Foundation - Physics Instructor Guide
... ELO 2.1 – Define the following as they relate to vectors: scalar quantity, vector quantity, vector component, and resultant. • Scalars - quantities that have magnitude only ⇒ independent of ...
... ELO 2.1 – Define the following as they relate to vectors: scalar quantity, vector quantity, vector component, and resultant. • Scalars - quantities that have magnitude only ⇒ independent of ...
CH. 2 forces sample test
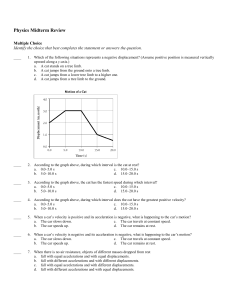
... Air resistance is a type of a. motion. b. acceleration. c. velocity. d. friction. The force of gravity on a person or object at the surface of a planet is known as a. mass. b. inertia. c. air resistance. d. weight. The law of universal gravitation states that any two objects in the universe, without ...
... Air resistance is a type of a. motion. b. acceleration. c. velocity. d. friction. The force of gravity on a person or object at the surface of a planet is known as a. mass. b. inertia. c. air resistance. d. weight. The law of universal gravitation states that any two objects in the universe, without ...
Physics 1st Semester Exam Answer Section
... 9. Consider drops of water leaking from a water faucet. As the drops fall they a. remain at a relatively fixed distance from each other. b. get farther apart. c. get closer together. ...
... 9. Consider drops of water leaking from a water faucet. As the drops fall they a. remain at a relatively fixed distance from each other. b. get farther apart. c. get closer together. ...
1st semester EXAM review and key
... 53. Why does it require much less force to accelerate a low-mass object than it does to accelerate a high-mass object the same amount? 54. How do mass and weight vary with altitude? 55. Distinguish between mass and weight. 56. When a car is moving, what happens to the velocity and acceleration of t ...
... 53. Why does it require much less force to accelerate a low-mass object than it does to accelerate a high-mass object the same amount? 54. How do mass and weight vary with altitude? 55. Distinguish between mass and weight. 56. When a car is moving, what happens to the velocity and acceleration of t ...
Ch 05 Applying Newtons Laws
... 13) A 400-kg box is lifted vertically upward with constant velocity by means of two cables pulling at 40.0° on either side of the vertical direction. What is the tension in each cable? A) 231 N B) 400 N C) 800 N D) 2560 N E) 3920 N Answer: D Var: 1 14) A 10.0-kg picture is held in place by two wire ...
... 13) A 400-kg box is lifted vertically upward with constant velocity by means of two cables pulling at 40.0° on either side of the vertical direction. What is the tension in each cable? A) 231 N B) 400 N C) 800 N D) 2560 N E) 3920 N Answer: D Var: 1 14) A 10.0-kg picture is held in place by two wire ...
Ex. 37 PowerPoint
... caused by friction are added to the system. Remember that in an ideal system, there is no loss of energy due to friction. A real system is one that has friction. All systems in nature are real systems. That is, all systems in nature lose some energy due to friction (usually in the form of heat and s ...
... caused by friction are added to the system. Remember that in an ideal system, there is no loss of energy due to friction. A real system is one that has friction. All systems in nature are real systems. That is, all systems in nature lose some energy due to friction (usually in the form of heat and s ...
Analysis of Symmetric Structures SYMMETRIC STRUCTURES
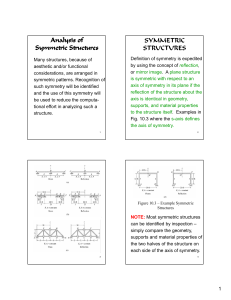
... is symmetric with respect to an axis of symmetry in its plane if the reflection of the structure about the axis is identical in geometry, supports, and material properties to the structure itself. Examples in Fig. 10.3 where the s-axis defines the axis of symmetry. ...
... is symmetric with respect to an axis of symmetry in its plane if the reflection of the structure about the axis is identical in geometry, supports, and material properties to the structure itself. Examples in Fig. 10.3 where the s-axis defines the axis of symmetry. ...
The Hopping Hoop
... The quantity I appearing in (8) and (9) is the moment of inertia of the system consisting of the hoop plus the attached object about the axis that passes through the system center of mass and is perpendicular to the plane of figure 7. Take the attached object to be a mathematical point and show that ...
... The quantity I appearing in (8) and (9) is the moment of inertia of the system consisting of the hoop plus the attached object about the axis that passes through the system center of mass and is perpendicular to the plane of figure 7. Take the attached object to be a mathematical point and show that ...
Newton`s third law
... When two or more objects are connected by strings, pulleys, or are rigidly connected, then they no longer move independently. The constraints between their positions, velocities and accelerations can be used to ease the solving of their motion. For example in the picture below, all three types of co ...
... When two or more objects are connected by strings, pulleys, or are rigidly connected, then they no longer move independently. The constraints between their positions, velocities and accelerations can be used to ease the solving of their motion. For example in the picture below, all three types of co ...
(1 Of 2) Air Track TEACHER
... plane, with either a constant velocity or a constant acceleration. If the cart rolls down the inclined plane with a constant velocity, or stays in place, then the net force on the cart is zero. This is one example of static equilibrium: all of the forces acting on the cart (weight as a result of gra ...
... plane, with either a constant velocity or a constant acceleration. If the cart rolls down the inclined plane with a constant velocity, or stays in place, then the net force on the cart is zero. This is one example of static equilibrium: all of the forces acting on the cart (weight as a result of gra ...
Chapter 2 Review Solutions SPH4C
... Students should also attempt to make connections between the lists under each heading. For example, under “functions” students should list the function of each simple and compound machine they have listed. They can then connect each function to other lists, including domestic applications, industria ...
... Students should also attempt to make connections between the lists under each heading. For example, under “functions” students should list the function of each simple and compound machine they have listed. They can then connect each function to other lists, including domestic applications, industria ...
Document
... RWFD buildings incorporate concrete or masonry walls, which are considered rigid inplane, with flexible horizontal in-plane steel or wood roof diaphragm systems. These rigid walls act as shear walls to provide seismic shear resistance. Concrete wall systems are most often tiltup concrete, a unique f ...
... RWFD buildings incorporate concrete or masonry walls, which are considered rigid inplane, with flexible horizontal in-plane steel or wood roof diaphragm systems. These rigid walls act as shear walls to provide seismic shear resistance. Concrete wall systems are most often tiltup concrete, a unique f ...