Newton`s Laws of Motion
... an object is determined by the mass of the object. force = mass x acceleration • The more mass an object has, the more force is needed. • The less mass an object has, the less force is needed. ...
... an object is determined by the mass of the object. force = mass x acceleration • The more mass an object has, the more force is needed. • The less mass an object has, the less force is needed. ...
EART 160: Planetary Sciences
... 1. A body at rest remains at rest and a body in motion at a constant speed remains in motion along a straight line unless acted on by a force. 2. The rate of change of velocity of a body is directly proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass of the body. 3. The actions of two b ...
... 1. A body at rest remains at rest and a body in motion at a constant speed remains in motion along a straight line unless acted on by a force. 2. The rate of change of velocity of a body is directly proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass of the body. 3. The actions of two b ...
PHYSICS 51: Introduction
... rest tend to stay at rest, objects in motion stay in motion.” More properly, “A body acted on by no net force moves with constant (or zero) velocity and zero acceleration.” ...
... rest tend to stay at rest, objects in motion stay in motion.” More properly, “A body acted on by no net force moves with constant (or zero) velocity and zero acceleration.” ...
2005 C Mechanics 1. (a) ____ increases
... resistance) and this net force equals Ma according to Newton's Second Law of Motion. Since F is decreasing as the ball moves upward, the net force decreases, thus, the acceleration decreases (b) -Mg - kv = Ma -g - ...
... resistance) and this net force equals Ma according to Newton's Second Law of Motion. Since F is decreasing as the ball moves upward, the net force decreases, thus, the acceleration decreases (b) -Mg - kv = Ma -g - ...
Name - forehandspace
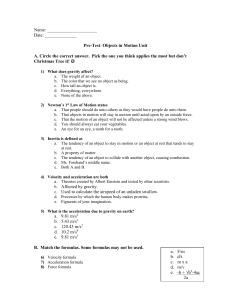
... A. Circle the correct answer. Pick the one you think applies the most but don’t Christmas Tree it! 1) What does gravity affect? a. The weight of an object. b. The color that we see an object as being. c. How tall an object is. d. Everything, everywhere. e. None of the above. 2) Newton’s 1st Law of ...
... A. Circle the correct answer. Pick the one you think applies the most but don’t Christmas Tree it! 1) What does gravity affect? a. The weight of an object. b. The color that we see an object as being. c. How tall an object is. d. Everything, everywhere. e. None of the above. 2) Newton’s 1st Law of ...
Unit 7 Bell Ringers - Trimble County Schools
... = 20 grams Tennis Ball = 57 grams Baseball = 145 grams Softball = 178 grams Velocity ...
... = 20 grams Tennis Ball = 57 grams Baseball = 145 grams Softball = 178 grams Velocity ...
answers
... Use complete sentences to answer the following questions. 14. Explain how mass and weight are different from each other. Mass is the amount of atoms that make up an object, weight is the force on the object due to gravity. If an object experiences a change in gravity, the weight will change, however ...
... Use complete sentences to answer the following questions. 14. Explain how mass and weight are different from each other. Mass is the amount of atoms that make up an object, weight is the force on the object due to gravity. If an object experiences a change in gravity, the weight will change, however ...
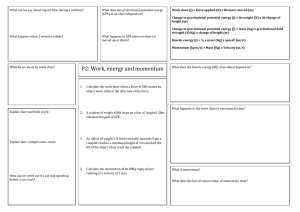
Forces Chapter 10 - Powers Physical Science
... According to the law of conservation of momentum, when two objects collide in the absence of friction, ...
... According to the law of conservation of momentum, when two objects collide in the absence of friction, ...
presentation source
... acceleration it experiences (in the absence of air resistance) is that due to gravity! Gravity acts downward, affecting only the vertical component of the velocity, Vy. The horizontal component of the velocity... ...
... acceleration it experiences (in the absence of air resistance) is that due to gravity! Gravity acts downward, affecting only the vertical component of the velocity, Vy. The horizontal component of the velocity... ...
a 2 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Ch. 7 Work and energy • Work • Kinetic energy • Potential energy • Work- kinetic energy theorem Ch. 8 Conservation of Energy • Mechanical energy • Conservation of energy ...
... Ch. 7 Work and energy • Work • Kinetic energy • Potential energy • Work- kinetic energy theorem Ch. 8 Conservation of Energy • Mechanical energy • Conservation of energy ...