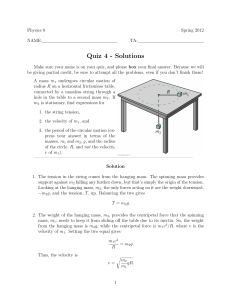
May 2008 - University of Michigan
... (b) Write down expressions for the total energy stored on the two capacitors before, immediately after, and a long time after the plate separation was changed. Explain any change quantitatively: where does any lost energy go, and what is the origin of any increase in energy? ...
... (b) Write down expressions for the total energy stored on the two capacitors before, immediately after, and a long time after the plate separation was changed. Explain any change quantitatively: where does any lost energy go, and what is the origin of any increase in energy? ...
chapter4
... Apply Newton’s Laws separately to each object The magnitude of the acceleration of both objects will be the ...
... Apply Newton’s Laws separately to each object The magnitude of the acceleration of both objects will be the ...
Lecture 2 Newton`s laws of motion
... Momentum is also a vector quantity that has the same direction as that of the velocity. Newton's First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia) Every object continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless made to change by a non-zero net force The inertia of an object is its tendency to resist changes ...
... Momentum is also a vector quantity that has the same direction as that of the velocity. Newton's First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia) Every object continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless made to change by a non-zero net force The inertia of an object is its tendency to resist changes ...
(field forces: magnetic force, gravitational force).
... scalar quantity). The weight of a body varies with its location near the Earth (or other astronomical body), whereas its mass is the same everywhere in the universe. The weight of a body is the force that causes it to be accelerated downward with the acceleration of gravity g. ...
... scalar quantity). The weight of a body varies with its location near the Earth (or other astronomical body), whereas its mass is the same everywhere in the universe. The weight of a body is the force that causes it to be accelerated downward with the acceleration of gravity g. ...
Link to Notes - Coweta County Schools
... the Earth The unit for weight is a N because it is a force exerted on you by the mass of the Earth (or whatever planet is pulling on you) ...
... the Earth The unit for weight is a N because it is a force exerted on you by the mass of the Earth (or whatever planet is pulling on you) ...
AP Physics C ID
... magnitudes of the velocities after the collisions in terms of v. b) Is this an elastic or inelastic collision? ...
... magnitudes of the velocities after the collisions in terms of v. b) Is this an elastic or inelastic collision? ...
Activity 80
... 40 MPH. Are the forces on the car balanced or unbalanced? Explain. The forces are balanced. The frictional forces within the car and from the road are balanced by the equal but opposite force applied by the engine. The net force is zero, and the car travels with constant speed and direction. ...
... 40 MPH. Are the forces on the car balanced or unbalanced? Explain. The forces are balanced. The frictional forces within the car and from the road are balanced by the equal but opposite force applied by the engine. The net force is zero, and the car travels with constant speed and direction. ...
force
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
June - Life Learning Cloud
... Check that you have the correct question paper. Answer ALL the questions. You must write your answer for each question in the space following the question. Whenever a numerical value of g is required, take g = 9.8 m s–2. When a calculator is used, the answer should be given to an appropriate degree ...
... Check that you have the correct question paper. Answer ALL the questions. You must write your answer for each question in the space following the question. Whenever a numerical value of g is required, take g = 9.8 m s–2. When a calculator is used, the answer should be given to an appropriate degree ...
File
... motion, and is directed towards the center of the circle. Example of centripetal force: the moon being held in orbit by gravity. Centrifugal Force: an imaginary force that seems to pull away from the center of the circle which is caused by inertia. Example of centrifugal force: carnival ...
... motion, and is directed towards the center of the circle. Example of centripetal force: the moon being held in orbit by gravity. Centrifugal Force: an imaginary force that seems to pull away from the center of the circle which is caused by inertia. Example of centrifugal force: carnival ...
F g - Humble ISD
... Can exist during physical contact(Tension, Friction, Applied Force) Can exist with NO physical contact, called FIELD FORCES ( gravitational, electric, etc) ...
... Can exist during physical contact(Tension, Friction, Applied Force) Can exist with NO physical contact, called FIELD FORCES ( gravitational, electric, etc) ...
Lecture Notes for Sections 14.1
... particles can be derived by integrating the equation of motion (F = ma) with respect to displacement. By substituting at = v (dv/ds) into Ft = mat, the result is integrated to yield an equation known as the principle of work and energy. This principle is useful for solving problems that involve forc ...
... particles can be derived by integrating the equation of motion (F = ma) with respect to displacement. By substituting at = v (dv/ds) into Ft = mat, the result is integrated to yield an equation known as the principle of work and energy. This principle is useful for solving problems that involve forc ...
Unit 2 Section 4 Notes Newton`s Laws of Motion
... an outside force. In other words, the net force acting on the object is zero. Example: A book sliding on any surface will eventually come to a stop due to friction. If it weren’t for friction, the book would continue to slide. ...
... an outside force. In other words, the net force acting on the object is zero. Example: A book sliding on any surface will eventually come to a stop due to friction. If it weren’t for friction, the book would continue to slide. ...
Lecture-VII
... One needs to apply this generalized version of Newton’s Second Law to systems in which mass flows between constituent objects. Analyzing the forces on a system in which there is a flow of mass becomes terribly confusing if we try to apply Newton's laws blindly. There is no fundamental difficulty in ...
... One needs to apply this generalized version of Newton’s Second Law to systems in which mass flows between constituent objects. Analyzing the forces on a system in which there is a flow of mass becomes terribly confusing if we try to apply Newton's laws blindly. There is no fundamental difficulty in ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... happens • Effect: This is what happens as a reaction to the cause • If your good friend beats you at video games, then you will smack that person with the nearest pillow. • In this case what’s the cause? The effect? ...
... happens • Effect: This is what happens as a reaction to the cause • If your good friend beats you at video games, then you will smack that person with the nearest pillow. • In this case what’s the cause? The effect? ...