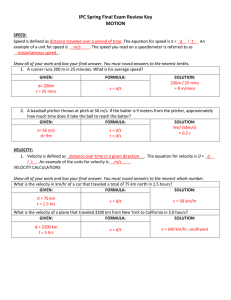
IPC Spring Final Exam Review Key MOTION
... B The object is moving in a positive direction and gaining speed (accelerating) at a rapid rate ACCELERATION: Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity over a change in time. The equation for acceleration is a = vf - vi / ∆t. An example of the units for acceleration is m/s2. Acceleration due ...
... B The object is moving in a positive direction and gaining speed (accelerating) at a rapid rate ACCELERATION: Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity over a change in time. The equation for acceleration is a = vf - vi / ∆t. An example of the units for acceleration is m/s2. Acceleration due ...
Newton2and3
... Newton’s Third Law states that every time one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction back on the first object. ...
... Newton’s Third Law states that every time one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction back on the first object. ...
1st Semester Review
... 4. Explain why is it possible for a truck that collects milk from farms to have an average velocity of 20.0 miles/hour if when its minimum speed while in motion was 30.0 miles/hour Solve problems around average velocity using the correct equation by writing Given, Find, Equation in term of the unkno ...
... 4. Explain why is it possible for a truck that collects milk from farms to have an average velocity of 20.0 miles/hour if when its minimum speed while in motion was 30.0 miles/hour Solve problems around average velocity using the correct equation by writing Given, Find, Equation in term of the unkno ...
Motion
... Defines inertia: resistance to change Mass is measure of inertia (kg) A body moving at constant velocity has zero Net Force acting on it ...
... Defines inertia: resistance to change Mass is measure of inertia (kg) A body moving at constant velocity has zero Net Force acting on it ...
Force
... be the difference between the two forces because they are in opposite directions. They are considered to be unbalanced forces. ...
... be the difference between the two forces because they are in opposite directions. They are considered to be unbalanced forces. ...
12. Work Power & Energy
... Total work done by all the forces acting on a body is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. ...
... Total work done by all the forces acting on a body is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... fish uses its fins to push water backwards. In turn, the water reacts by pushing the fish forwards, propelling the fish through the water. The size of the force on the water equals the size of the force on the fish; the direction of the force on the water (backwards) is opposite the direction of the ...
... fish uses its fins to push water backwards. In turn, the water reacts by pushing the fish forwards, propelling the fish through the water. The size of the force on the water equals the size of the force on the fish; the direction of the force on the water (backwards) is opposite the direction of the ...
Momentum
... Impulse is not a property of the object, but something that it can give or get from an interaction. Notice that it is not motion that gives us an impulse (v) but a change in motion (Dv). ...
... Impulse is not a property of the object, but something that it can give or get from an interaction. Notice that it is not motion that gives us an impulse (v) but a change in motion (Dv). ...
Physics Study Guide - The Oakwood School
... The application of a force over an area produces pressure. When the force is perpendicular to the surface area, the pressure equals the force divided by the area over which it acts. The acceleration of all objects in free fall is the same, regardless of their mass. When air resistance is present ...
... The application of a force over an area produces pressure. When the force is perpendicular to the surface area, the pressure equals the force divided by the area over which it acts. The acceleration of all objects in free fall is the same, regardless of their mass. When air resistance is present ...
AP Physics – Circular Motion and Gravity
... any of the previous forces. If gravity is causing circular motion then Fc = Fg . If friction, then Fc = Ffr . ...
... any of the previous forces. If gravity is causing circular motion then Fc = Fg . If friction, then Fc = Ffr . ...
Circular Motion - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... any of the previous forces. If gravity is causing circular motion then Fc Fg . If friction, then Fc Ffr . ...
... any of the previous forces. If gravity is causing circular motion then Fc Fg . If friction, then Fc Ffr . ...
Force Equals Mass Times Acceleration
... To use this formula, you need to understand the unit used to measure force. In honor of Newton’s contribution to our understanding of force and motion, the standard unit of force is called the newton (N). Because force equals mass times acceleration, force is measured in units of mass (kilograms) ti ...
... To use this formula, you need to understand the unit used to measure force. In honor of Newton’s contribution to our understanding of force and motion, the standard unit of force is called the newton (N). Because force equals mass times acceleration, force is measured in units of mass (kilograms) ti ...























