Ch11a Powerpoint
... Circular motion describes motion of any point on the radius. Angular motion is descriptive of motion of the entire radius. When a ball is held as the arm moves in a windmill fashion ball is moving with circular motion. arm acts as a radius moving with angular motion. ...
... Circular motion describes motion of any point on the radius. Angular motion is descriptive of motion of the entire radius. When a ball is held as the arm moves in a windmill fashion ball is moving with circular motion. arm acts as a radius moving with angular motion. ...
Big Science Idea - Science
... More than one force can act on an object at a time. The forces can push or pull in any direction. What happens to the object when the forces act depends on two things: → How strong the forces are → The direction of the forces When more than one force acts on an object, the forces combine to form a n ...
... More than one force can act on an object at a time. The forces can push or pull in any direction. What happens to the object when the forces act depends on two things: → How strong the forces are → The direction of the forces When more than one force acts on an object, the forces combine to form a n ...
chapter12
... A physical pendulum can be used to measure the moment of inertia of a flat rigid object ...
... A physical pendulum can be used to measure the moment of inertia of a flat rigid object ...
Work-Energy Principle
... Figure 6: Free body diagram of vehicle falling along curve. The two forces on the vehicle are the normal force, N , and the force due to gravity mg. Figure by MIT OCW. ...
... Figure 6: Free body diagram of vehicle falling along curve. The two forces on the vehicle are the normal force, N , and the force due to gravity mg. Figure by MIT OCW. ...
Physphax Review
... 28. Two basic types: a/ contact: normal, tension, friction. b/ at a distance: weight & other field forces 29. Isolate all forces with a free-body diagram. Draw only forces (no v, p, etc) acting on the object. Resultant force depends on angle between vectors: Add if 00, Subtract if 1800, etc, as in # ...
... 28. Two basic types: a/ contact: normal, tension, friction. b/ at a distance: weight & other field forces 29. Isolate all forces with a free-body diagram. Draw only forces (no v, p, etc) acting on the object. Resultant force depends on angle between vectors: Add if 00, Subtract if 1800, etc, as in # ...
Regents Review Sheets - Benjamin N. Cardozo High School
... 28. Two basic types: a/ contact: normal, tension, friction. b/ at a distance: weight & other field forces 29. Isolate all forces with a free-body diagram. Draw only forces (no v, p, etc) acting on the object. Resultant force depends on angle between vectors: Add if 00, Subtract if 1800, etc, as in # ...
... 28. Two basic types: a/ contact: normal, tension, friction. b/ at a distance: weight & other field forces 29. Isolate all forces with a free-body diagram. Draw only forces (no v, p, etc) acting on the object. Resultant force depends on angle between vectors: Add if 00, Subtract if 1800, etc, as in # ...
Mav Mark 10/17/11 - Madison County Schools
... • Unbalanced forces acting on an object result in a net force and cause a change in the object’s motion. Balanced forces acting on an object do not change the object’s motion. ...
... • Unbalanced forces acting on an object result in a net force and cause a change in the object’s motion. Balanced forces acting on an object do not change the object’s motion. ...
Are You suprised
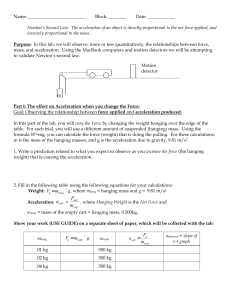
... Purpose: In this lab, we will observe, more or less quantitatively, the relationships between force, mass, and acceleration. Using the MacBook computers and motion detectors we will be attempting to validate Newton’s second law. Motion detector ...
... Purpose: In this lab, we will observe, more or less quantitatively, the relationships between force, mass, and acceleration. Using the MacBook computers and motion detectors we will be attempting to validate Newton’s second law. Motion detector ...
Chapter 2 - Bakersfield College
... A. Isaac Newton formulated the three laws of motion. B. The first law of motion states: If no net force acts on it, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant velocity. C. A force is any influence that can cause an object to be accelerated. D. Every acc ...
... A. Isaac Newton formulated the three laws of motion. B. The first law of motion states: If no net force acts on it, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant velocity. C. A force is any influence that can cause an object to be accelerated. D. Every acc ...
Forces Webquest Focus Questions
... All objects in the universe attract each other through ______________. ...
... All objects in the universe attract each other through ______________. ...
Lecture1_Inertia
... An object subject to a constant net external force will D. move with increasing speed. If any unbalanced force can start an object moving…then a continuously applied force can only make it move faster and faster. People are confused when friction is high enough that an object slows to rest shortly a ...
... An object subject to a constant net external force will D. move with increasing speed. If any unbalanced force can start an object moving…then a continuously applied force can only make it move faster and faster. People are confused when friction is high enough that an object slows to rest shortly a ...
1.2 Single Particle Kinematics
... reaction seems not to hold. For example, a current i1 flowing through a wire segment d~s1 ~ = µ0 i1 d~s1 × contributes, according to the law of Biot and Savart, a magnetic field dB ~r/4π|r|3 at a point ~r away from the current element. If a current i2 flows through a segment of wire d~s2 at that poi ...
... reaction seems not to hold. For example, a current i1 flowing through a wire segment d~s1 ~ = µ0 i1 d~s1 × contributes, according to the law of Biot and Savart, a magnetic field dB ~r/4π|r|3 at a point ~r away from the current element. If a current i2 flows through a segment of wire d~s2 at that poi ...
No Slide Title
... More general: PEgravity=-GMEarthm/r PE=0 at infinity distance from the center of the earth See example 7.12 for consistency between these two. Example: escape speed: what should the minimum initial velocity of a rocket be if we want to make sure it will not fall back to earth? KEi+PEi=0.5mv2-GMEarth ...
... More general: PEgravity=-GMEarthm/r PE=0 at infinity distance from the center of the earth See example 7.12 for consistency between these two. Example: escape speed: what should the minimum initial velocity of a rocket be if we want to make sure it will not fall back to earth? KEi+PEi=0.5mv2-GMEarth ...
Document
... Polygon Method To add vectors using the polygon method, position vectors so that they are tail (dot) to head (arrow). The resultant is the vector from the initial point (tail) of the first vector to the terminal point (head) of the second. When you move the vector(s), make sure that the magnitude a ...
... Polygon Method To add vectors using the polygon method, position vectors so that they are tail (dot) to head (arrow). The resultant is the vector from the initial point (tail) of the first vector to the terminal point (head) of the second. When you move the vector(s), make sure that the magnitude a ...
Newton`s Second Law
... • Engine Force (FE) – Force applied to propel the train along the tracks. • Opposition Force (Fo) – friction between the tracks, wind resistance, etc. that attempts to slow the train down. • Which force was larger? • What is the acceleration of the train? Negative, Zero, or Positive. • Is this an eq ...
... • Engine Force (FE) – Force applied to propel the train along the tracks. • Opposition Force (Fo) – friction between the tracks, wind resistance, etc. that attempts to slow the train down. • Which force was larger? • What is the acceleration of the train? Negative, Zero, or Positive. • Is this an eq ...
File - Phy 2048-0002
... speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure Quantum mechanics I. Newton’s first law: If no net force acts on a body, then the body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and di ...
... speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure Quantum mechanics I. Newton’s first law: If no net force acts on a body, then the body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and di ...