Newton`s Laws of Motion (power point file)
... – Attractive forces exist between bodies (e.g. a body and the Earth) that are proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them ...
... – Attractive forces exist between bodies (e.g. a body and the Earth) that are proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... – Attractive forces exist between bodies (e.g. a body and the Earth) that are proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them ...
... – Attractive forces exist between bodies (e.g. a body and the Earth) that are proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them ...
Forces and Newtons laws
... Newton’s first law The ball travels with constant velocity until its reaches the other side (which it never does!). Galileo realised that this was the natural state of objects when no (resultant ) forces act. ...
... Newton’s first law The ball travels with constant velocity until its reaches the other side (which it never does!). Galileo realised that this was the natural state of objects when no (resultant ) forces act. ...
Forces in Motion
... same for all objects. The force of gravity is greater between Earth and an object with a large mass than between Earth and a less massive object. Greater force must be applied to a large mass than to a small mass to produce the same acceleration. The difference in force is canceled by the diff ...
... same for all objects. The force of gravity is greater between Earth and an object with a large mass than between Earth and a less massive object. Greater force must be applied to a large mass than to a small mass to produce the same acceleration. The difference in force is canceled by the diff ...
17 M3 January 2006
... A particle P of mass 0.8 kg is attached to one end of a light inelastic string, of natural length 1.2 m and modulus of elasticity 24 N. The other end of the string is attached to a fixed point A. A horizontal force of magnitude F newtons is applied to P. The particle P in in equilibrium with the str ...
... A particle P of mass 0.8 kg is attached to one end of a light inelastic string, of natural length 1.2 m and modulus of elasticity 24 N. The other end of the string is attached to a fixed point A. A horizontal force of magnitude F newtons is applied to P. The particle P in in equilibrium with the str ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - CEC
... Now let’s introduce the second part of Newton’s first law, which is that objects in motion tend to stay in motion until something hits them. An example of this is what happens if an astronaut throws something while in outer space. The item will continue in the same direction and at the same speed un ...
... Now let’s introduce the second part of Newton’s first law, which is that objects in motion tend to stay in motion until something hits them. An example of this is what happens if an astronaut throws something while in outer space. The item will continue in the same direction and at the same speed un ...
force - SCIENCE
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion • Force Pairs Do Not Act on the Same Object A force is always exerted by one object on another object. This rule is true for all forces, including action and reaction forces. • Action and reaction forces in a pair do not act on the same object. If they did, the net forc ...
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion • Force Pairs Do Not Act on the Same Object A force is always exerted by one object on another object. This rule is true for all forces, including action and reaction forces. • Action and reaction forces in a pair do not act on the same object. If they did, the net forc ...
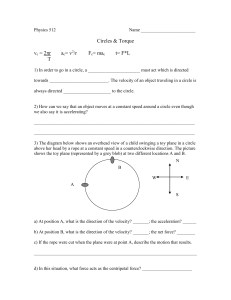
Physics 512 - Scarsdale Schools
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
Gravitation - Siena College
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation Each mass particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that varies directly as the product of the two masses and inversely as the square of the distance between them. ...
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation Each mass particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that varies directly as the product of the two masses and inversely as the square of the distance between them. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... motion. They are equal in size and opposite in direction. Push both of your hand together with the same force. The force is equal in size and opposite in direction, therefore there is no motion. ...
... motion. They are equal in size and opposite in direction. Push both of your hand together with the same force. The force is equal in size and opposite in direction, therefore there is no motion. ...
Section 8-2 Center of Mass
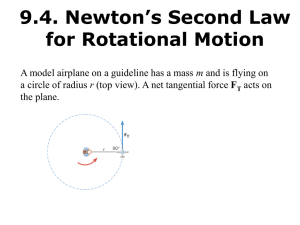
... e. Linear speed of a point on the rotating object increases with as the object’s distance from the center (r) increases. f. Although every point on the rotating object has the same angular speed (ω), not every point has the same linear (tangential) speed. 8. Centripetal Acceleration – acceleration d ...
... e. Linear speed of a point on the rotating object increases with as the object’s distance from the center (r) increases. f. Although every point on the rotating object has the same angular speed (ω), not every point has the same linear (tangential) speed. 8. Centripetal Acceleration – acceleration d ...