June - Life Learning Cloud
... A particle P moves along a straight line. The speed of P at time t seconds (t ≥ 0) is v m s–1, where v = (pt2 + qt + r) and p, q and r are constants. When t = 2 the speed of P has its minimum value. When t = 0, v = 11 and when t = 2 , v = 3. Find (a) the acceleration of P when t = 3, ...
... A particle P moves along a straight line. The speed of P at time t seconds (t ≥ 0) is v m s–1, where v = (pt2 + qt + r) and p, q and r are constants. When t = 2 the speed of P has its minimum value. When t = 0, v = 11 and when t = 2 , v = 3. Find (a) the acceleration of P when t = 3, ...
Raising and Lowering
... A box is lowered with uniformly decreasing speed and less negative velocity. Draw a motion diagram for the box. Is the net force on the box, up, down or zero? Draw a force diagram for the box. Acceleration is positive, e.g. velocity might change from -10 to -5, an increase of +5. The net force = ma ...
... A box is lowered with uniformly decreasing speed and less negative velocity. Draw a motion diagram for the box. Is the net force on the box, up, down or zero? Draw a force diagram for the box. Acceleration is positive, e.g. velocity might change from -10 to -5, an increase of +5. The net force = ma ...
Unit 2: Vector Dynamics
... 25. Which of the following is not a statement of one of Newton’s laws of motion? a. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. b. If no net force acts on an object, the object will remain at rest, or continue to move at a constant velocity. c. The acceleration of freely f ...
... 25. Which of the following is not a statement of one of Newton’s laws of motion? a. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. b. If no net force acts on an object, the object will remain at rest, or continue to move at a constant velocity. c. The acceleration of freely f ...
3 inertia newtons fi..
... because of its inertia (until the back of the seat applies a forward force to make it move with the bus). From the point of view of someone on the bus, it appears that the package is moving backward; however, someone watching from outside the bus would see the bus move forward and the package trying ...
... because of its inertia (until the back of the seat applies a forward force to make it move with the bus). From the point of view of someone on the bus, it appears that the package is moving backward; however, someone watching from outside the bus would see the bus move forward and the package trying ...
Lab 5 – Circular Motion and Forces
... Once you have become proficient at whirling the stopper so that the mark on the string stays even with the bottom of the tube, you’re ready to take data. 3. In the data table on the workshe ...
... Once you have become proficient at whirling the stopper so that the mark on the string stays even with the bottom of the tube, you’re ready to take data. 3. In the data table on the workshe ...
Fictive forces
... This expression defines the coordinates x0 , y 0 , og z 0 , which is the position of the object measured in the rotating coordinate system. First, we find the velocity of the object as measured in both systems by taking the time derivative of equation 17.18: ...
... This expression defines the coordinates x0 , y 0 , og z 0 , which is the position of the object measured in the rotating coordinate system. First, we find the velocity of the object as measured in both systems by taking the time derivative of equation 17.18: ...
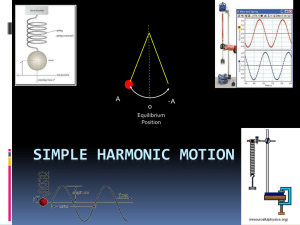
Simple Harmonic motion
... forth replicating the SHM of the mass attached to a spring seen earlier. ...
... forth replicating the SHM of the mass attached to a spring seen earlier. ...
FE4
... The laws governing the motion of an object, as given in the previous chapters, apply only when all the forces acting on the object are taken into account. In the real world all objects move through fluids so we must include the forces exerted by the extremely large number of fluid molecules. In some ...
... The laws governing the motion of an object, as given in the previous chapters, apply only when all the forces acting on the object are taken into account. In the real world all objects move through fluids so we must include the forces exerted by the extremely large number of fluid molecules. In some ...
Physics
... • Distance measures the path taken • To measure distance, you measure the length of the path that the object took. • Displacement measures only the difference between the final and starting positions ...
... • Distance measures the path taken • To measure distance, you measure the length of the path that the object took. • Displacement measures only the difference between the final and starting positions ...
Form A
... 11. A sled is pulled at a constant speed up to the top of a 100.0 m long snow covered (frictionless) hill that makes an angle of 10° upward with respect the horizontal. The sled is pulled with a rope that makes a 20° angle with respect to the direction of travel. If the rope does 5000 J of work in p ...
... 11. A sled is pulled at a constant speed up to the top of a 100.0 m long snow covered (frictionless) hill that makes an angle of 10° upward with respect the horizontal. The sled is pulled with a rope that makes a 20° angle with respect to the direction of travel. If the rope does 5000 J of work in p ...
Momentum Practice Problems - Perez Biology and Physical science
... Which is more difficult to stop: A tractor-trailer truck barreling down the highway at 35 meters per second, or a small two-seater sports car traveling the same speed? You probably guessed that it takes more force to stop a large truck than a small car. In physics terms, we say that the truck has gr ...
... Which is more difficult to stop: A tractor-trailer truck barreling down the highway at 35 meters per second, or a small two-seater sports car traveling the same speed? You probably guessed that it takes more force to stop a large truck than a small car. In physics terms, we say that the truck has gr ...