Physics 2010 Summer 2011 REVIEW FOR MIDTERM 2
... If this elevator were on Mars (mass = 6.26 × 1023 kg, radius = 3.39 × 106 m, G = 6.673 × 10-11 N@m2/kg2), what would be Dawn’s apparent weight while accelerating downward at 1.5 m/s2? ...
... If this elevator were on Mars (mass = 6.26 × 1023 kg, radius = 3.39 × 106 m, G = 6.673 × 10-11 N@m2/kg2), what would be Dawn’s apparent weight while accelerating downward at 1.5 m/s2? ...
Momentum
... A car with mass 1.5×103 kg traveling east at a speed of 25 m/s collides at an intersection with a 2.5×103 kg van traveling north at a speed of 20 m/s. Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the wreckage after the collision, assuming that the vehicles undergo a perfectly inelastic collis ...
... A car with mass 1.5×103 kg traveling east at a speed of 25 m/s collides at an intersection with a 2.5×103 kg van traveling north at a speed of 20 m/s. Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the wreckage after the collision, assuming that the vehicles undergo a perfectly inelastic collis ...
newton`s second law of motion—force and acceleration
... The force of friction between the surfaces depends on the kinds of material in contact and how much the surfaces are pressed together. For example, rubber against concrete produces more friction than steel against steel. That’s why concrete road dividers have replaced steel rails. The friction produ ...
... The force of friction between the surfaces depends on the kinds of material in contact and how much the surfaces are pressed together. For example, rubber against concrete produces more friction than steel against steel. That’s why concrete road dividers have replaced steel rails. The friction produ ...
Physical Science - Iredell
... • Describe motion qualitatively and quantitatively in terms of an object’s change of position, distance traveled, and displacement. PSc.1.1.2 • Compare speed and velocity as a scalar-vector pair. Velocity is a relationship between displacement and time: v=Δd/Δt • Apply concepts of average speed and ...
... • Describe motion qualitatively and quantitatively in terms of an object’s change of position, distance traveled, and displacement. PSc.1.1.2 • Compare speed and velocity as a scalar-vector pair. Velocity is a relationship between displacement and time: v=Δd/Δt • Apply concepts of average speed and ...
Interim Assessment Sample Question
... mathematical procedures including vector addition and righttriangle geometry to solve physical problems ...
... mathematical procedures including vector addition and righttriangle geometry to solve physical problems ...
10 Circular Motion - Aurora City Schools
... Centripetal force, Fc, is measured in newtons when m is expressed in kilograms, v in meters/second, and r in meters. ...
... Centripetal force, Fc, is measured in newtons when m is expressed in kilograms, v in meters/second, and r in meters. ...
Momentum and Impulse
... The units of impulse are N s (Newton Seconds). Impulse is a vector quantity. ...
... The units of impulse are N s (Newton Seconds). Impulse is a vector quantity. ...
Chapter 11 - Angular Momentum
... System of Particles; General Motion The angular momentum of a system of particles can change only if there is an external torque—torques due to internal forces cancel. ...
... System of Particles; General Motion The angular momentum of a system of particles can change only if there is an external torque—torques due to internal forces cancel. ...
Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion
... The model airplane has a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced by the lift generated by its wings. Find the tension in the 17 m gu ...
... The model airplane has a mass of 0.90 kg and moves at constant speed on a circle that is parallel to the ground. The path of the airplane and the guideline lie in the same horizontal plane because the weight of the plane is balanced by the lift generated by its wings. Find the tension in the 17 m gu ...
0175 Lecture Notes - Force of Impact Equation Derivation
... This gets us closer to Newton’s original second law which is ∑ F = . The net force acting on an dt object equals the derivative of the momentum of that object with respect to time. If you ever take a calculus based physics course, like AP Physics C, you will get an opportunity to work with this equa ...
... This gets us closer to Newton’s original second law which is ∑ F = . The net force acting on an dt object equals the derivative of the momentum of that object with respect to time. If you ever take a calculus based physics course, like AP Physics C, you will get an opportunity to work with this equa ...
28 Copyright A. Steane, Oxford University 2010, 2011
... Table 3.1: Useful relations involving γ. β = v/c is the speed in units of the speed of light. dt/dτ relates the time between events on a worldline to the proper time, for a particle of speed v. dt0 /dt relates the time between events on a worldline for two reference frames of relative velocity v, wi ...
... Table 3.1: Useful relations involving γ. β = v/c is the speed in units of the speed of light. dt/dτ relates the time between events on a worldline to the proper time, for a particle of speed v. dt0 /dt relates the time between events on a worldline for two reference frames of relative velocity v, wi ...
CHAPTER 4 RIGID BODY ROTATION
... their derivation at this stage. Later in this series, I hope to add a longer chapter on Lagrangian mechanics, when all will be made clear (maybe). In the meantime, for those who are not content just to accept Euler’s equations but must also understand their derivation, this section gives a five-minu ...
... their derivation at this stage. Later in this series, I hope to add a longer chapter on Lagrangian mechanics, when all will be made clear (maybe). In the meantime, for those who are not content just to accept Euler’s equations but must also understand their derivation, this section gives a five-minu ...
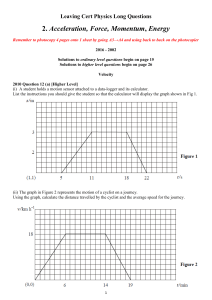
2. Acceleration, Force, Momentum, Energy
... On 16 August, 1960, Joseph Kittinger established a record for the highest altitude parachute jump. This record remains unbroken. Kittinger jumped from a height of 31 km. He fell for 13 seconds and then his 1.8metre canopy parachute opened. This stabilised his fall. Only four minutes and 36 seconds m ...
... On 16 August, 1960, Joseph Kittinger established a record for the highest altitude parachute jump. This record remains unbroken. Kittinger jumped from a height of 31 km. He fell for 13 seconds and then his 1.8metre canopy parachute opened. This stabilised his fall. Only four minutes and 36 seconds m ...

















![Newton`s 1st Law Chapter 4 [ Edit ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014791822_1-2c861cb90e155a9bec8e50db1f7a973a-300x300.png)