Chapter 7 Systems of particles
... the total external force were applied at that point.” These are general results that apply equally well to a solid object. ...
... the total external force were applied at that point.” These are general results that apply equally well to a solid object. ...
Newton`s First Law Drawing Force Diagrams Adding Vectors
... Newton’s 1st Law (Law of Inertia) • An object – at rest tends to stay at rest or... – in motion tends to stay in motion with a constant (uniform) speed and direction (i.e., constant velocity) (must travel in a straight line) – unless acted upon by a “net external force” (“unbalanced force”) (if so, ...
... Newton’s 1st Law (Law of Inertia) • An object – at rest tends to stay at rest or... – in motion tends to stay in motion with a constant (uniform) speed and direction (i.e., constant velocity) (must travel in a straight line) – unless acted upon by a “net external force” (“unbalanced force”) (if so, ...
slides
... • To illustrate, we derive the equations of motion for a 1DOF system – Consider a particle of mass m – Using Newton’s second law: ...
... • To illustrate, we derive the equations of motion for a 1DOF system – Consider a particle of mass m – Using Newton’s second law: ...
4.) A running football player has a momentum of 500 kg·m/s and a
... 12.) A baseball pitcher claims he can throw a 0.145 kg baseball with as much momentum as a speeding bullet. Assume that a 3.00 g bullet moves at a speed of 1.5x103 m/s. What must the baseball's speed be if the pitcher is correct? ...
... 12.) A baseball pitcher claims he can throw a 0.145 kg baseball with as much momentum as a speeding bullet. Assume that a 3.00 g bullet moves at a speed of 1.5x103 m/s. What must the baseball's speed be if the pitcher is correct? ...
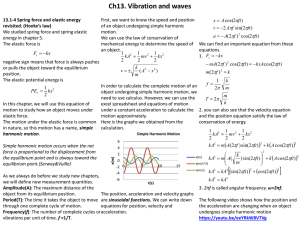
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... Calculate the total energy of the system and A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wa ...
... Calculate the total energy of the system and A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wa ...
Physics
... TN Standards - Motion • CLE.3202.3.1: Investigate the relationships among speed, position, time, velocity, and acceleration • CLE.3202.Inq.2: Design and conduct scientific investigations to explore new phenomena, verify, previous results, test how well a theory predicts, and ...
... TN Standards - Motion • CLE.3202.3.1: Investigate the relationships among speed, position, time, velocity, and acceleration • CLE.3202.Inq.2: Design and conduct scientific investigations to explore new phenomena, verify, previous results, test how well a theory predicts, and ...
Part 1 - Go to webpages.dcu.ie
... • Car A is travelling at a constant speed of 60 km/h as it rounds a circular curve of 300 m radius. At the instant shown it is at = 45°. Car B is passing the centre of the circle at the same instant. Car A is located relative to B using polar coordinates with the pole moving with B. For this insta ...
... • Car A is travelling at a constant speed of 60 km/h as it rounds a circular curve of 300 m radius. At the instant shown it is at = 45°. Car B is passing the centre of the circle at the same instant. Car A is located relative to B using polar coordinates with the pole moving with B. For this insta ...
Slide 1
... Newton's 2nd law deals with a single object on which a force is exerted. The 3rd and last law of motion discovered by Newton explains what happens to the object that is exerting the force. The 3rd law can be summarized by stating that: For every action there is an equal and ...
... Newton's 2nd law deals with a single object on which a force is exerted. The 3rd and last law of motion discovered by Newton explains what happens to the object that is exerting the force. The 3rd law can be summarized by stating that: For every action there is an equal and ...
Chapter5-Matter in Motion
... Motion: _________________________________________________ the change in an object’s position over time when compared _________________________________________________ with a reference point Reference point: ____________________________________________ Place that appears to stay in place when compar ...
... Motion: _________________________________________________ the change in an object’s position over time when compared _________________________________________________ with a reference point Reference point: ____________________________________________ Place that appears to stay in place when compar ...
Linear Momentum - White Plains Public Schools
... A swing seat of mass M is connected to a fixed point P by a massless cord of length L. A child also of mass M sits on the seat and begins to swing with zero velocity at a position at which the cord makes a 60o angle with the vertical as shown in Figure I. The swing continues down until the cord is e ...
... A swing seat of mass M is connected to a fixed point P by a massless cord of length L. A child also of mass M sits on the seat and begins to swing with zero velocity at a position at which the cord makes a 60o angle with the vertical as shown in Figure I. The swing continues down until the cord is e ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... 3. A crate weighing 562 N is resting on a plane inclined 30.0o above the horizontal. Find the component of the weight forces that are parallel and perpendicular to the plane. (parallel = 281 N; perpendicular = 487 N) 4. A force of 40.0 N accelerates a 5.0 kg block at 6.0 m/s2 along a horizontal surf ...
... 3. A crate weighing 562 N is resting on a plane inclined 30.0o above the horizontal. Find the component of the weight forces that are parallel and perpendicular to the plane. (parallel = 281 N; perpendicular = 487 N) 4. A force of 40.0 N accelerates a 5.0 kg block at 6.0 m/s2 along a horizontal surf ...
Chapter 6 Forces in Motion
... Acceleration Stops at the Terminal Velocity • As an object falls, air resistance continues to increase until it exactly matches the downward force of gravity. The object has then reached its terminal velocity…or a net force of zero ...
... Acceleration Stops at the Terminal Velocity • As an object falls, air resistance continues to increase until it exactly matches the downward force of gravity. The object has then reached its terminal velocity…or a net force of zero ...