Document
... For a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis through O with an angular velocity w, O ...
... For a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis through O with an angular velocity w, O ...
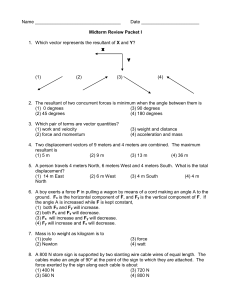
POP4e: Ch. 1 Problems
... object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forces act at the same point on the object. (d) The object is in equilibrium if the net force and ...
... object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forces act at the same point on the object. (d) The object is in equilibrium if the net force and ...
Momentum
... When one object is moving hits an object that is moving at a different velocity some momentum is passed on or transferred. When a moving object hit a nonmoving object all the momentum is transferred to the object that was not moving. ...
... When one object is moving hits an object that is moving at a different velocity some momentum is passed on or transferred. When a moving object hit a nonmoving object all the momentum is transferred to the object that was not moving. ...
28. Unit 11 Study Guide
... There is a significantly greater frictional force between the first marble and the concrete surface than between the second marble and the icy surface. How will the increase in friction affect the distance the first marble travels? ~More friction will cause the first marble to slow down and stop BEF ...
... There is a significantly greater frictional force between the first marble and the concrete surface than between the second marble and the icy surface. How will the increase in friction affect the distance the first marble travels? ~More friction will cause the first marble to slow down and stop BEF ...
Explanation of Newton´s laws with simple and accessible
... Abstract— In this paper one proposes the accomplishment of different demonstrative experiments and of classroom, by means of which we achieve the base to explain the essence of Newton's laws, achieving a major attention and motivation of the pupil. These experiments are simple and that anyone can ac ...
... Abstract— In this paper one proposes the accomplishment of different demonstrative experiments and of classroom, by means of which we achieve the base to explain the essence of Newton's laws, achieving a major attention and motivation of the pupil. These experiments are simple and that anyone can ac ...
net force
... Action and Reaction • Newton’s first two laws explain how the motion of a single object changes • Newton’s 3rd law explains what happens when an object exerts a force on another object • Newton’s 3rd Law: For every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction ...
... Action and Reaction • Newton’s first two laws explain how the motion of a single object changes • Newton’s 3rd law explains what happens when an object exerts a force on another object • Newton’s 3rd Law: For every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction ...
linacs_CAS_al_2 - Indico
... the synchronous particles enters/exits a cavity. • For a given cavity length there is an optimum velocity (or beta) such that a particle traveling at this velocity goes through the cavity in half ...
... the synchronous particles enters/exits a cavity. • For a given cavity length there is an optimum velocity (or beta) such that a particle traveling at this velocity goes through the cavity in half ...
teacher background information force
... zero), the magnitude of the net force acting on the object is equal to zero. This law states that if the forces are balanced, meaning the magnitude of the net force is equal to zero, then an object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant velocity (same direction, same speed). Ne ...
... zero), the magnitude of the net force acting on the object is equal to zero. This law states that if the forces are balanced, meaning the magnitude of the net force is equal to zero, then an object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant velocity (same direction, same speed). Ne ...
File - Akers Physics
... • Linear momentum, the product of an object’s inertial mass and linear velocity p=mv is conserved in a closed system. • Describes how difficult it is to stop a moving object. • Angular momentum (L) the product of an objects moment of inertia and its angular velocity about the center of mass, is also ...
... • Linear momentum, the product of an object’s inertial mass and linear velocity p=mv is conserved in a closed system. • Describes how difficult it is to stop a moving object. • Angular momentum (L) the product of an objects moment of inertia and its angular velocity about the center of mass, is also ...
Newton`s Second Law
... • Engine Force (FE) – Force applied to propel the train along the tracks. • Opposition Force (Fo) – friction between the tracks, wind resistance, etc. that attempts to slow the train down. • Which force was larger? • What is the acceleration of the train? Negative, Zero, or Positive. • Is this an eq ...
... • Engine Force (FE) – Force applied to propel the train along the tracks. • Opposition Force (Fo) – friction between the tracks, wind resistance, etc. that attempts to slow the train down. • Which force was larger? • What is the acceleration of the train? Negative, Zero, or Positive. • Is this an eq ...
SPW Chapter 4 PPT
... • Momentum, however, can be transferred from one object to another. • The law of conservation of momentum states that if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t change. ...
... • Momentum, however, can be transferred from one object to another. • The law of conservation of momentum states that if a group of objects exerts forces only on each other, their total momentum doesn’t change. ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion Conclusion
... 4.4 Equilibrium Application of Newton’s Laws of Motion ...
... 4.4 Equilibrium Application of Newton’s Laws of Motion ...