review question for mid exam 2
... motion. However, once the box is sliding, you can apply a smaller force to maintain its motion. Why? 22. State any one of Newton’s laws of motion, one that you like the most, and describe what it means in your own words. 23. You are standing inside a stationary bus. The bus suddenly starts moving fo ...
... motion. However, once the box is sliding, you can apply a smaller force to maintain its motion. Why? 22. State any one of Newton’s laws of motion, one that you like the most, and describe what it means in your own words. 23. You are standing inside a stationary bus. The bus suddenly starts moving fo ...
Forces, Mass, and Motion
... that mass measures “stuff” gives us an immediate way to compare the masses of objects of the same composition, like different size pieces of iron. We could define a certain piece of iron to be a standard kilogram (We will use our double iron bar as a standard kilogram.), then two of the bars would b ...
... that mass measures “stuff” gives us an immediate way to compare the masses of objects of the same composition, like different size pieces of iron. We could define a certain piece of iron to be a standard kilogram (We will use our double iron bar as a standard kilogram.), then two of the bars would b ...
Speed/Motion Notes!
... What is the acceleration of a roller coaster that starts with a velocity of 4 m/s and accelerates to 22m/s in 3 sec.? A=(22m/s-4m/s)/3s A=18m/s//3s A=6m/s/s or 6m/s2 ...
... What is the acceleration of a roller coaster that starts with a velocity of 4 m/s and accelerates to 22m/s in 3 sec.? A=(22m/s-4m/s)/3s A=18m/s//3s A=6m/s/s or 6m/s2 ...
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
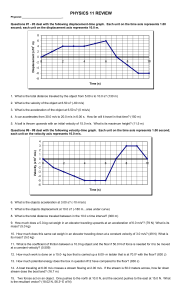
... (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels downwards? (24.2 m/s) 22. A woman moving a large 80.0-kg trunk, attaches a rope ...
... (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels downwards? (24.2 m/s) 22. A woman moving a large 80.0-kg trunk, attaches a rope ...
MCA PPT Review - Math On Monday
... down because the Earth pulls on it due to its gravity. Close to the surface, the acceleration due to gravity of the Earth is about 9.8 m/s2. This means during free fall the velocity will change by 9.8 m/s every second. All objects, regardless of their masses, fall at the same rate on Earth, provided ...
... down because the Earth pulls on it due to its gravity. Close to the surface, the acceleration due to gravity of the Earth is about 9.8 m/s2. This means during free fall the velocity will change by 9.8 m/s every second. All objects, regardless of their masses, fall at the same rate on Earth, provided ...
Unit 4 Objectives: Circular Motion Standard: SP1. Students will
... the rope affect the motion (velocity) of the object? The object’s velocity would be slower b/c it wouldn’t need to go as fast to get around the circle b/c the radius is smaller. For example – Use the 1’s rule to show this v = 2πr/t If you assume that the radius of the object is 1 m to begin with ...
... the rope affect the motion (velocity) of the object? The object’s velocity would be slower b/c it wouldn’t need to go as fast to get around the circle b/c the radius is smaller. For example – Use the 1’s rule to show this v = 2πr/t If you assume that the radius of the object is 1 m to begin with ...
Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
... constant velocity throughout all three turns. At which turn will there be the greatest centripetal acceleration? If the bobsled moves at 35 m/s throughout the course and turn B has a radius of 20m and turn C is 50m how many G’s of acceleration is the sledder feeling through turns B & C ? ...
... constant velocity throughout all three turns. At which turn will there be the greatest centripetal acceleration? If the bobsled moves at 35 m/s throughout the course and turn B has a radius of 20m and turn C is 50m how many G’s of acceleration is the sledder feeling through turns B & C ? ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... Rotation- If the axis of rotation is inside the object, the object is rotating (spinning). Ex. Earth rotates around its center point Revolution- If the axis of rotation is outside the object, the object is revolving. Ex. Earth revolves around the sun ...
... Rotation- If the axis of rotation is inside the object, the object is rotating (spinning). Ex. Earth rotates around its center point Revolution- If the axis of rotation is outside the object, the object is revolving. Ex. Earth revolves around the sun ...
Name
... 35. Matt with a mass of 125 kg is running at a velocity of 10 m/s. What is his momentum? a. 1250 kg b. 125 kg/m/s c. 1250 m/s/s d. 1250 kg/m/s 36. The force of an object, with a certain mass is accelerating at a certain rate. The rate can be determined using the equation (Force = Mass X Acceleration ...
... 35. Matt with a mass of 125 kg is running at a velocity of 10 m/s. What is his momentum? a. 1250 kg b. 125 kg/m/s c. 1250 m/s/s d. 1250 kg/m/s 36. The force of an object, with a certain mass is accelerating at a certain rate. The rate can be determined using the equation (Force = Mass X Acceleration ...
Solutions to Homework Set #3 Phys2414 – Fall 2005
... the cars is zero. In terms of our variables, this would be xf,h − xf,p = 0 We can use this property if we subtract the equation of motion of the Porsche from the equation of motion of the Honda. Doing this gives us (xf,h − xi,h ) − (xf,p − xi,p ) = [vh (tf − ti )] − [vp (tf − ti )] Rearranging the t ...
... the cars is zero. In terms of our variables, this would be xf,h − xf,p = 0 We can use this property if we subtract the equation of motion of the Porsche from the equation of motion of the Honda. Doing this gives us (xf,h − xi,h ) − (xf,p − xi,p ) = [vh (tf − ti )] − [vp (tf − ti )] Rearranging the t ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... Rotation- If the axis of rotation is inside the object, the object is rotating (spinning). Ex. Earth rotates around its center point Revolution- If the axis of rotation is outside the object, the object is revolving. Ex. Earth revolves around the sun ...
... Rotation- If the axis of rotation is inside the object, the object is rotating (spinning). Ex. Earth rotates around its center point Revolution- If the axis of rotation is outside the object, the object is revolving. Ex. Earth revolves around the sun ...
Types of Variation
... A vector is a quantity that is expressed using both a magnitude and a direction. Directions can be communicated algebraically (+/-), common references (left, right, up, down), using compass notation (N, S, E, W), or using trigonometry (angle in standard position). Vectors are adding using the “head- ...
... A vector is a quantity that is expressed using both a magnitude and a direction. Directions can be communicated algebraically (+/-), common references (left, right, up, down), using compass notation (N, S, E, W), or using trigonometry (angle in standard position). Vectors are adding using the “head- ...
Homework Problems
... 21. The moon orbits the earth once every 27.3 days. What is the centripetal acceleration of the moon? 22. A spacecraft orbits the moon in a circular orbit of radius 8.01 x 10 8 m. What is the velocity of the spacecraft as it orbits? 23. What is the gravitational attraction between the earth and the ...
... 21. The moon orbits the earth once every 27.3 days. What is the centripetal acceleration of the moon? 22. A spacecraft orbits the moon in a circular orbit of radius 8.01 x 10 8 m. What is the velocity of the spacecraft as it orbits? 23. What is the gravitational attraction between the earth and the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - ABOUT TEAL
... Friction acts exactly at the one point of contact and is tangential, i.e. perpendicular to the radius One peculiarity: Sliding along a surface, friction does negative work Rolling without slipping, friction does zero work 8.01L IAP 2007 ...
... Friction acts exactly at the one point of contact and is tangential, i.e. perpendicular to the radius One peculiarity: Sliding along a surface, friction does negative work Rolling without slipping, friction does zero work 8.01L IAP 2007 ...