chapter5b
... To determine if the horse (sled) moves: consider only the horizontal forces exerted ON the horse (sled) , then apply 2nd Newton’s Law: ΣF = m a. ...
... To determine if the horse (sled) moves: consider only the horizontal forces exerted ON the horse (sled) , then apply 2nd Newton’s Law: ΣF = m a. ...
Dynamics Multiple Choice Homework
... 24. Earth pulls downward on a pen, of mass m, which is sitting on a table; the magnitude of the force is mg. If that is called the action force, what is the reaction force? A. The table pushing up on the pen with a force equal to mg B. The pen pushing down on the table with a force equal to mg C. T ...
... 24. Earth pulls downward on a pen, of mass m, which is sitting on a table; the magnitude of the force is mg. If that is called the action force, what is the reaction force? A. The table pushing up on the pen with a force equal to mg B. The pen pushing down on the table with a force equal to mg C. T ...
Lectures in physics Part 1: Mechanics Przemysław Borys 7.11.2013
... terms of simple numbers. An example of such quantity is the velocity. It is not sufficient to say that a car moves at 50km/h, we need to supplement this idea by the direction he moves to. A quantity which consists of a magnitude and the direction information is called a vector. A vector can be of tw ...
... terms of simple numbers. An example of such quantity is the velocity. It is not sufficient to say that a car moves at 50km/h, we need to supplement this idea by the direction he moves to. A quantity which consists of a magnitude and the direction information is called a vector. A vector can be of tw ...
The work-energy theorem
... work-energy theorem. In this investigation, you will investigate the way in which the work-energy theorem allows you to determine the kinetic energy of the ...
... work-energy theorem. In this investigation, you will investigate the way in which the work-energy theorem allows you to determine the kinetic energy of the ...
Answers
... Forces on Angles – Top/Down View 2.1.2A – Explain how net force is determined in a top/down view force vector diagram. Determine the vector that is “missing” from a system given a single vector and resultant. Sketch the resultant force in each of the following sets of diagrams. ...
... Forces on Angles – Top/Down View 2.1.2A – Explain how net force is determined in a top/down view force vector diagram. Determine the vector that is “missing” from a system given a single vector and resultant. Sketch the resultant force in each of the following sets of diagrams. ...
Free Body Diagrams
... Aim: What are the different types of Friction? LO: Relate friction to the normal force LO: Calculate friction for different surface combinations LO: AGENDA Do Now - Worksheet Notes Worksheet HW# Due ...
... Aim: What are the different types of Friction? LO: Relate friction to the normal force LO: Calculate friction for different surface combinations LO: AGENDA Do Now - Worksheet Notes Worksheet HW# Due ...
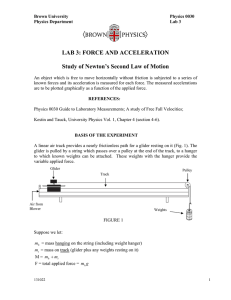
LAB 3: FORCE AND ACCELERATION Study of Newton`s Second
... position and letting go without imparting any initial velocity). Pick a U photocell position near to the rest position, and an L position near the pulley, note the measured transit time from U to L and repeat several times. If the transit times are not essentially the same, you are giving the glider ...
... position and letting go without imparting any initial velocity). Pick a U photocell position near to the rest position, and an L position near the pulley, note the measured transit time from U to L and repeat several times. If the transit times are not essentially the same, you are giving the glider ...