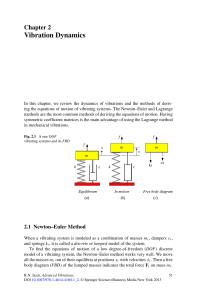
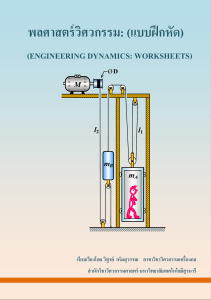
Vibration Dynamics
... in which, x is a column array of describing coordinates of the system, and f is a column array of the associated applied forces. The square matrices [m], [c], [k] are the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices. Example 30 (The one, two, and three DOF model of vehicles) The one, two, and three DOF mod ...
... in which, x is a column array of describing coordinates of the system, and f is a column array of the associated applied forces. The square matrices [m], [c], [k] are the mass, damping, and stiffness matrices. Example 30 (The one, two, and three DOF model of vehicles) The one, two, and three DOF mod ...
LCP1 INTUITIVE PHYSICS
... LCP1 begins with the intuitive understanding of motion, then continues to discuss motion in qualitative terms first, before appealing to the Galileo’s kinematics and Newton’s dynamics in quantitative terms. We will continue discussing these laws in LCP 2 by following the history of the concepts abou ...
... LCP1 begins with the intuitive understanding of motion, then continues to discuss motion in qualitative terms first, before appealing to the Galileo’s kinematics and Newton’s dynamics in quantitative terms. We will continue discussing these laws in LCP 2 by following the history of the concepts abou ...
Motional Emf - OpenStax CNX
... the uniform magnetic eld. The magnetic eld B is into the page, perpendicular to the moving rod and rails and, hence, to the area enclosed by them. (b) Lenz's law gives the directions of the induced eld and current, and the polarity of the induced emf. Since the ux is increasing, the induced eld ...
... the uniform magnetic eld. The magnetic eld B is into the page, perpendicular to the moving rod and rails and, hence, to the area enclosed by them. (b) Lenz's law gives the directions of the induced eld and current, and the polarity of the induced emf. Since the ux is increasing, the induced eld ...
momentum class notes
... and opposite in direction (they cancel each other) 4. If no net force or net impulse acts on a system the momentum of that system cannot change 5. Law of conservation of momentum– In the absence of an external force, the momentum of a system remains unchanged ...
... and opposite in direction (they cancel each other) 4. If no net force or net impulse acts on a system the momentum of that system cannot change 5. Law of conservation of momentum– In the absence of an external force, the momentum of a system remains unchanged ...
Chapter 2
... would convert km/h to m/s. A change in velocity of 5.0 km/h converts to 1.4 m/s and the acceleration would be 1.4 m/s/s. The units “m/s per s” mean what change of velocity (1.4 m/s) is occurring every second. The combination “m/s/s” is rather cumbersome, so it is typically treated mathematically to ...
... would convert km/h to m/s. A change in velocity of 5.0 km/h converts to 1.4 m/s and the acceleration would be 1.4 m/s/s. The units “m/s per s” mean what change of velocity (1.4 m/s) is occurring every second. The combination “m/s/s” is rather cumbersome, so it is typically treated mathematically to ...
D. © 2013 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
... minimum radius of curvature at point 3 such that a positive normal force is a) the force exerted by the track on exerted by the track. the car at point 2, and b) the minimum safe value of the radius of curvature at point 3. ...
... minimum radius of curvature at point 3 such that a positive normal force is a) the force exerted by the track on exerted by the track. the car at point 2, and b) the minimum safe value of the radius of curvature at point 3. ...
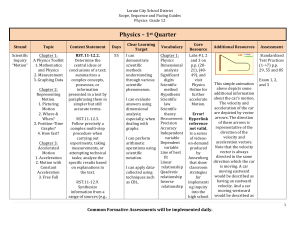
Physics – 1st Quarter
... In earlier grades, Newton’s laws of motion were introduced; gravitational forces and fields were described conceptually; the gravitational force (weight) acting on objects near Earth’s surface was calculated; fricti ...
... In earlier grades, Newton’s laws of motion were introduced; gravitational forces and fields were described conceptually; the gravitational force (weight) acting on objects near Earth’s surface was calculated; fricti ...
Chapter 5: Conservation of Linear momentum
... conserved. In the three experiments in Table 5.1, this quantity is constant for the system. But, will this pattern continue to hold in other situations? Let’s test this idea by using it to predict the outcome of the experiment in Testing Experiment Table 5.2. Testing Experiment Table 5.2 Testing the ...
... conserved. In the three experiments in Table 5.1, this quantity is constant for the system. But, will this pattern continue to hold in other situations? Let’s test this idea by using it to predict the outcome of the experiment in Testing Experiment Table 5.2. Testing Experiment Table 5.2 Testing the ...
r - Ateneonline
... Example: Consider Margaret’s walk to the store in the example on slides 3 and 4. If the first leg of her walk takes 10 minutes, the second takes 8 minutes, and the third 7 minutes, compute her average velocity and average speed during each leg and for the overall trip. Use the definitions: r ...
... Example: Consider Margaret’s walk to the store in the example on slides 3 and 4. If the first leg of her walk takes 10 minutes, the second takes 8 minutes, and the third 7 minutes, compute her average velocity and average speed during each leg and for the overall trip. Use the definitions: r ...
Model Two
... does not appear to influence aspects of the motion in a perpendicular direction (the vertical). Imagine a coin dropped from shoulder height. The elapsed time for the coin to hit the ground, the rate at which its vertical position is changing, and its vertical acceleration are the same whether you do ...
... does not appear to influence aspects of the motion in a perpendicular direction (the vertical). Imagine a coin dropped from shoulder height. The elapsed time for the coin to hit the ground, the rate at which its vertical position is changing, and its vertical acceleration are the same whether you do ...