Script - Making Neuroscience Fun
... Air molecules are moving, they are “caught” by the external ear. This causes the membrane connecting the outer ear (tympanic membrane) to the middle ear move. This then makes the 3 little bones in the middle ear move (malleus - means hammer – incus – means anvil – and stapes – means stirrup). Look…a ...
... Air molecules are moving, they are “caught” by the external ear. This causes the membrane connecting the outer ear (tympanic membrane) to the middle ear move. This then makes the 3 little bones in the middle ear move (malleus - means hammer – incus – means anvil – and stapes – means stirrup). Look…a ...
An Update on Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder in Children
... in individuals with ANSD are not completely understood, but psychophysical studies have shown similarly exaggerated noise effects in both simultaneous (where the signal is presented within the noise) and non-simultaneous (where the noise occurs immediately before or after the signal) masking experim ...
... in individuals with ANSD are not completely understood, but psychophysical studies have shown similarly exaggerated noise effects in both simultaneous (where the signal is presented within the noise) and non-simultaneous (where the noise occurs immediately before or after the signal) masking experim ...
Hearing Test
... Principle: compare bone conduction of patient with that of physician. Equipment: Tunning Fork 512 Hz Procedure : Strike the fork against hard object and place it on the mastoid of patient the place it on mastoid process of physician ...
... Principle: compare bone conduction of patient with that of physician. Equipment: Tunning Fork 512 Hz Procedure : Strike the fork against hard object and place it on the mastoid of patient the place it on mastoid process of physician ...
Adult Cochlear Implant Programme - Central Manchester University
... Sound is transmitted as sound waves that are collected by the outer ear and sent down the ear canal to the eardrum. The sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate which sets the three tiny bones (the ‘ossicles’) in the middle ear in motion. The motion of these bones causes fluid in the inner ear (the ...
... Sound is transmitted as sound waves that are collected by the outer ear and sent down the ear canal to the eardrum. The sound waves cause the eardrum to vibrate which sets the three tiny bones (the ‘ossicles’) in the middle ear in motion. The motion of these bones causes fluid in the inner ear (the ...
What does the report look like?
... This game assesses the ability to make sense of known words when presented rapidly (compressed in time). The words begin at 80% of normal duration and get more and more compressed until the listener can no longer identify the target word. This skill requires the listener to use decreasing amounts of ...
... This game assesses the ability to make sense of known words when presented rapidly (compressed in time). The words begin at 80% of normal duration and get more and more compressed until the listener can no longer identify the target word. This skill requires the listener to use decreasing amounts of ...
Multiple-choice exam questions in Advanced
... d) The 5-HT1A receptor acts as a somatodendritic autoreceptor in both fish and mammals. 27. Sensory transduction by hair cells in the cochlea. a) Hair cells are postsynaptic to secondary order auditory neurons. b) Bending of the cilia toward the longest cilium produces hyperpolarization. c) Neurotra ...
... d) The 5-HT1A receptor acts as a somatodendritic autoreceptor in both fish and mammals. 27. Sensory transduction by hair cells in the cochlea. a) Hair cells are postsynaptic to secondary order auditory neurons. b) Bending of the cilia toward the longest cilium produces hyperpolarization. c) Neurotra ...
THESIS DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY (Ph.D.)
... throughout the major resonance of the concha and the external ear canal. This increase enhances the frequency dependent efficiency of the energy transfer to the middle ear (Pickles, 2008). The middle ear is located in the temporal bone and consists of the tympanic membrane and the ossicular chain (m ...
... throughout the major resonance of the concha and the external ear canal. This increase enhances the frequency dependent efficiency of the energy transfer to the middle ear (Pickles, 2008). The middle ear is located in the temporal bone and consists of the tympanic membrane and the ossicular chain (m ...
G 20 Noise III
... the bone-conduction hearing loss at 2 kHz is more than 40 dB and the hearing loss for numbers is more than 25 dB and the pure tone audiogram reveals a local loss of hearing at high frequencies (valley or drop at high frequencies) ...
... the bone-conduction hearing loss at 2 kHz is more than 40 dB and the hearing loss for numbers is more than 25 dB and the pure tone audiogram reveals a local loss of hearing at high frequencies (valley or drop at high frequencies) ...
