Syllabus Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level PHYSICS
... Papers 1 and 2 will assess the AS parts of the Core. Section A of Paper 4 will assess the A2 parts of the Core. Section B of Paper 4 will assess Applications of Physics (Section VII). The A2 parts of the syllabus, which will be examined only in the full Advanced Level qualification, are indicated in ...
... Papers 1 and 2 will assess the AS parts of the Core. Section A of Paper 4 will assess the A2 parts of the Core. Section B of Paper 4 will assess Applications of Physics (Section VII). The A2 parts of the syllabus, which will be examined only in the full Advanced Level qualification, are indicated in ...
The Physics of Quantum Mechanics
... 1. From amplitude to probability. For every possible action there is an associated amplitude, such that probability for the action = |amplitude for the action|2 . 2. Actions in series. If an action takes place through two stages, the amplitude for that action is the product of the amplitudes for eac ...
... 1. From amplitude to probability. For every possible action there is an associated amplitude, such that probability for the action = |amplitude for the action|2 . 2. Actions in series. If an action takes place through two stages, the amplitude for that action is the product of the amplitudes for eac ...
MHD toy model of the solar radiative zone
... where Ωeq is the rotation rate at the equator and θ is the colatitude. The numbers a and b are determined by the observations. Near the lower region of the convective zone a = 0.17 and b = 0.08 (Schou et al. [4]). Meanwhile the radiative zone is near-uniformly rotating at a rate Ωrz ' 0.93Ωeq where ...
... where Ωeq is the rotation rate at the equator and θ is the colatitude. The numbers a and b are determined by the observations. Near the lower region of the convective zone a = 0.17 and b = 0.08 (Schou et al. [4]). Meanwhile the radiative zone is near-uniformly rotating at a rate Ωrz ' 0.93Ωeq where ...
Chapter 7
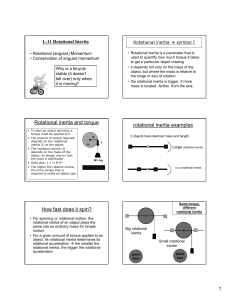
... • Orbiting objects are in free fall. • To see how this idea is true, we can use a thought experiment that Newton developed. Consider a cannon sitting on a high mountaintop. Each successive cannonball has a greater initial speed, so the horizontal distance that the ball travels increases. If the init ...
... • Orbiting objects are in free fall. • To see how this idea is true, we can use a thought experiment that Newton developed. Consider a cannon sitting on a high mountaintop. Each successive cannonball has a greater initial speed, so the horizontal distance that the ball travels increases. If the init ...
Going Down
... The answer was given by Sir Isaac Newton more than 300 years ago. He explained the way in which forces—pushes and pulls— influence motion. Newton summed up his explanations in three clear and concise laws. These laws explain what—and how much—is needed to make an object move. They also explain what ...
... The answer was given by Sir Isaac Newton more than 300 years ago. He explained the way in which forces—pushes and pulls— influence motion. Newton summed up his explanations in three clear and concise laws. These laws explain what—and how much—is needed to make an object move. They also explain what ...
Chapter 12
... farther and the scale reading increases. Units of Force Force is measured in newtons, abbreviated as N. One newton is the force that causes a 1-kilogram mass to accelerate at a rate of 1 meter per second each second (1 m /s2). In fact, 1 newton is equal to 1 kilogram-meter per second squared (1 N = ...
... farther and the scale reading increases. Units of Force Force is measured in newtons, abbreviated as N. One newton is the force that causes a 1-kilogram mass to accelerate at a rate of 1 meter per second each second (1 m /s2). In fact, 1 newton is equal to 1 kilogram-meter per second squared (1 N = ...
Wells Problem Workbook Pack
... from start to the point in question and add the absolute values of the areas (ignore negatives). - AVERAGE velocity or speed over 1 individual segment only use v(bar) = (Vi + Vf) / 2 (velocity would have a direction, speed would not) or v(bar) = d / t (d = displacement for velocity, d = distance for ...
... from start to the point in question and add the absolute values of the areas (ignore negatives). - AVERAGE velocity or speed over 1 individual segment only use v(bar) = (Vi + Vf) / 2 (velocity would have a direction, speed would not) or v(bar) = d / t (d = displacement for velocity, d = distance for ...
Current-induced magnetic vortex motion by spin
... Figure 2共b兲 shows the time evolution of volume-averaged magnetization, which exhibits the spiral motion of vortex core. It is noted that the rotational direction is opposite to the case of analytical result because of the replacement បS / a3 → −M s / ␥0. Figure 3 shows that vortex displacement as a ...
... Figure 2共b兲 shows the time evolution of volume-averaged magnetization, which exhibits the spiral motion of vortex core. It is noted that the rotational direction is opposite to the case of analytical result because of the replacement បS / a3 → −M s / ␥0. Figure 3 shows that vortex displacement as a ...