Non-Inertial Frames
... baseball we simply switch to its CM frame. Euler’s theorem, which we will state without proof, is that the most general motion of any body relative to a fixed point O is a rotation about some axis through O. (See Goldstein, Poole & Safko for a proof.) To specify this rotation about a given point O, ...
... baseball we simply switch to its CM frame. Euler’s theorem, which we will state without proof, is that the most general motion of any body relative to a fixed point O is a rotation about some axis through O. (See Goldstein, Poole & Safko for a proof.) To specify this rotation about a given point O, ...
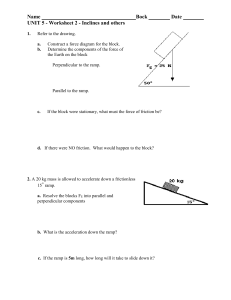
Newton`s Laws First Law --an object at rest tends to stay at rest AND
... If teams pull with the same force, in opposite directions, net force on the rope is ZERO and ---> Rope doesn’t move ...
... If teams pull with the same force, in opposite directions, net force on the rope is ZERO and ---> Rope doesn’t move ...
Student Notes
... • All objects have at least two forces acting on them, sometimes more • Ex. Holding a book in the air – One force is gravity – One force is your muscles holding the book up in the air ...
... • All objects have at least two forces acting on them, sometimes more • Ex. Holding a book in the air – One force is gravity – One force is your muscles holding the book up in the air ...
Solutions from Yosumism website Problem 61 Problem 62:
... The only physics involved in this problem is equating the centripetal force with the Lorentz ...
... The only physics involved in this problem is equating the centripetal force with the Lorentz ...
Forces
... If the mass of a helicopter is 4,500 kg. and the net force on it is 18,000 N, what is the helicopter’s acceleration? ...
... If the mass of a helicopter is 4,500 kg. and the net force on it is 18,000 N, what is the helicopter’s acceleration? ...
Section 12.2 Newton`s First and Second Laws of Motion IPLS
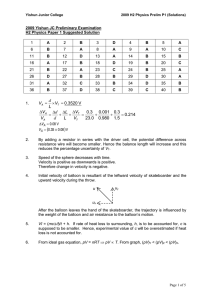
... Match each scientist with his accomplishment. Accomplishment b 1. Italian scientist who experimented with force and motion c 2. Scientist who introduced laws describing force and motion a 3. An ancient Greek philosopher who made many scientific discoveries through observation and logical reasoning ...
... Match each scientist with his accomplishment. Accomplishment b 1. Italian scientist who experimented with force and motion c 2. Scientist who introduced laws describing force and motion a 3. An ancient Greek philosopher who made many scientific discoveries through observation and logical reasoning ...
C_Energy Notes PGP
... of 20.0 kg. It is pulled at constant speed by a rope inclined at 25o above the horizontal, and it moves a distance of 100 m on a horizontal surface. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the ground is 0.40, ...
... of 20.0 kg. It is pulled at constant speed by a rope inclined at 25o above the horizontal, and it moves a distance of 100 m on a horizontal surface. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the ground is 0.40, ...
Newton`s Laws Webquest
... _________________ is a push or pull on an object. ____________________________ is the difference between two opposing forces. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that if a net force acts on an object, the object will ____________________ in the direction of the force. Acceleration is a change in _____ ...
... _________________ is a push or pull on an object. ____________________________ is the difference between two opposing forces. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that if a net force acts on an object, the object will ____________________ in the direction of the force. Acceleration is a change in _____ ...
Forces and Motion
... Part 1: Matter in Motion (4 weeks) Identify the relationship between motion and a reference point. Identify the two factors that speed depends on. Determine the difference between speed and velocity Analyze the relationship of velocity to acceleration Interpret a graph showing acceleration Determine ...
... Part 1: Matter in Motion (4 weeks) Identify the relationship between motion and a reference point. Identify the two factors that speed depends on. Determine the difference between speed and velocity Analyze the relationship of velocity to acceleration Interpret a graph showing acceleration Determine ...
Example2 - mrdsample
... Rotational Kinetic Energy Recall that the translational kinetic energy of a moving object is given by ...
... Rotational Kinetic Energy Recall that the translational kinetic energy of a moving object is given by ...
Force motion and machines powerpoint
... Weight and mass • Mass is a measurement of how much matter is in something. • Weight is a measurement of how gravity is pulling down on something. • Weight is affected by gravity, mass is not! ...
... Weight and mass • Mass is a measurement of how much matter is in something. • Weight is a measurement of how gravity is pulling down on something. • Weight is affected by gravity, mass is not! ...
Physics and Beyond PowerPoint
... No, force is not something an object has, like mass and volume. An object may posses the capability of exerting force on another object but it does not possess force. 2. A car accelerates along a road. Strictly speaking, what is the force that moves the car ? It really is the road that pushes the ca ...
... No, force is not something an object has, like mass and volume. An object may posses the capability of exerting force on another object but it does not possess force. 2. A car accelerates along a road. Strictly speaking, what is the force that moves the car ? It really is the road that pushes the ca ...
AP Physics Daily Problem #120
... A wire has a diameter of 1.5mm and a length of 30m. If the wire is made of silver, what is the resistance of the ...
... A wire has a diameter of 1.5mm and a length of 30m. If the wire is made of silver, what is the resistance of the ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits
In classical mechanics, Newton's theorem of revolving orbits identifies the type of central force needed to multiply the angular speed of a particle by a factor k without affecting its radial motion (Figures 1 and 2). Newton applied his theorem to understanding the overall rotation of orbits (apsidal precession, Figure 3) that is observed for the Moon and planets. The term ""radial motion"" signifies the motion towards or away from the center of force, whereas the angular motion is perpendicular to the radial motion.Isaac Newton derived this theorem in Propositions 43–45 of Book I of his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, first published in 1687. In Proposition 43, he showed that the added force must be a central force, one whose magnitude depends only upon the distance r between the particle and a point fixed in space (the center). In Proposition 44, he derived a formula for the force, showing that it was an inverse-cube force, one that varies as the inverse cube of r. In Proposition 45 Newton extended his theorem to arbitrary central forces by assuming that the particle moved in nearly circular orbit.As noted by astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar in his 1995 commentary on Newton's Principia, this theorem remained largely unknown and undeveloped for over three centuries. Since 1997, the theorem has been studied by Donald Lynden-Bell and collaborators. Its first exact extension came in 2000 with the work of Mahomed and Vawda.