Circular
... the track. If R is the reaction acting on the ball bearing at the highest point A of the loop, which of A small object P of mass 0.3 kg is attached to one end of a light, rigid rod of length 0.5 m, which is free to rotate about the other end O as shown. The object is swung to rotate in a vertical ci ...
... the track. If R is the reaction acting on the ball bearing at the highest point A of the loop, which of A small object P of mass 0.3 kg is attached to one end of a light, rigid rod of length 0.5 m, which is free to rotate about the other end O as shown. The object is swung to rotate in a vertical ci ...
Let`s Pause for Two Questions from the Audience
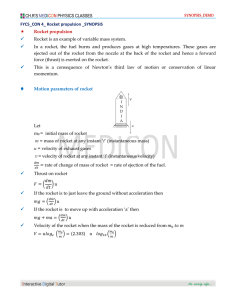
... ΣF represents the net force acting on an object. m represents the mass of an object, which is a numerical measure of its inertia. a represents the acceleration of the object. ...
... ΣF represents the net force acting on an object. m represents the mass of an object, which is a numerical measure of its inertia. a represents the acceleration of the object. ...
I. Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Is the following statement true or false? An astronaut has less mass on the moon since the moon exerts a weaker gravitational force. False! Mass does not depend on gravity, weight does. The astronaut has less weight on the moon. ...
... Is the following statement true or false? An astronaut has less mass on the moon since the moon exerts a weaker gravitational force. False! Mass does not depend on gravity, weight does. The astronaut has less weight on the moon. ...
Motion in accelerated reference frames
... All these forces are seen to be in the plane perpendicular to the fixed rotation axis. Example 1.4 A free particle (unaffected by any physical forces) is observed from a reference frame that rotates with a constant angular velocity ω = ω ez with respect to an inertial frame (ω = const.). Find the equa ...
... All these forces are seen to be in the plane perpendicular to the fixed rotation axis. Example 1.4 A free particle (unaffected by any physical forces) is observed from a reference frame that rotates with a constant angular velocity ω = ω ez with respect to an inertial frame (ω = const.). Find the equa ...
J S U N I L T U... Force Created by Jsunil Tutorial Panjabi colony Gali no. 01
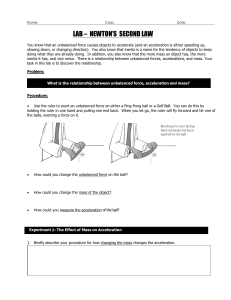
... : An agent that change or try to change the state of an object is called force . A force may be i. Push ii. Pull iii. Gravitational force iv . Frictional force The force applied on a body can bring about the following changes: ☼ It can change the state of rest of a body or change its position ☼ It c ...
... : An agent that change or try to change the state of an object is called force . A force may be i. Push ii. Pull iii. Gravitational force iv . Frictional force The force applied on a body can bring about the following changes: ☼ It can change the state of rest of a body or change its position ☼ It c ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - Brookville Local Schools
... Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the force of the old ball. Now imagine the original ball moving a ...
... Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the force of the old ball. Now imagine the original ball moving a ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion - U
... If the object was sitting still, it will remain stationary. If it was moving at a constant velocity, it will keep moving. It takes net external force to change the motion of an object. ...
... If the object was sitting still, it will remain stationary. If it was moving at a constant velocity, it will keep moving. It takes net external force to change the motion of an object. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... In the absence of a force of friction, the book would continue in motion with the same speed and direction - forever! (Or at least to the end of the table top.) ...
... In the absence of a force of friction, the book would continue in motion with the same speed and direction - forever! (Or at least to the end of the table top.) ...
Work Done By Forces Conservative vs. Nonconservative Forces
... glancing collision, the heights of the two objects when they collide have to different) ○ The collision has to be elastic ○ I don’t have a proof of this, and I am interested in proving it at some point. ...
... glancing collision, the heights of the two objects when they collide have to different) ○ The collision has to be elastic ○ I don’t have a proof of this, and I am interested in proving it at some point. ...
My Skydiving Mishaps: A Quick Lesson in
... immediate acceleration downwards. What the instructors neglected to mention was that if you miss the first instruction and move your leg off the step, there is a very likely chance that your leg will smack into that very step, as it is in the way of your immediate direction down. And that is indeed ...
... immediate acceleration downwards. What the instructors neglected to mention was that if you miss the first instruction and move your leg off the step, there is a very likely chance that your leg will smack into that very step, as it is in the way of your immediate direction down. And that is indeed ...
Force and Circular Motion ppt
... change in direction • Velocity is a vector so acceleration can be produced by a change in magnitude and direction • Centripetal Acceleration is acceleration caused by a change in direction, directed toward the center of a circular path ...
... change in direction • Velocity is a vector so acceleration can be produced by a change in magnitude and direction • Centripetal Acceleration is acceleration caused by a change in direction, directed toward the center of a circular path ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
Hooke`s Law Lab
... F =-kx Where F is the restoring force, k is a constant of proportionality and x is the distance the object has been displaced from its equilibrium position. The minus sign signifies that the restoring force acts in the opposite direction to the displacement of the body from the equilibrium position. ...
... F =-kx Where F is the restoring force, k is a constant of proportionality and x is the distance the object has been displaced from its equilibrium position. The minus sign signifies that the restoring force acts in the opposite direction to the displacement of the body from the equilibrium position. ...
Class Notes
... newton (N) - the amount of force required to accelerate a one kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared. Forces and the accelerations they cause are vector quantities, so we can use the techniques of adding and resolving vectors to analyze the acceleration of objects that have any nu ...
... newton (N) - the amount of force required to accelerate a one kilogram mass at a rate of one meter per second squared. Forces and the accelerations they cause are vector quantities, so we can use the techniques of adding and resolving vectors to analyze the acceleration of objects that have any nu ...
Aging and Stiffness
... Newton’s Laws of Motion IIb. Law of Angular Acceleration – a torque will accelerate an object in the direction of the torque, at a rate inversely proportional to the moment of inertia of the object T=I Torque – the rotational effect of a force applied at a distance to an axis ...
... Newton’s Laws of Motion IIb. Law of Angular Acceleration – a torque will accelerate an object in the direction of the torque, at a rate inversely proportional to the moment of inertia of the object T=I Torque – the rotational effect of a force applied at a distance to an axis ...