Problem: Average Velocity (1988)
... arise from one force, or from a combination of sources. Fc = F = mac Fc = F = m v2 / r Centripetal forces always arise from other forces. Since speed of object remains constant, kinetic energy remains constant, and work is zero. Friction, tension, normal force, gravity and the magnetic force are c ...
... arise from one force, or from a combination of sources. Fc = F = mac Fc = F = m v2 / r Centripetal forces always arise from other forces. Since speed of object remains constant, kinetic energy remains constant, and work is zero. Friction, tension, normal force, gravity and the magnetic force are c ...
Physics Beyond 2000
... uniform motion in a straight line unless it is acted upon by external forces . • Linear air track – Vehicle without external force – Vehicle under constant force ...
... uniform motion in a straight line unless it is acted upon by external forces . • Linear air track – Vehicle without external force – Vehicle under constant force ...
Lecture 5.1
... with negligible friction and at (almost) constant speed on any level surface. After the puck has left the instructor’s hands the horizontal forces on the puck are: ...
... with negligible friction and at (almost) constant speed on any level surface. After the puck has left the instructor’s hands the horizontal forces on the puck are: ...
Forces
... required to accelerate a 1 kg mass 1 m/s2. – So 1N causes a mass to change its velocity at a rate of 1m/sec. – Example: A 1kg object is accelerated by a 1N force. If it starts with Vi = 0, what is Vf after one second? Two? Four? • Hint: a = 1m/sec2 ...
... required to accelerate a 1 kg mass 1 m/s2. – So 1N causes a mass to change its velocity at a rate of 1m/sec. – Example: A 1kg object is accelerated by a 1N force. If it starts with Vi = 0, what is Vf after one second? Two? Four? • Hint: a = 1m/sec2 ...
Physics Section 3 Newton`s Laws of Motion 3.6 Second Law of
... s_____ l___ of m_____ shows that force can be defined as the product of mass and acceleration. F stands for F_____. NET stands for the sum of all the forces impacting the object. m stands for m____. a stands for a_____. Net force is shown by the equation FNET = ma. The s_____ l___ of m_____ shows th ...
... s_____ l___ of m_____ shows that force can be defined as the product of mass and acceleration. F stands for F_____. NET stands for the sum of all the forces impacting the object. m stands for m____. a stands for a_____. Net force is shown by the equation FNET = ma. The s_____ l___ of m_____ shows th ...
F 1 - s3.amazonaws.com
... 2. Objects at the ends of a taut rope have the same magnitude velocity and acceleration 3. Frictionless and massless pulleys only change direction of rope, not the tension. ...
... 2. Objects at the ends of a taut rope have the same magnitude velocity and acceleration 3. Frictionless and massless pulleys only change direction of rope, not the tension. ...
Forces - Red Eagle Physics!
... • “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” – The forces that are mutually exerted on two objects are called an “action-reaction pair” – Action and reaction forces do not always result in equilibrium… • Hammer and nail ...
... • “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” – The forces that are mutually exerted on two objects are called an “action-reaction pair” – Action and reaction forces do not always result in equilibrium… • Hammer and nail ...
Momentum - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... Collisions and explosions happen so quickly that it is often impossible to calculate anything more than an average force. This is because the force changes so quickly. By examining the momentum before and after the interaction between 2 objects, we can determine impulse. ...
... Collisions and explosions happen so quickly that it is often impossible to calculate anything more than an average force. This is because the force changes so quickly. By examining the momentum before and after the interaction between 2 objects, we can determine impulse. ...
Forces and Motion
... Lastly, gravity. This is a force of attraction being applied between 2 objects. This is occurring because the earth has mass greater than every object, like for example, if you drop an acorn or a piano, it will gain velocity at the same rate. Gravity or the gravitational force is a force of attract ...
... Lastly, gravity. This is a force of attraction being applied between 2 objects. This is occurring because the earth has mass greater than every object, like for example, if you drop an acorn or a piano, it will gain velocity at the same rate. Gravity or the gravitational force is a force of attract ...
Week 8 - Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces
... any other examples for which a force has a significant effect on the motion without doing any work? Solution: The answer is that it can, without doing any work, change the direction of the velocity and therefore it’s motion. If the particle only has changes to it’s velocity and not it’s speed the ki ...
... any other examples for which a force has a significant effect on the motion without doing any work? Solution: The answer is that it can, without doing any work, change the direction of the velocity and therefore it’s motion. If the particle only has changes to it’s velocity and not it’s speed the ki ...
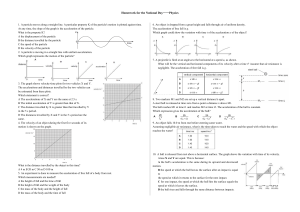
Homework for the National Day——Physics 1. A particle moves
... (c) Use your answers in (a) and (b) to determine the time T taken for the boy to catch up with the girl. ...
... (c) Use your answers in (a) and (b) to determine the time T taken for the boy to catch up with the girl. ...
Form B
... Which vehicle experiences the largest force? The largest magnitude of force is always experienced by the vehicle with the Newton's 3rd law: At the point of contact, the forces have equal magnitudes and opposite directions on the two objects. A) largest initial speed B) smallest initial speed C) larg ...
... Which vehicle experiences the largest force? The largest magnitude of force is always experienced by the vehicle with the Newton's 3rd law: At the point of contact, the forces have equal magnitudes and opposite directions on the two objects. A) largest initial speed B) smallest initial speed C) larg ...
Fall Final Review 15-16 File
... Examples: Complete all examples in the space provided. Show all work including units. 1. Consider the two displacement vectors given below and complete / evaluate each of the following. a = 2.0m north b = 2.0m east a) What two parts does every vector have (by definition)? b) What is the significance ...
... Examples: Complete all examples in the space provided. Show all work including units. 1. Consider the two displacement vectors given below and complete / evaluate each of the following. a = 2.0m north b = 2.0m east a) What two parts does every vector have (by definition)? b) What is the significance ...