gravity theory based on mass–energy equivalence
... In this theory, an object is a mass density field in the fabric of space (FS) that satisfies mass–energy equivalence. In contrast with General Relativity (GR), the theory posits a preferred reference frame — namely the reference frame in which the FS is at rest. Also in contrast with GR, gravity bet ...
... In this theory, an object is a mass density field in the fabric of space (FS) that satisfies mass–energy equivalence. In contrast with General Relativity (GR), the theory posits a preferred reference frame — namely the reference frame in which the FS is at rest. Also in contrast with GR, gravity bet ...
PHYSICS HOMEWORK #1 KINEMATICS DISPLACEMENT & VELOCITY
... magnitudes of the two vectors. [Note! A vector, which is a directed line segment, can be used to represent any physical quantity which requires both direction and magnitude for a complete description.] Examples: a. 3.0 miles North + 2.0 miles North = 5.0 miles North b. 8.0 miles East + 5.0 miles Wes ...
... magnitudes of the two vectors. [Note! A vector, which is a directed line segment, can be used to represent any physical quantity which requires both direction and magnitude for a complete description.] Examples: a. 3.0 miles North + 2.0 miles North = 5.0 miles North b. 8.0 miles East + 5.0 miles Wes ...
Chapter 10 Angular Momentum
... Angular Momentum 965 Determine the Concept The hardboiled egg is solid inside, so everything rotates with a uniform angular speed. By contrast, when you start an uncooked egg spinning, the yolk will not immediately spin with the shell, and when you stop it from spinning the yolk will initially cont ...
... Angular Momentum 965 Determine the Concept The hardboiled egg is solid inside, so everything rotates with a uniform angular speed. By contrast, when you start an uncooked egg spinning, the yolk will not immediately spin with the shell, and when you stop it from spinning the yolk will initially cont ...
Classical Mechanics and Human Movement
... Mathematica, published in 1687, Sir Isaac Newton presented these laws in mathematical language. The laws of motion can be summarized as follows: A body in our universe is subjected to a multitude of forces exerted by other bodies. The forces exchanged between any two bodies are equal in magnitude bu ...
... Mathematica, published in 1687, Sir Isaac Newton presented these laws in mathematical language. The laws of motion can be summarized as follows: A body in our universe is subjected to a multitude of forces exerted by other bodies. The forces exchanged between any two bodies are equal in magnitude bu ...
13_InstructorSolutions
... EVALUATE: The amplitude and the maximum speed depend on the total energy of the system but the angular frequency is independent of the amount of energy in the system and just depends on the force constant of the spring and the mass of the object. IDENTIFY: K = 12 mv 2 , U grav = mgy and U el = 12 kx ...
... EVALUATE: The amplitude and the maximum speed depend on the total energy of the system but the angular frequency is independent of the amount of energy in the system and just depends on the force constant of the spring and the mass of the object. IDENTIFY: K = 12 mv 2 , U grav = mgy and U el = 12 kx ...
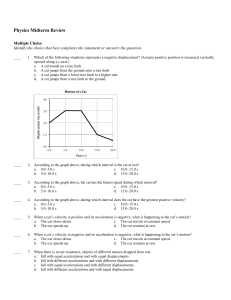
Physics Midterm Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... 38. Describe the graph of the vertical component of velocity versus time for the motion of the ball shown in the figure above. Identify any constants that would appear in the graph. 39. Why is force not a scalar quantity? 40. A block of wood supported by two concrete blocks is chopped in half by a k ...
... 38. Describe the graph of the vertical component of velocity versus time for the motion of the ball shown in the figure above. Identify any constants that would appear in the graph. 39. Why is force not a scalar quantity? 40. A block of wood supported by two concrete blocks is chopped in half by a k ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... Conservation of Momentum Momentum in a Closed, Isolated System Systems can contain any number of objects, and the objects can stick together or come apart in a collision. Under these conditions, the law of conservation of momentum states that the momentum of any closed, isolated system does not chan ...
... Conservation of Momentum Momentum in a Closed, Isolated System Systems can contain any number of objects, and the objects can stick together or come apart in a collision. Under these conditions, the law of conservation of momentum states that the momentum of any closed, isolated system does not chan ...
Physical Response to Collision between Deformable Objects
... In the real world, bodies are controlled by nature’s laws that automatically avoid them to interpenetrate. They are made of matter and matter is impenetrable. Just remember that elementary law of Physics that says that two bodies cannot occupy the same space at the same time. In Computer Graphics’ v ...
... In the real world, bodies are controlled by nature’s laws that automatically avoid them to interpenetrate. They are made of matter and matter is impenetrable. Just remember that elementary law of Physics that says that two bodies cannot occupy the same space at the same time. In Computer Graphics’ v ...
Chapter 7: Linear Momentum and Collisions
... Picture the Problem: The speeds and masses of four objects are given. Strategy: Multiply the mass and the speed of each object to find its momentum, and then use the results to rank the momenta of the four objects. pA = mA vA = (10 kg )(10 m/s ) = 100 kg ⋅ m/s ...
... Picture the Problem: The speeds and masses of four objects are given. Strategy: Multiply the mass and the speed of each object to find its momentum, and then use the results to rank the momenta of the four objects. pA = mA vA = (10 kg )(10 m/s ) = 100 kg ⋅ m/s ...