Selection Criteria for Cochlear Implants
... No useful benefit from HA: Birth – 2 years: restricted access to speech sounds with HA (aided thresholds outside speech spectrum at 2000Hz and above) 2-5 years: lack of progress in development of ...
... No useful benefit from HA: Birth – 2 years: restricted access to speech sounds with HA (aided thresholds outside speech spectrum at 2000Hz and above) 2-5 years: lack of progress in development of ...
The Outer Ear - BirdBrain Science
... Over 300 more free Science and History articles are waiting to inspire your students at BirdBrainScience.com ...
... Over 300 more free Science and History articles are waiting to inspire your students at BirdBrainScience.com ...
hearing and equilibrium activities
... The Weber test will be used to determine if conductive and sensorineural hearing loss is present. In the Weber test a vibrating tuning fork is placed in the middle of the forehead, equi-distant from the patient's ears on top of thin skin in contact with the bone. In a normal patient, the Weber tunin ...
... The Weber test will be used to determine if conductive and sensorineural hearing loss is present. In the Weber test a vibrating tuning fork is placed in the middle of the forehead, equi-distant from the patient's ears on top of thin skin in contact with the bone. In a normal patient, the Weber tunin ...
How we DON*T Hear
... A conductive loss is up to 60 dB Most of the time it can be medically corrected, either through drugs or surgery ...
... A conductive loss is up to 60 dB Most of the time it can be medically corrected, either through drugs or surgery ...
Nerve activates contraction
... the corneal tissue. A clicking sound can be heard as each microscopic layer of tissue is vaporized. This process will last from seconds to minutes, depending on the amount of correction ...
... the corneal tissue. A clicking sound can be heard as each microscopic layer of tissue is vaporized. This process will last from seconds to minutes, depending on the amount of correction ...
Recent Advances in the Treatment of Sensorineural Deafness
... result of cochlear dead regions or severe auditory distortions, caused by recruitment. Vickers et al4 tested 10 subjects with high-frequency hearing loss; for 3 subjects without a cochlear dead region, comprehension improved with high-frequency amplification; for 7 patients with a cochlear dead regi ...
... result of cochlear dead regions or severe auditory distortions, caused by recruitment. Vickers et al4 tested 10 subjects with high-frequency hearing loss; for 3 subjects without a cochlear dead region, comprehension improved with high-frequency amplification; for 7 patients with a cochlear dead regi ...
Addressing ANSD (Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder)
... Audiology evaluations are similar for any type of hearing loss but the results for a young child with ANSD may identify broad, not exact, levels of hearing. Hearing may also decrease or remain the same over time. Even when there is no change in hearing, testing should be ongoing. If there appears to ...
... Audiology evaluations are similar for any type of hearing loss but the results for a young child with ANSD may identify broad, not exact, levels of hearing. Hearing may also decrease or remain the same over time. Even when there is no change in hearing, testing should be ongoing. If there appears to ...
Regenerating Brain from endogenous stem cells
... In animal studies, following targeted controlled cell death with a minimal inflammatory response, endogenous stem cells can perform a surprising level of anatomical repair both in permissive (hippocampus) and non-permissive (cortex) areas ...
... In animal studies, following targeted controlled cell death with a minimal inflammatory response, endogenous stem cells can perform a surprising level of anatomical repair both in permissive (hippocampus) and non-permissive (cortex) areas ...
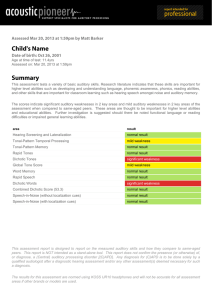
BSA Annual Conference Programme Keele University 1 st – 3rd
... UK, §ENT Department, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands Hearing requires sound being transduced into electrical signals in the brain. The key step in this mechano-electrical transduction (MET) occurs in about a hundred ion channels atop each of the auditory hair cells in ...
... UK, §ENT Department, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands Hearing requires sound being transduced into electrical signals in the brain. The key step in this mechano-electrical transduction (MET) occurs in about a hundred ion channels atop each of the auditory hair cells in ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.