearing protector use – Refer employee to eval/exam if add. testing necessary or if medi ...
EEG based detection of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss
... oto-acoustic emissions (TEOAE) and automated auditory brainstem response (AABR). Auditory brainstem response (ABR) is an electrical potential signal emanated from the scalp of the brain by presenting a sound stimulus to assess the functioning of auditory neuropathy by using electroencephalography [3 ...
... oto-acoustic emissions (TEOAE) and automated auditory brainstem response (AABR). Auditory brainstem response (ABR) is an electrical potential signal emanated from the scalp of the brain by presenting a sound stimulus to assess the functioning of auditory neuropathy by using electroencephalography [3 ...
Evoked Potential Studies
... Three types of evoked potentials include somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs), visual evoked potentials (VEP), and brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEPs). These tests can be performed as outpatient diagnostic testing or inpatient for intraoperative monitoring. Somatosensory evoked potential ...
... Three types of evoked potentials include somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs), visual evoked potentials (VEP), and brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEPs). These tests can be performed as outpatient diagnostic testing or inpatient for intraoperative monitoring. Somatosensory evoked potential ...
postoperatively, the patient’s uncor- revealed a serous retinal detach-
... past, although photographs are not available. Animal studies of Schnabel optic atrophy have demonstrated that prolonged rises in intraocular pressure may lead to ruptures in the inner limiting membrane and subsequent penetration of vitreous into ...
... past, although photographs are not available. Animal studies of Schnabel optic atrophy have demonstrated that prolonged rises in intraocular pressure may lead to ruptures in the inner limiting membrane and subsequent penetration of vitreous into ...
Chapter 177: Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
... from 8 patients with sudden hearing loss found that atrophy of the organ of Corti and loss of cochlear neurons were the most common changes noted, again suggesting viral infection. They also point out that autoimmune disease of the inner ear associated with hearing loss results in fibrosis and ossif ...
... from 8 patients with sudden hearing loss found that atrophy of the organ of Corti and loss of cochlear neurons were the most common changes noted, again suggesting viral infection. They also point out that autoimmune disease of the inner ear associated with hearing loss results in fibrosis and ossif ...
Types of Hearing Loss - Dizziness and Balance
... Hearing loss can develop at any age and may be caused by many different factors. Hearing loss is most often categorized as sensorineural, conductive, or mixed. Sensorineural Hearing Loss Also called “nerve-related” hearing loss, it occurs when the inner ear or the actual hearing nerve itself becomes ...
... Hearing loss can develop at any age and may be caused by many different factors. Hearing loss is most often categorized as sensorineural, conductive, or mixed. Sensorineural Hearing Loss Also called “nerve-related” hearing loss, it occurs when the inner ear or the actual hearing nerve itself becomes ...
PDF Version
... Other techniques, such as oto-acoustic emissions or automated testing of short-latency auditory evoked potentials, can be used in maternity wards to screen for neonatal hearing loss. Brainstem auditory evoked potentials are also useful for obtaining initial data on high-frequency hearing thresholds. ...
... Other techniques, such as oto-acoustic emissions or automated testing of short-latency auditory evoked potentials, can be used in maternity wards to screen for neonatal hearing loss. Brainstem auditory evoked potentials are also useful for obtaining initial data on high-frequency hearing thresholds. ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.