PPT - Hss-1.us
... – Friction between solid objects is often referred to as Dry Friction – Frictional forces between two fluids (gases or liquids) as called Fluid Friction which is related to its viscosity. – In addition to these there is also Internal Friction which illustrates a body's ability to recover from extern ...
... – Friction between solid objects is often referred to as Dry Friction – Frictional forces between two fluids (gases or liquids) as called Fluid Friction which is related to its viscosity. – In addition to these there is also Internal Friction which illustrates a body's ability to recover from extern ...
Newton`s 2nd Law - fhssciencerocks
... One Newton is equal to 0.225 lbs. One pound is equal to 4.448 Newtons If you push an empty cart with the same force you would use to push a full cart, the empty one will have a much greater acceleration ...
... One Newton is equal to 0.225 lbs. One pound is equal to 4.448 Newtons If you push an empty cart with the same force you would use to push a full cart, the empty one will have a much greater acceleration ...
Circular Motion vr The Period T - FSU
... A particle of mass m moves with constant speed v on a circle of radius R. The following holds (pick one): 1. The centripetal force is v 2/R towards the center. 2. The centripetal force is m v 2/R towards the center. 3. The centripetal force is m v 2/R away from the center. 4. The centripetal force i ...
... A particle of mass m moves with constant speed v on a circle of radius R. The following holds (pick one): 1. The centripetal force is v 2/R towards the center. 2. The centripetal force is m v 2/R towards the center. 3. The centripetal force is m v 2/R away from the center. 4. The centripetal force i ...
Physical Science Worksheet: Chapters 10 and 11
... A) reaction forces. B) action forces. C) balanced forces. D) unbalanced forces. 23. The SI unit of force, named for the scientist who described the relationship between motion and force, is called the A) newton. B) einstein. C) curie. D) pasteur. 24. If the net force acting on a stationary object is ...
... A) reaction forces. B) action forces. C) balanced forces. D) unbalanced forces. 23. The SI unit of force, named for the scientist who described the relationship between motion and force, is called the A) newton. B) einstein. C) curie. D) pasteur. 24. If the net force acting on a stationary object is ...
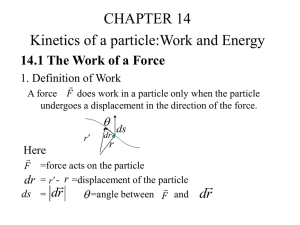
14.1 The Work of a Force
... The particle’s initial kinetic energy plus the work done by all the forces acting on the particle as it moves from its initial to its final position is equal to the particle’s final kinetic energy. T1 U12 T2 or 12 mv12 U12 12 mv2 2 z ...
... The particle’s initial kinetic energy plus the work done by all the forces acting on the particle as it moves from its initial to its final position is equal to the particle’s final kinetic energy. T1 U12 T2 or 12 mv12 U12 12 mv2 2 z ...
Newton`s Second Law - Madison County Schools
... Zookeepers lift a stretcher that holds a sedated lion. The total mass of the lion and stretcher is 175 kg, and the upward acceleration of the lion and stretcher is 0.657 m/s2. What force is needed to produce this acceleration of the lion and the stretcher? 1. List the given and unknown values. ...
... Zookeepers lift a stretcher that holds a sedated lion. The total mass of the lion and stretcher is 175 kg, and the upward acceleration of the lion and stretcher is 0.657 m/s2. What force is needed to produce this acceleration of the lion and the stretcher? 1. List the given and unknown values. ...
A Newton pair of forces
... 5. The apparatus in the diagram is designed to verify Newton’s second law of motion. Give a careful account of how this experiment should be carried out. ...
... 5. The apparatus in the diagram is designed to verify Newton’s second law of motion. Give a careful account of how this experiment should be carried out. ...
Text 1 (1.1 What is physics?) Children have an insatiable curiosity
... Although every force is a manifestation of one of the fundamental interactions mentioned in Section 1.1, it is sometimes convenient to refer to a force as being either a contact force or an action at a distance. Contact forces arise when one body is in physical contact with another. Examples include ...
... Although every force is a manifestation of one of the fundamental interactions mentioned in Section 1.1, it is sometimes convenient to refer to a force as being either a contact force or an action at a distance. Contact forces arise when one body is in physical contact with another. Examples include ...
Over head 2
... the card to accelerate horizontally. • Why did this happen? The force was applied to the card only – Inertia kept the coin from moving. • Do you think it would be different if you pulled it slowly? It should go with the card everytime. ...
... the card to accelerate horizontally. • Why did this happen? The force was applied to the card only – Inertia kept the coin from moving. • Do you think it would be different if you pulled it slowly? It should go with the card everytime. ...
Problem set 13
... 1. h12i Consider force free motion of a symmetric top with I1 = I2 , as discussed in the lecture. Suppose the axis of the top makes an angle θ , 0 with the fixed direction of L. (a) h6i Find the angle α between the angular velocity vector Ω and angular momentum vector L (α is half the opening angle ...
... 1. h12i Consider force free motion of a symmetric top with I1 = I2 , as discussed in the lecture. Suppose the axis of the top makes an angle θ , 0 with the fixed direction of L. (a) h6i Find the angle α between the angular velocity vector Ω and angular momentum vector L (α is half the opening angle ...
1 st Law
... Dropped objects with different weights from the Leaning Tower of Pisa Found that all objects fall at the same rate if you can account for air resistance ...
... Dropped objects with different weights from the Leaning Tower of Pisa Found that all objects fall at the same rate if you can account for air resistance ...
chapter 7 notes - School District of La Crosse
... III. Periodic motion-The motion of the object repeats itself. A pendulum, a Yo Yo A. circular motion-The product of 2 forces acting on an object. 1. F1- the outward force of inertiatangent to the motion of the object. 2. F2- the inward force called centripetal force. ...
... III. Periodic motion-The motion of the object repeats itself. A pendulum, a Yo Yo A. circular motion-The product of 2 forces acting on an object. 1. F1- the outward force of inertiatangent to the motion of the object. 2. F2- the inward force called centripetal force. ...