Objective(s) - Net Start Class
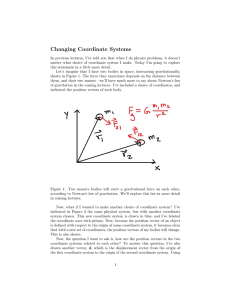
... balanced, therefore the net force is zero. In this case the object will not move and stay at rest. The other possible result is that the net force is not zero, and the object will move in the direction of the stronger force, if these two forces act on the same line or dimension.The net force therefo ...
... balanced, therefore the net force is zero. In this case the object will not move and stay at rest. The other possible result is that the net force is not zero, and the object will move in the direction of the stronger force, if these two forces act on the same line or dimension.The net force therefo ...
Reminder: Acceleration
... Don’t confuse mass and weight! Newton’s 2nd Law is only valid in Inertial Frames of Reference – In an accelerating car, there is no force pushing you into the seat instead, the seat is exerting an accelerating force on you – In a falling elevator, there is a force (weight) acting on you, even if you ...
... Don’t confuse mass and weight! Newton’s 2nd Law is only valid in Inertial Frames of Reference – In an accelerating car, there is no force pushing you into the seat instead, the seat is exerting an accelerating force on you – In a falling elevator, there is a force (weight) acting on you, even if you ...
PS Unit 2 Motion
... Measuring Motion: Acceleration • Acceleration – the rate of change of velocity – change in speed or direction • Centripetal acceleration – circular motion (even if speed is constant, direction is always changing) ex. Moon accelerates around Earth ...
... Measuring Motion: Acceleration • Acceleration – the rate of change of velocity – change in speed or direction • Centripetal acceleration – circular motion (even if speed is constant, direction is always changing) ex. Moon accelerates around Earth ...
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... Frequency (f) : The number of turns in one second is called the frequency of the motion and it is equal to ; f=1/T or T.f=1 PERIOD (T) FREQUENCY (f) SECOND (s) 1/s or s-1 ...
... Frequency (f) : The number of turns in one second is called the frequency of the motion and it is equal to ; f=1/T or T.f=1 PERIOD (T) FREQUENCY (f) SECOND (s) 1/s or s-1 ...
Name Student ID
... respectively. Calculate the x- and y-components of the initial velocity vector, v0, of the object. A) v0x = 12.0 m/s and v0y = 31.0 m/s B) v0x = 27.0 m/s and v0y = 31.0 m/s C) v0x = -3.00 m/s and v0y = 16.0 m/s D) v0x = -3.00 m/s and v0y = 1.00 m/s E) v0x = 27.0 m/s and v0y = 16.0 m/s ...
... respectively. Calculate the x- and y-components of the initial velocity vector, v0, of the object. A) v0x = 12.0 m/s and v0y = 31.0 m/s B) v0x = 27.0 m/s and v0y = 31.0 m/s C) v0x = -3.00 m/s and v0y = 16.0 m/s D) v0x = -3.00 m/s and v0y = 1.00 m/s E) v0x = 27.0 m/s and v0y = 16.0 m/s ...
SS Review for Final
... a pair of component vectors, A and B, that would combine to form resultant vector R? ...
... a pair of component vectors, A and B, that would combine to form resultant vector R? ...