Uniform Circular Motion
... Other forms, such as 4! 2 R 2 f / T or 2! R" f , while valid, are uncommon. Often we decide which expression to use based on information that describes the orbit. A convenient measure might be the orbit’s radius. We may also independently know the period, or the frequency, or the angular velocity, o ...
... Other forms, such as 4! 2 R 2 f / T or 2! R" f , while valid, are uncommon. Often we decide which expression to use based on information that describes the orbit. A convenient measure might be the orbit’s radius. We may also independently know the period, or the frequency, or the angular velocity, o ...
here
... 12. You push on a wall. What is the reaction pair to this force? 13. A horse pulls on a cart so that it moves forward at a constant velocity. What is the reaction pair to this force? 14. An Attwood machine with a cart of mass m1=450g is accelerated at 1.2m/s2 by a hanging mass. What is the value of ...
... 12. You push on a wall. What is the reaction pair to this force? 13. A horse pulls on a cart so that it moves forward at a constant velocity. What is the reaction pair to this force? 14. An Attwood machine with a cart of mass m1=450g is accelerated at 1.2m/s2 by a hanging mass. What is the value of ...
Motion & Forces
... you notice a tree on the side of the road begin to move forward. You have mistakenly set yourself as the reference point. ...
... you notice a tree on the side of the road begin to move forward. You have mistakenly set yourself as the reference point. ...
Mechanics 1 – Revision notes
... A is at point (0,3), has velocity (2i + j) ms-1 and acceleration (i – 2j) ms-2 B is at point (2,1), has velocity (3i - j) ms-1 and acceleration (2i) ms-2 Find the vector AB six seconds later, and the distance between the particles at that time Displacement : in vector form r is used instead of s Usi ...
... A is at point (0,3), has velocity (2i + j) ms-1 and acceleration (i – 2j) ms-2 B is at point (2,1), has velocity (3i - j) ms-1 and acceleration (2i) ms-2 Find the vector AB six seconds later, and the distance between the particles at that time Displacement : in vector form r is used instead of s Usi ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... Results of Physical measurements in different reference frames could be different Observations of the same motion in a stationary frame would be different than the ones made in the frame moving together with the moving object. Consider that you are driving a car. To you, the objects in the car do no ...
... Results of Physical measurements in different reference frames could be different Observations of the same motion in a stationary frame would be different than the ones made in the frame moving together with the moving object. Consider that you are driving a car. To you, the objects in the car do no ...
Newton`s First Law
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • Definition: An object in motion stays in motion, or an object at rest stays at rest until an unbalanced net force acts on it. • Under these conditions the first law says that if an object is not pushed or pulled upon, its velocity will naturally remain constant. This ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion • Definition: An object in motion stays in motion, or an object at rest stays at rest until an unbalanced net force acts on it. • Under these conditions the first law says that if an object is not pushed or pulled upon, its velocity will naturally remain constant. This ...
Speed & Velocity
... The unit of speed is the meter per second (m/s). Because speed has magnitude only, it scalar quantity. Velocity on the other hand is a vector because it is defined by magnitude and direction thus: Velocity is the distance moved in a defined direction per unit time. ...
... The unit of speed is the meter per second (m/s). Because speed has magnitude only, it scalar quantity. Velocity on the other hand is a vector because it is defined by magnitude and direction thus: Velocity is the distance moved in a defined direction per unit time. ...
Motion
... A student walks 3 blocks south, 4 blocks west, and 3 blocks north. What is the displacement of the student? ...
... A student walks 3 blocks south, 4 blocks west, and 3 blocks north. What is the displacement of the student? ...
Centripetal acceleration
... Rotational motion Angular motion (t)= (0)+(0)t+½t2 (t)= (0)+t ...
... Rotational motion Angular motion (t)= (0)+(0)t+½t2 (t)= (0)+t ...
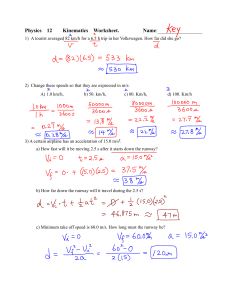
week 1\Day 1\Phy 12 Kinematics HW d 1 Key
... 6) A boy on a skateboard accelerates uniformly down a hill, starting from rest. During the third one second interval from rest, he travels 7.5 m. What is the rate of acceleration of the skateboarder? ...
... 6) A boy on a skateboard accelerates uniformly down a hill, starting from rest. During the third one second interval from rest, he travels 7.5 m. What is the rate of acceleration of the skateboarder? ...