The Special Senses
... At one end of inner ear, these two tubes (one inside the other) coil about 2 & 2/3 times to form the cochlea. Vibrations of the oval window make the perilymph vibrate. This must be transmitted to the endolymph within the cochlea before the hair cells can detect it. ...
... At one end of inner ear, these two tubes (one inside the other) coil about 2 & 2/3 times to form the cochlea. Vibrations of the oval window make the perilymph vibrate. This must be transmitted to the endolymph within the cochlea before the hair cells can detect it. ...
Physics 193 Physics of Music The Ear
... UIUC Physics 193 POM Physics of Music/Musical Instruments ...
... UIUC Physics 193 POM Physics of Music/Musical Instruments ...
Isolation Of Stem Cells May Be A Treatment For Hearing Loss
... United States, 30% of people over the age of 65 have a handicapping hearing loss and of those, one in 500 people become deaf before reaching adulthood. In most cases, the target is the highly specialized hair cells. Docked inside the spiral duct of the human cochlea are ~15,000 hair cells, which are ...
... United States, 30% of people over the age of 65 have a handicapping hearing loss and of those, one in 500 people become deaf before reaching adulthood. In most cases, the target is the highly specialized hair cells. Docked inside the spiral duct of the human cochlea are ~15,000 hair cells, which are ...
case report - journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences
... damage to the inner hair cells specialized sensory cells in the inner ear that transmit information about sounds through the nervous system to the brain. Outer hair cells help amplify sound vibrations entering the inner ear from the middle ear. When hearing is working normally, the inner hair cells ...
... damage to the inner hair cells specialized sensory cells in the inner ear that transmit information about sounds through the nervous system to the brain. Outer hair cells help amplify sound vibrations entering the inner ear from the middle ear. When hearing is working normally, the inner hair cells ...
Auditory Perception P1
... The Auditory Nerve Q uickTim e ™ and a TI FF ( LZW) decom pr essor ar e needed t o seet his pict ur e. ...
... The Auditory Nerve Q uickTim e ™ and a TI FF ( LZW) decom pr essor ar e needed t o seet his pict ur e. ...
Opti-Fox: Towards the Automatic Tuning of Cochlear Implants
... profound hearing losses can be treated with cochlear implants (CI). When implanting a CI, some 10 to 20 contacts are surgically placed into the cochlea. Within the device, sound is analysed by the external “speech processor” which resembles a classical behind-the-ear hearing aid, and implanted elect ...
... profound hearing losses can be treated with cochlear implants (CI). When implanting a CI, some 10 to 20 contacts are surgically placed into the cochlea. Within the device, sound is analysed by the external “speech processor” which resembles a classical behind-the-ear hearing aid, and implanted elect ...
Lecture IV pathology - Neurobiology of Hearing
... • Noise damage affects the delicate sensory hairs of the hair cells • Noise (and also some drugs) can cause swelling of the afferent nerve endings onto the inner hair cells probably through ...
... • Noise damage affects the delicate sensory hairs of the hair cells • Noise (and also some drugs) can cause swelling of the afferent nerve endings onto the inner hair cells probably through ...
The Outer Ear
... • Aurical develops from the first 2 pharyngeal arches • EAC develops from the first pharyngeal groove • TM develops from ______________: inner layer from endoderm, middle layer from mesoderm, and outer layer from ectoderm ...
... • Aurical develops from the first 2 pharyngeal arches • EAC develops from the first pharyngeal groove • TM develops from ______________: inner layer from endoderm, middle layer from mesoderm, and outer layer from ectoderm ...
Children with congenital unilateral sensorineural hearing loss: The
... one ear and some degree of hearing impairment in the other ear. The reduced or complete absence of auditory stimulation from one ear to the brain can cause neural reorganization and effortful listening. Several studies have shown that children with untreated U ...
... one ear and some degree of hearing impairment in the other ear. The reduced or complete absence of auditory stimulation from one ear to the brain can cause neural reorganization and effortful listening. Several studies have shown that children with untreated U ...
An ABR (auditory brainstem response) is a neurological test of
... An ABR (auditory brainstem response) is a neurological test of auditory (hearing) function which can evaluate the integrity of the hearing pathway. Clicks or tone bursts are presented to the ear and the response is measured by electrodes typically placed on the forehead and ear lobes. This test does ...
