Chandler`s Downward Acceleration Of WTC1
... since the measured acceleration is downward, the net force is also downward. Since the net force in this case is made up of gravity (acting downward) and structural resistance (acting upward), the upward resistance must be weaker than the gravitational force. However the gravitational force on the u ...
... since the measured acceleration is downward, the net force is also downward. Since the net force in this case is made up of gravity (acting downward) and structural resistance (acting upward), the upward resistance must be weaker than the gravitational force. However the gravitational force on the u ...
(Theory of electromagnetism and the light) Author: Arman
... the spring and after that we extension that to these formulas. We have in the Hock law that F=-k x and the negative mark of the law is for the third law of the Newton that when we enter a force to the spring it will enter a force as the same that and in the different sign. So here we have the same o ...
... the spring and after that we extension that to these formulas. We have in the Hock law that F=-k x and the negative mark of the law is for the third law of the Newton that when we enter a force to the spring it will enter a force as the same that and in the different sign. So here we have the same o ...
PPT
... “At x=0 all spring potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and so the velocity will be greatest at this point.” ...
... “At x=0 all spring potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and so the velocity will be greatest at this point.” ...
Algebra course map sample
... How do you factor a quadratic expression completely? How do you know if there are roots to a quadratic equation? How do you find the roots of a quadratic equation? How can you predict what a parabola will look like? How can you find the equation of a parabola? What is special about zero? ...
... How do you factor a quadratic expression completely? How do you know if there are roots to a quadratic equation? How do you find the roots of a quadratic equation? How can you predict what a parabola will look like? How can you find the equation of a parabola? What is special about zero? ...
chapter 7
... total linear momentum of any system is the resultant of the linear momenta of the constituents. The people who are standing around have zero momentum. Those who move randomly carry momentum randomly in all directions. Since there is such a large number of people, there is, on average, just as much l ...
... total linear momentum of any system is the resultant of the linear momenta of the constituents. The people who are standing around have zero momentum. Those who move randomly carry momentum randomly in all directions. Since there is such a large number of people, there is, on average, just as much l ...
PPMF201A - Lecture 2
... gently attached to it. The spring is then set up horizontally with the 0.300-kg mass resting on a frictionless table. The mass is pushed so that the spring is compressed 0.100 m from the equilibrium point, and released from rest. Determine: (a) the spring stiffness constant k and angular frequency ω ...
... gently attached to it. The spring is then set up horizontally with the 0.300-kg mass resting on a frictionless table. The mass is pushed so that the spring is compressed 0.100 m from the equilibrium point, and released from rest. Determine: (a) the spring stiffness constant k and angular frequency ω ...
Analyzing a Dual Fan Carts Motion (Low Tech).
... This experiment can produce significant errors between F and ma if not performed carefully. Check the students’ setups after they adjust the track angle so that the cart maintains a constant velocity along the track when given a nudge. This balances the slowing effects of friction between the cart a ...
... This experiment can produce significant errors between F and ma if not performed carefully. Check the students’ setups after they adjust the track angle so that the cart maintains a constant velocity along the track when given a nudge. This balances the slowing effects of friction between the cart a ...
Physics – Module 1 – Moving About
... Instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any particular point in time. Average speed is the distance traveled during a particular period of time divided by the time itself. Instantaneous and average speeds are both scalar quantities. Velocity is a measure of the time rate of displacement. It ...
... Instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any particular point in time. Average speed is the distance traveled during a particular period of time divided by the time itself. Instantaneous and average speeds are both scalar quantities. Velocity is a measure of the time rate of displacement. It ...
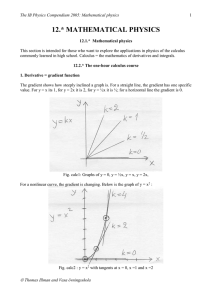
12. MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS
... integration constant. In physics we can mostly set C = 0, for example as in: (u + at)dt = ... = ut + ½at2 but we should really have ... = s0 + ut + ½at2 where s0 is the displacement at the time t = 0. But this can usually be set to zero by defining s = 0 when t = 0; that is we start measuring the t ...
... integration constant. In physics we can mostly set C = 0, for example as in: (u + at)dt = ... = ut + ½at2 but we should really have ... = s0 + ut + ½at2 where s0 is the displacement at the time t = 0. But this can usually be set to zero by defining s = 0 when t = 0; that is we start measuring the t ...
V p
... Two equations, two unknowns. How would you solve? You would probably solve (1) for Vpfx (or VHefx) in terms of the other unknown, plug the result into (2), and solve the quadratic. Not impossibly difficult here, but what do you do about the sign? And what about more complex problems, where the hel ...
... Two equations, two unknowns. How would you solve? You would probably solve (1) for Vpfx (or VHefx) in terms of the other unknown, plug the result into (2), and solve the quadratic. Not impossibly difficult here, but what do you do about the sign? And what about more complex problems, where the hel ...
Quantum mechanics and path integrals
... integral quantization. Path integrals (also sometimes called functional integrals) are an infinite-dimensional analogue of ordinary integrals, and so before learning about path integrals, we will first work through the corresponding derivatives, known as functional derivatives. We will begin by stud ...
... integral quantization. Path integrals (also sometimes called functional integrals) are an infinite-dimensional analogue of ordinary integrals, and so before learning about path integrals, we will first work through the corresponding derivatives, known as functional derivatives. We will begin by stud ...
Gravity and Tides A New Scientific Era Isaac Newton (1643
... •! This acceleration is constantly changing the moon’s direction of Earth motion, holding it on its almost circular ...
... •! This acceleration is constantly changing the moon’s direction of Earth motion, holding it on its almost circular ...
Physics_Test_01
... continue to travel at constant velocity due to their inertia which is slower than the tram which is accelerating, thus they move backwards relative to the tram. ...
... continue to travel at constant velocity due to their inertia which is slower than the tram which is accelerating, thus they move backwards relative to the tram. ...
Chapter 7 - TESD home
... A ballistic pendulum is a device that was used to measure the speed of bullets before electronic timing devices were developed. The device consists of a large block of wood of mass, M = 5.4 kg, hanging from two long cords. A bullet of mass, m = 9.5 g is fired into the block, coming quickly to rest. ...
... A ballistic pendulum is a device that was used to measure the speed of bullets before electronic timing devices were developed. The device consists of a large block of wood of mass, M = 5.4 kg, hanging from two long cords. A bullet of mass, m = 9.5 g is fired into the block, coming quickly to rest. ...