CHS Ch 3 study guide
... b. A skydiver first exits plane, not yet encountering air resistance c. A skydiver encountering air resistance but still accelerating d. A skydiver at constant velocity e. A skydiver hanging in the air because his parachute hangs in a tree f. ...
... b. A skydiver first exits plane, not yet encountering air resistance c. A skydiver encountering air resistance but still accelerating d. A skydiver at constant velocity e. A skydiver hanging in the air because his parachute hangs in a tree f. ...
Force and Motion
... time Ball T is released and allowed to fall. The motion of both balls begins from the same height. A. Ball T will reach the ground first. B. Ball S will reach the ground first. C. Balls S and T will reach the ground at the same time. D. We must know the masses to decide. ...
... time Ball T is released and allowed to fall. The motion of both balls begins from the same height. A. Ball T will reach the ground first. B. Ball S will reach the ground first. C. Balls S and T will reach the ground at the same time. D. We must know the masses to decide. ...
1 Net Force, Acceleration and Mass Date ______ The acceleration
... The acceleration of the object depends on the ________ _____________ on the object and the _______________ of the object. The acceleration of an object is ______________ proportional to the net force acting on the object. The acceleration of an object is ______________ proportional to the object's ...
... The acceleration of the object depends on the ________ _____________ on the object and the _______________ of the object. The acceleration of an object is ______________ proportional to the net force acting on the object. The acceleration of an object is ______________ proportional to the object's ...
speed momentum acceleration
... Write ONE, TWO, or THREE 1. The relationship between an objects mass, its acceleration and its force: TWO 2. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction: THREE 3. Every object in motion tends to stay in motion unless another force is acted on it: ONE 4. Inertia: ONE 5. Shooting a rocket ...
... Write ONE, TWO, or THREE 1. The relationship between an objects mass, its acceleration and its force: TWO 2. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction: THREE 3. Every object in motion tends to stay in motion unless another force is acted on it: ONE 4. Inertia: ONE 5. Shooting a rocket ...
Linear Motion
... Instantaneous Velocity of an object is its instantaneous speed plus the direction it is traveling. Velocity is a vector. ...
... Instantaneous Velocity of an object is its instantaneous speed plus the direction it is traveling. Velocity is a vector. ...
Force and Motion Review Questions
... balanced forces frictional forces gravitational forces net forces ...
... balanced forces frictional forces gravitational forces net forces ...
Name
... 19. In your drawing above, the block is at rest so net force on the block is __________. 20. The F = 0. Explain what this means. ...
... 19. In your drawing above, the block is at rest so net force on the block is __________. 20. The F = 0. Explain what this means. ...
Review1 - UCF Physics
... Drawing a FBD of forces on an object (on, not by) 1. Choose the object to analyze. Draw it as a dot. 2. What forces physically touch this object? This object, not some other 3. What “action at a distance” forces act on the object? Gravity is the only one for this PHYS2053 4. Draw these forces as ar ...
... Drawing a FBD of forces on an object (on, not by) 1. Choose the object to analyze. Draw it as a dot. 2. What forces physically touch this object? This object, not some other 3. What “action at a distance” forces act on the object? Gravity is the only one for this PHYS2053 4. Draw these forces as ar ...
Applying Newtons Laws PPT
... Do Now: An object with mass m is moving with an initial velocity vo and speeds up to a final velocity of v in time t when an unbalanced force F is applied to it. From this information, derive Newton’s 2nd Law, F = ma ...
... Do Now: An object with mass m is moving with an initial velocity vo and speeds up to a final velocity of v in time t when an unbalanced force F is applied to it. From this information, derive Newton’s 2nd Law, F = ma ...
CH11 Notes - Moline High School
... Net force – all the forces acting on an object Balanced forces – net force equal to zero - no change in motion Unbalanced forces – net forces does not equal ...
... Net force – all the forces acting on an object Balanced forces – net force equal to zero - no change in motion Unbalanced forces – net forces does not equal ...
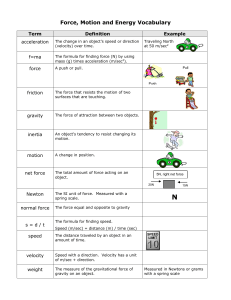
FORCE and MOTION UNIT VOCABULARY
... The change in an object’s speed or direction (velocity) over time. ...
... The change in an object’s speed or direction (velocity) over time. ...
lecture ch7-8-Circles
... than “with his knees” can be injured by large forces exerted on the muscles and vertebrae. The spine pivots mainly at the fifth lumbar vertebra, with the principal supporting force provided by the erector spinalis muscle in the back. Consider the model of a person bending forward to lift a 200-N obj ...
... than “with his knees” can be injured by large forces exerted on the muscles and vertebrae. The spine pivots mainly at the fifth lumbar vertebra, with the principal supporting force provided by the erector spinalis muscle in the back. Consider the model of a person bending forward to lift a 200-N obj ...
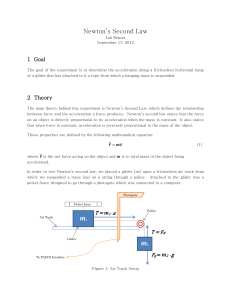
Newton`s Second Law
... states that the net force acting on a mass causes the mass to accelerate in the direction of the net force. ...
... states that the net force acting on a mass causes the mass to accelerate in the direction of the net force. ...
Relationships between linear and angular motion Examples
... • Radial acceleration (aR) - the linear acceleration that serves to describe the change in direction of an object following a curved path. – Radial acceleration is a linear quantity – It is always directed inward, toward the center of a curved path. ...
... • Radial acceleration (aR) - the linear acceleration that serves to describe the change in direction of an object following a curved path. – Radial acceleration is a linear quantity – It is always directed inward, toward the center of a curved path. ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Mass is the amount of matter in your body • Weight is the amount of force acting on your body • So on the Moon, you would have the same mass as on Earth but weigh less on the Moon since the Moon is less massive than Earth ...
... • Mass is the amount of matter in your body • Weight is the amount of force acting on your body • So on the Moon, you would have the same mass as on Earth but weigh less on the Moon since the Moon is less massive than Earth ...