... An ABR (auditory brainstem response) is a neurological test of auditory (hearing) function which can evaluate the integrity of the hearing pathway. Clicks or tone bursts are presented to the ear and the response is measured by electrodes typically placed on the forehead and ear lobes. This test does ...
psychoacoustics and the effects of hearing loss
... Psychoacoustic Effects for Hearing Impaired Children Assessment of the audibility and clarity of the speech that children hear via their hearing aids is usually determined using at least three methods – observing reactions and spoken responses to spoken messages, formal speech perception tests and l ...
... Psychoacoustic Effects for Hearing Impaired Children Assessment of the audibility and clarity of the speech that children hear via their hearing aids is usually determined using at least three methods – observing reactions and spoken responses to spoken messages, formal speech perception tests and l ...
Auditory, Tactile, and Vestibular Systems
... Alarm should be at least 15 dB above the background noise, preferably 30 dB to guarantee it will be heard. Must not be above the noise level that can damage hearing. Alarm should not be startling. Alarm should rise in intensity. Should not interfere with critical speech communication. Alarm should b ...
... Alarm should be at least 15 dB above the background noise, preferably 30 dB to guarantee it will be heard. Must not be above the noise level that can damage hearing. Alarm should not be startling. Alarm should rise in intensity. Should not interfere with critical speech communication. Alarm should b ...
Document
... Feedback from children (8+) •“Now I can hear in both ears” •“It’s not hard to get used to or take care of” •“It’s easier to hear what people say to me” ...
... Feedback from children (8+) •“Now I can hear in both ears” •“It’s not hard to get used to or take care of” •“It’s easier to hear what people say to me” ...
Perception Chapter 11: Hearing and Listening
... procedure where a certain intensity level of sound (say 60dB) is assigned an arbitrary number to describe its loudness. Subject is then presented a series of sounds which vary in their intensity. Subject assigns a number to describe the loudness of the sound relative to the standard sound. ...
... procedure where a certain intensity level of sound (say 60dB) is assigned an arbitrary number to describe its loudness. Subject is then presented a series of sounds which vary in their intensity. Subject assigns a number to describe the loudness of the sound relative to the standard sound. ...
Document
... Cochlea The inner ear structure called the cochlea is a snail-shell like structure divided into three fluid-filled parts. Two are canals (Scala tympani and Scala Vestibuli) for the transmission of pressure and in the third is the sensitive organ of Corti, which detects pressure impulses and responds ...
... Cochlea The inner ear structure called the cochlea is a snail-shell like structure divided into three fluid-filled parts. Two are canals (Scala tympani and Scala Vestibuli) for the transmission of pressure and in the third is the sensitive organ of Corti, which detects pressure impulses and responds ...
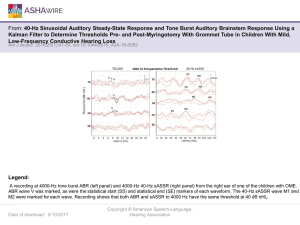
40-Hz Sinusoidal Auditory Steady-State Response and Tone Burst
... From: 40-Hz Sinusoidal Auditory Steady-State Response and Tone Burst Auditory Brainstem Response Using a Kalman Filter to Determine Thresholds Pre- and Post-Myringotomy With Grommet Tube in Children With Mild, Low-Frequency Conductive Hearing Loss Am J Audiol. 2016;25(1):41-53. doi:10.1044/2015_AJA- ...
... From: 40-Hz Sinusoidal Auditory Steady-State Response and Tone Burst Auditory Brainstem Response Using a Kalman Filter to Determine Thresholds Pre- and Post-Myringotomy With Grommet Tube in Children With Mild, Low-Frequency Conductive Hearing Loss Am J Audiol. 2016;25(1):41-53. doi:10.1044/2015_AJA- ...
Cochlear Implantation in Congenital Cochlear Abnormalities
... view is the facial nerve. In congenitally deaf children Balkany et at' have stated that there is greater risk for the facial nerve to follow an aberrant course within the temporal bone. Preoperative imaging can provide valuable information in identifying the position of any possible aberrant facial ...
... view is the facial nerve. In congenitally deaf children Balkany et at' have stated that there is greater risk for the facial nerve to follow an aberrant course within the temporal bone. Preoperative imaging can provide valuable information in identifying the position of any possible aberrant facial ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.