PowerPoint Lesson
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
Connecting Force and Motion, and Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Example: The force you are exerting on your seat is the same force your seat is exerting on you - You are pushing the seat down and the seat is holding you up. 2. Back to the initial question: What happens? You fall in a. Why? When you leap from the boat, the boat exerts a force on your feet, moving ...
... Example: The force you are exerting on your seat is the same force your seat is exerting on you - You are pushing the seat down and the seat is holding you up. 2. Back to the initial question: What happens? You fall in a. Why? When you leap from the boat, the boat exerts a force on your feet, moving ...
Intro Sheet
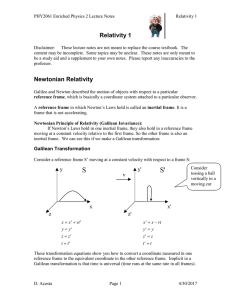
... An object can be drawn as if it was extracted from its environment and the interactions with the environment identified. A force exerted on an object can be represented as an arrow whose length represents the magnitude of the force and whose direction shows the direction of the force. A coordinate s ...
... An object can be drawn as if it was extracted from its environment and the interactions with the environment identified. A force exerted on an object can be represented as an arrow whose length represents the magnitude of the force and whose direction shows the direction of the force. A coordinate s ...
Forces - Needham.K12.ma.us
... continue to move without help. Think of the bike again. If someone is riding a bike and jumps off before the bike is stopped what happens? The bike continues on until it falls over. The tendency of an object to remain still, or keep moving in a straight line at a steady speed is called ...
... continue to move without help. Think of the bike again. If someone is riding a bike and jumps off before the bike is stopped what happens? The bike continues on until it falls over. The tendency of an object to remain still, or keep moving in a straight line at a steady speed is called ...
Newtons First Law
... If one force is greater than the other the object will move in the direction of the larger force Motion only changes if forces are unbalanced Motion changes in the direction of the greater force ...
... If one force is greater than the other the object will move in the direction of the larger force Motion only changes if forces are unbalanced Motion changes in the direction of the greater force ...
Review Game - SCHOOLinSITES
... paint sticks to the canvas, the total momentum of the paint and canvas a. is zero. c. is equal and opposite. b. increases. d. decreases. ...
... paint sticks to the canvas, the total momentum of the paint and canvas a. is zero. c. is equal and opposite. b. increases. d. decreases. ...
Class 10 Newton’s third law | Friction PHY 231 Fall 2004
... equal and opposite force (somewhere in the universe) balancing it out. This means that the net force of these two forces must be zero. F=ma => there can be no acceleration; nothing accelerates. 1. True, but Newton’s 3rd law only works part of the time 2. False, Newton’s 3rd law is wrong 3. False, Ne ...
... equal and opposite force (somewhere in the universe) balancing it out. This means that the net force of these two forces must be zero. F=ma => there can be no acceleration; nothing accelerates. 1. True, but Newton’s 3rd law only works part of the time 2. False, Newton’s 3rd law is wrong 3. False, Ne ...
Chapter 5 (Cont.) Newton`s Laws of Motion
... accelerating an object • Newton’s first law: if the net force on an object is zero, its velocity is constant • Inertial frame of reference: one in which the first law holds • Newton’s second law: • Free-body diagram: a sketch showing all the forces on an object Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, In ...
... accelerating an object • Newton’s first law: if the net force on an object is zero, its velocity is constant • Inertial frame of reference: one in which the first law holds • Newton’s second law: • Free-body diagram: a sketch showing all the forces on an object Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, In ...
ii. The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Feynman
... Motion with constant speed and constant acceleration Examples Vectors & Scalars; Vector addition (geometrical) ; Vector components, Unit vector, Addition of vectors by components; Vector multiplication, Scalar and vector product and their physical significance Examples Motion in two dimensions; Disp ...
... Motion with constant speed and constant acceleration Examples Vectors & Scalars; Vector addition (geometrical) ; Vector components, Unit vector, Addition of vectors by components; Vector multiplication, Scalar and vector product and their physical significance Examples Motion in two dimensions; Disp ...