Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
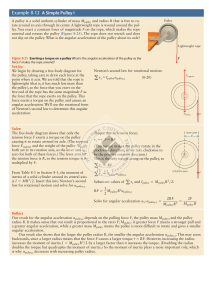
... – If the string breaks, the object doesn’t move radially outward. – It continues along its tangent straight-line path—because no force acts on it. (Newton’s first law) ...
... – If the string breaks, the object doesn’t move radially outward. – It continues along its tangent straight-line path—because no force acts on it. (Newton’s first law) ...
Speed and Velocity
... 4. A ball of mass M at the end of a string is swung in a horizontal circular path of radius R at constant speed V. Which combination of changes would require the greatest increase in the centripetal force acting on the ball? (1) Doubling V and doubling R ...
... 4. A ball of mass M at the end of a string is swung in a horizontal circular path of radius R at constant speed V. Which combination of changes would require the greatest increase in the centripetal force acting on the ball? (1) Doubling V and doubling R ...
File
... the gravitational force between two masses decreases rapidly as the distance between the masses increases. No matter how far apart two objects are, the gravitational force between them never completely goes to zero. Because the gravitational force between two objects never disappears, gravity is ...
... the gravitational force between two masses decreases rapidly as the distance between the masses increases. No matter how far apart two objects are, the gravitational force between them never completely goes to zero. Because the gravitational force between two objects never disappears, gravity is ...
Forces & the Laws of Motion
... • An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion in a straight line, with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by a net external force • Inertia: the tendency of an object to maintain its state of uniform linear motion • When net force on an object is zero, accelera ...
... • An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion in a straight line, with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by a net external force • Inertia: the tendency of an object to maintain its state of uniform linear motion • When net force on an object is zero, accelera ...
Announcements
... l Maybe it didn’t happen in reality, but the reasoning is roughly correct l Newton had the insight to realize that the force between the Earth and the apple is the same as the force between the Earth and the Moon ...
... l Maybe it didn’t happen in reality, but the reasoning is roughly correct l Newton had the insight to realize that the force between the Earth and the apple is the same as the force between the Earth and the Moon ...
work - cloudfront.net
... • Solution no displacement • 2 .A book falls off a table and free falls to the ground. • Solution: yes, there is gravity acting on the object which causes displacement • 3. A waiter carries a tray full of meals above his head by one arm straight across the room at constant speed. (Careful! This is a ...
... • Solution no displacement • 2 .A book falls off a table and free falls to the ground. • Solution: yes, there is gravity acting on the object which causes displacement • 3. A waiter carries a tray full of meals above his head by one arm straight across the room at constant speed. (Careful! This is a ...
force of gravity
... analysis of data carefully collected over a span of several years by his Danish predecessor and teacher, Tycho Brahe. Kepler's three laws of planetary motion can be briefly described as follows: ...
... analysis of data carefully collected over a span of several years by his Danish predecessor and teacher, Tycho Brahe. Kepler's three laws of planetary motion can be briefly described as follows: ...
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits
In classical mechanics, Newton's theorem of revolving orbits identifies the type of central force needed to multiply the angular speed of a particle by a factor k without affecting its radial motion (Figures 1 and 2). Newton applied his theorem to understanding the overall rotation of orbits (apsidal precession, Figure 3) that is observed for the Moon and planets. The term ""radial motion"" signifies the motion towards or away from the center of force, whereas the angular motion is perpendicular to the radial motion.Isaac Newton derived this theorem in Propositions 43–45 of Book I of his Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, first published in 1687. In Proposition 43, he showed that the added force must be a central force, one whose magnitude depends only upon the distance r between the particle and a point fixed in space (the center). In Proposition 44, he derived a formula for the force, showing that it was an inverse-cube force, one that varies as the inverse cube of r. In Proposition 45 Newton extended his theorem to arbitrary central forces by assuming that the particle moved in nearly circular orbit.As noted by astrophysicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar in his 1995 commentary on Newton's Principia, this theorem remained largely unknown and undeveloped for over three centuries. Since 1997, the theorem has been studied by Donald Lynden-Bell and collaborators. Its first exact extension came in 2000 with the work of Mahomed and Vawda.