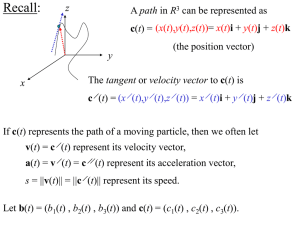
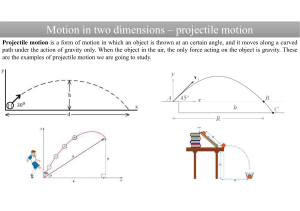
No Slide Title
... always over the same point above the equator. Given G = 6.6710–11 when working with meters, kilograms, and seconds, and given the mass of the earth is 5.981024 kilograms, find the radius necessary for a geosynchronous orbit above the equator. We want the period of the orbit to be 1 day = 606024 ...
... always over the same point above the equator. Given G = 6.6710–11 when working with meters, kilograms, and seconds, and given the mass of the earth is 5.981024 kilograms, find the radius necessary for a geosynchronous orbit above the equator. We want the period of the orbit to be 1 day = 606024 ...
2 - Pleasant Hill School District
... • When a plane breaks the sound barrier (faster than the speed of sound, 334 m/s) it produces a loud shock wave called a sonic boom. • Suppose an F-18 flying overhead breaks the barrier, and you hear the sonic boom 12 sec. after it was produced. How high in the air was the jet flying? ...
... • When a plane breaks the sound barrier (faster than the speed of sound, 334 m/s) it produces a loud shock wave called a sonic boom. • Suppose an F-18 flying overhead breaks the barrier, and you hear the sonic boom 12 sec. after it was produced. How high in the air was the jet flying? ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... 2. Frame of Reference – the background motion is measured against 3. Distance – how far an object has moved 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d ...
... 2. Frame of Reference – the background motion is measured against 3. Distance – how far an object has moved 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d ...
Topic #8: X and Y COMPONENTS of VECTORS
... for this: “A force of 100n North and 100n East acting on the same object: find their resultant, FR.” The answer was: FR = 141newtons NorthEast But what do you call the other two vectors, namely the 100n North and 100n East vectors that combined to make the resultant? These are called the COMPONENTS ...
... for this: “A force of 100n North and 100n East acting on the same object: find their resultant, FR.” The answer was: FR = 141newtons NorthEast But what do you call the other two vectors, namely the 100n North and 100n East vectors that combined to make the resultant? These are called the COMPONENTS ...
Circular Motion - Northwest ISD Moodle
... around a circle with a fixed radius Can the velocity be accelerated even though it has constant speed? Yes, because the velocity may change due to direction. If direction changes and velocity changes then an object can accelerate. ...
... around a circle with a fixed radius Can the velocity be accelerated even though it has constant speed? Yes, because the velocity may change due to direction. If direction changes and velocity changes then an object can accelerate. ...
Physics 130 - UND: University of North Dakota
... Now a third rocket sled is added as shown in the top view below. All three stick together after the collision. What is the final velocity of the system? vSYS,f = ? ...
... Now a third rocket sled is added as shown in the top view below. All three stick together after the collision. What is the final velocity of the system? vSYS,f = ? ...
FINAL EXAM REVIEW GUIDE
... A grocer rolls a can across a moving conveyor belt on a counter. If the can is rolled due south with a speed of 0.25 m/s relative to the counter and the conveyor belt’s velocity is 0.55 m/s to the east, what will the can’s velocity be relative to the counter? (ANS: 0.6 m/s @ 24° S of E) ...
... A grocer rolls a can across a moving conveyor belt on a counter. If the can is rolled due south with a speed of 0.25 m/s relative to the counter and the conveyor belt’s velocity is 0.55 m/s to the east, what will the can’s velocity be relative to the counter? (ANS: 0.6 m/s @ 24° S of E) ...
Terminal Velocity - Northern Illinois University
... Kinetic friction is a constant force. • If there is a net force an object would accelerate forever ...
... Kinetic friction is a constant force. • If there is a net force an object would accelerate forever ...
problems
... 4. N men, each with mass m, stand on a railway flatcar of mass M . They jump off one end of the flatcar with velocity u relative to the car. The car rolls in the opposite direction without friction. Assuming that m << M , (a) What is the final velocity of the flatcar if all the men jump off at once? ...
... 4. N men, each with mass m, stand on a railway flatcar of mass M . They jump off one end of the flatcar with velocity u relative to the car. The car rolls in the opposite direction without friction. Assuming that m << M , (a) What is the final velocity of the flatcar if all the men jump off at once? ...