5Kepler2s
... Isaac Newton (1642-1727) used Galileo and Kepler’s Laws to discover the laws of motion and gravity ...
... Isaac Newton (1642-1727) used Galileo and Kepler’s Laws to discover the laws of motion and gravity ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion An object’s acceleration depends on its mass and on the net force acting on it. ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion An object’s acceleration depends on its mass and on the net force acting on it. ...
part 1
... or an object moving in a straight line continues to move with the same velocity along that line unless an external force causes it to do otherwise. If you have two objects with different masses, the one with more mass is said to have more inertia (a greater tendency to not change its current speed o ...
... or an object moving in a straight line continues to move with the same velocity along that line unless an external force causes it to do otherwise. If you have two objects with different masses, the one with more mass is said to have more inertia (a greater tendency to not change its current speed o ...
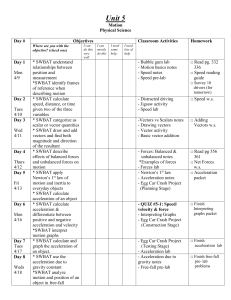
Unit 5 plan motion
... position and measurement *SWBAT identify frames of reference when describing motion * SWBAT calculate speed, distance, or time given two of the three variables * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBA ...
... position and measurement *SWBAT identify frames of reference when describing motion * SWBAT calculate speed, distance, or time given two of the three variables * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBA ...
Physics 101: Lecture 12 Work and Energy
... An important concept in physics ÎAlternative approach to mechanics Many applications beyond mechanics ÎThermodynamics (movement of heat) ÎQuantum mechanics... Very useful tools ÎYou will learn new (sometimes much easier) ways to solve problems ...
... An important concept in physics ÎAlternative approach to mechanics Many applications beyond mechanics ÎThermodynamics (movement of heat) ÎQuantum mechanics... Very useful tools ÎYou will learn new (sometimes much easier) ways to solve problems ...
Solar Energy Test (part 1)
... How does it relate to forces and motion? What does speeding up look like on a v-t What direction is the surface force (due graph? Slowing down? Constant speed? to friction relative to the direction of motion? Calculating Motion Know how to find velocity and speed if Calculating Forces you know dista ...
... How does it relate to forces and motion? What does speeding up look like on a v-t What direction is the surface force (due graph? Slowing down? Constant speed? to friction relative to the direction of motion? Calculating Motion Know how to find velocity and speed if Calculating Forces you know dista ...
Motion, Forces, and Energy
... produced by a net (total) force is directly related to the magnitude of the force, the direction as the force, and inversely related to the mass of the object. • More force = more acceleration • More mass = less acceleration ...
... produced by a net (total) force is directly related to the magnitude of the force, the direction as the force, and inversely related to the mass of the object. • More force = more acceleration • More mass = less acceleration ...
Relative Motion
... An object subject to no external forces moves with a constant velocity if viewed from an inertial reference frame. – If no forces act, there is no acceleration. ...
... An object subject to no external forces moves with a constant velocity if viewed from an inertial reference frame. – If no forces act, there is no acceleration. ...
Review - Hingham Schools
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
Unit 1 content
... 2 m s-2 = m. a = 1000 x 2 = 2 000 N Total force applied accelerates tractor and car at 2 m s-2 = m. a = 6000 x 2 = 12 000 N ...
... 2 m s-2 = m. a = 1000 x 2 = 2 000 N Total force applied accelerates tractor and car at 2 m s-2 = m. a = 6000 x 2 = 12 000 N ...
Midterm Exam 1
... Units, etc used in astronomy; relative size scales. History of astronomy from ancient Greeks until mid-1600’s. – What did the ancient Greeks have right? What did they have wrong? – How we went from geocentric (Earth at center) models to heliocentric (Sun at center) models of Solar System. – Ptolemy’ ...
... Units, etc used in astronomy; relative size scales. History of astronomy from ancient Greeks until mid-1600’s. – What did the ancient Greeks have right? What did they have wrong? – How we went from geocentric (Earth at center) models to heliocentric (Sun at center) models of Solar System. – Ptolemy’ ...
Benchmark 1 Notes
... 4D: Newton’s Laws of Motion Newton’s First Law An object in motion will stay in motion or at rest unless acted upon by an outside UNBALANCED force. Inertia- tendency of an object to travel in a straight line. Newton’s Second Law Force equals mass times acceleration. F=ma Sometimes, you wil ...
... 4D: Newton’s Laws of Motion Newton’s First Law An object in motion will stay in motion or at rest unless acted upon by an outside UNBALANCED force. Inertia- tendency of an object to travel in a straight line. Newton’s Second Law Force equals mass times acceleration. F=ma Sometimes, you wil ...
ert146 lect kinetic of motion
... To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle’s free-body diagram, showing all forces acting on the particle. Next, draw the kinetic diagram, showing the inertial force ma acting in the same direction as the resultant force FR. ...
... To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle’s free-body diagram, showing all forces acting on the particle. Next, draw the kinetic diagram, showing the inertial force ma acting in the same direction as the resultant force FR. ...
FORCES AND MOTIONS TEST REVIEW FORCE BALANCED
... 8. IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING SCENARIOS USING YOUR MEMORY CUES FOR SPEED, VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 8. IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING SCENARIOS USING YOUR MEMORY CUES FOR SPEED, VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. A. B. C. D. E. ...
Newton*s Laws - MTHS - Kelly
... change. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg). Mass is not weight. 1 kg of mass weighs 9.8 Newtons(N) Weight is a downward force due to gravity. ...
... change. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg). Mass is not weight. 1 kg of mass weighs 9.8 Newtons(N) Weight is a downward force due to gravity. ...
bezout identities with inequality constraints
... Note: force is a vector quantity – it has both magnitude and direction! ...
... Note: force is a vector quantity – it has both magnitude and direction! ...