Test 2 Review
... Changing Motion and Turning. According to Newton's First Law, an object in motion continues moving in a straight line unless it is acted on by a force. Planets orbit the sun in an almost circular path. They are not violating Newton's First Law. They are obeying Newton's Second Law. The sun is exerti ...
... Changing Motion and Turning. According to Newton's First Law, an object in motion continues moving in a straight line unless it is acted on by a force. Planets orbit the sun in an almost circular path. They are not violating Newton's First Law. They are obeying Newton's Second Law. The sun is exerti ...
Summary of the unit on force, motion, and energy
... Another way to state the Law of Inertia is: In the absence of external forces (or when the external forces cancel), an object will maintain constant velocity. Velocity includes both speed and direction. For example, hockey puck coasts in a straight line until deflected by an external force (like a h ...
... Another way to state the Law of Inertia is: In the absence of external forces (or when the external forces cancel), an object will maintain constant velocity. Velocity includes both speed and direction. For example, hockey puck coasts in a straight line until deflected by an external force (like a h ...
Circle Challenges - Utah Education Network
... Topic:!Finding!the!value!of!“B”!in!a!quadratic!of!the!form! Ax + Bx + C !in!order!to!create!a!perfect! ...
... Topic:!Finding!the!value!of!“B”!in!a!quadratic!of!the!form! Ax + Bx + C !in!order!to!create!a!perfect! ...
OCR Physics A Using scalars and vectors Specification references
... Scalar quantities have magnitude but no direction. For example, speed, distance, and time are all scalar quantities. Vector quantities have magnitude and direction. Velocity is a vector quantity: it is speed in a certain direction. When we calculate velocity, v, we need to know the displacement, s. ...
... Scalar quantities have magnitude but no direction. For example, speed, distance, and time are all scalar quantities. Vector quantities have magnitude and direction. Velocity is a vector quantity: it is speed in a certain direction. When we calculate velocity, v, we need to know the displacement, s. ...
hw4a4b_help hint
... 3. pick x – y axis. ( based on acceleration direction for convenience) 4. break up all forces into x-y components 5. Fnet x= m ax , Fnet y= m ay (x,y independent) 6. solve for any two unknowns ( from the above two equations) (Again Math skills here. ) In most cases either ax or ay is zero, if you ch ...
... 3. pick x – y axis. ( based on acceleration direction for convenience) 4. break up all forces into x-y components 5. Fnet x= m ax , Fnet y= m ay (x,y independent) 6. solve for any two unknowns ( from the above two equations) (Again Math skills here. ) In most cases either ax or ay is zero, if you ch ...
Parallel axis theorem
... Newton's Second Law Newton's Second Law as stated below applies to a wide range of physical phenomena, but it is not a fundamental principle like the Conservation Laws. It is applicable only if the force is the net external force. It does not apply directly to situations where the mass is changing, ...
... Newton's Second Law Newton's Second Law as stated below applies to a wide range of physical phenomena, but it is not a fundamental principle like the Conservation Laws. It is applicable only if the force is the net external force. It does not apply directly to situations where the mass is changing, ...
Name(s) Hr. ____ Investigating Newton`s Second Law by Pulling a
... Background: Isaac Newton comes up with three laws (or guidelines) of motion. These laws integrate (or bring together) the concept of the force (push or pull) with our concepts of motion. The first law states that to change the state of motion of an object, we need to place an unbalanced force on tha ...
... Background: Isaac Newton comes up with three laws (or guidelines) of motion. These laws integrate (or bring together) the concept of the force (push or pull) with our concepts of motion. The first law states that to change the state of motion of an object, we need to place an unbalanced force on tha ...
Exercises on Force and Motion Exercise 1.1 A small object is subject
... The California Department of Motor Vehicle Handbook states that if one is driving at a speed of 65 mph and applies the brakes, then it takes a distance of 234.7 feet to come to a stop. What value for acceleration does the DMV use for a car? If we assume that the car slows down with a constant accele ...
... The California Department of Motor Vehicle Handbook states that if one is driving at a speed of 65 mph and applies the brakes, then it takes a distance of 234.7 feet to come to a stop. What value for acceleration does the DMV use for a car? If we assume that the car slows down with a constant accele ...
04_lecture_outline
... is the same. (Twice the force on twice the mass gives the same acceleration g!) ‒ The acceleration of both sets of bricks is the same, (more precisely, ...
... is the same. (Twice the force on twice the mass gives the same acceleration g!) ‒ The acceleration of both sets of bricks is the same, (more precisely, ...
Slides 69-70 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. ...
... 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. ...
Physics218_lecture_006
... B. Net force acting on the table is zero because normal force exerted by the table onto the laptop exactly compensates the force exerted by the laptop (=mg) C. Net force acting on the table is zero because normal force exerted by the floor on the table compensates the force exerted by the laptop on ...
... B. Net force acting on the table is zero because normal force exerted by the table onto the laptop exactly compensates the force exerted by the laptop (=mg) C. Net force acting on the table is zero because normal force exerted by the floor on the table compensates the force exerted by the laptop on ...
Dynamic Modeling of Biped Robot using Lagrangian
... Property 1. The mass matrix is symmetric and positive definite. This can be deduced from the property of the kinetic energy. Property 2. The matrix is skew matrix, if the matrix is described in terms of Christoffel symbols. Property 3. The dynamic equations described in (2) are dependent linearly on ...
... Property 1. The mass matrix is symmetric and positive definite. This can be deduced from the property of the kinetic energy. Property 2. The matrix is skew matrix, if the matrix is described in terms of Christoffel symbols. Property 3. The dynamic equations described in (2) are dependent linearly on ...
Classical Mechanics
... 1. A small ball of mass m is dropped immediately behind a large one of mass M from a height h mach larger then the size of the balls. What is the relationship between m and M if the large ball stops at the floor? Under this condition, how high does the small ball rise? Assume the balls are perfectly ...
... 1. A small ball of mass m is dropped immediately behind a large one of mass M from a height h mach larger then the size of the balls. What is the relationship between m and M if the large ball stops at the floor? Under this condition, how high does the small ball rise? Assume the balls are perfectly ...
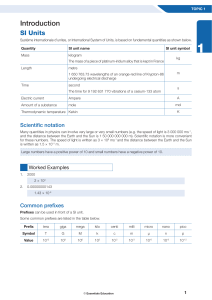
Introduction - Essentials Education
... and temperature. Quantities that have both magnitude and direction are called vector quantities. One example is force (a push or a pull). This is because an object can be pulled or pushed in a given direction e.g. 5 N east. We will come across many vector quantities throughout this course. We will d ...
... and temperature. Quantities that have both magnitude and direction are called vector quantities. One example is force (a push or a pull). This is because an object can be pulled or pushed in a given direction e.g. 5 N east. We will come across many vector quantities throughout this course. We will d ...
Structural Dynamics Prof. P. Banerji Department of Civil Engineering
... So, I just want to state it right at the beginning that, this is not a course on solving linear differential equations, you will have to understand how to solve linear differential equations but that is not the focus of the course. The focus of the course is to establish dynamic factors, which we ca ...
... So, I just want to state it right at the beginning that, this is not a course on solving linear differential equations, you will have to understand how to solve linear differential equations but that is not the focus of the course. The focus of the course is to establish dynamic factors, which we ca ...