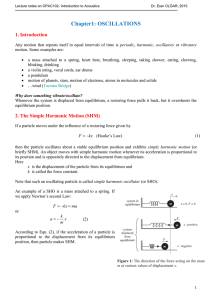
1.8 Circular Motion
... Since a body moving in a circle (or a circular arc) is accelerating, it follows from Newton’s first law of motion that there must be a force acting on it to cause the acceleration. The direction of this force is also towards the centre, therefore this force is called centripetal force. By Newton’s s ...
... Since a body moving in a circle (or a circular arc) is accelerating, it follows from Newton’s first law of motion that there must be a force acting on it to cause the acceleration. The direction of this force is also towards the centre, therefore this force is called centripetal force. By Newton’s s ...
AP B MC Midterm Answers 2004
... 42. A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a package on the seat of the car to slide toward the right side of the car. Which of the following is true of the net force on the package while it is sliding? a) The force is directed away from the cent ...
... 42. A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a package on the seat of the car to slide toward the right side of the car. Which of the following is true of the net force on the package while it is sliding? a) The force is directed away from the cent ...
Classical mechanics
... speed of light, nor of subatomic particles moving inside atoms. The years from about 1900 to 1930 saw the development of relativistic mechanics primarily to describe fastmoving bodies and of quantum mechanics primarily to describe subatomic systems. Faced with this competition, one might expect clas ...
... speed of light, nor of subatomic particles moving inside atoms. The years from about 1900 to 1930 saw the development of relativistic mechanics primarily to describe fastmoving bodies and of quantum mechanics primarily to describe subatomic systems. Faced with this competition, one might expect clas ...
2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected
... If an object is to be in translational equilibrium, there must be no net force on it. This translates into three separate requirements—that there be no force in the x-direction, the y-direction, or the z-direction. ...
... If an object is to be in translational equilibrium, there must be no net force on it. This translates into three separate requirements—that there be no force in the x-direction, the y-direction, or the z-direction. ...
Forces! - Ottawa Hills Local School District
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
File
... subsystems may be chosen where one or more conservation laws apply. 2. Is there an external force? If so, is the collision time short enough that you can ignore it? 3. Draw diagrams of the initial and final situations, with momentum vectors labeled. 4. Choose a coordinate system. ...
... subsystems may be chosen where one or more conservation laws apply. 2. Is there an external force? If so, is the collision time short enough that you can ignore it? 3. Draw diagrams of the initial and final situations, with momentum vectors labeled. 4. Choose a coordinate system. ...
Chapter 7
... • The system includes all the objects interacting with each other • Can be generalized to any number of objects ...
... • The system includes all the objects interacting with each other • Can be generalized to any number of objects ...
Wednesday, April 2, 2008
... I F t p p f p i 0 mv r r 70kg 7.7m / s j 540 jN s ...
... I F t p p f p i 0 mv r r 70kg 7.7m / s j 540 jN s ...
hw2 - forces - Uplift North Hills Prep
... 16. In her physics lab, Molly puts a 1.0-kg mass on a 2.0-kg block of wood. She pulls the combination across another wooden board with a constant speed to determine the coefficient of sliding friction between the two surfaces. If Molly must pull with a force of 6.0 N, what coefficient of sliding fri ...
... 16. In her physics lab, Molly puts a 1.0-kg mass on a 2.0-kg block of wood. She pulls the combination across another wooden board with a constant speed to determine the coefficient of sliding friction between the two surfaces. If Molly must pull with a force of 6.0 N, what coefficient of sliding fri ...
4-6 - mrhsluniewskiscience
... very light fishing line that has a breaking strength of 28 N. The fisherman unfortunately loses the fish as the line snaps. What can you say about the mass of the fish? Practice #2: A 15.0-kg bucket is lowered by a rope in which there is 163 N of tension. What is the acceleration of the bucket? Is i ...
... very light fishing line that has a breaking strength of 28 N. The fisherman unfortunately loses the fish as the line snaps. What can you say about the mass of the fish? Practice #2: A 15.0-kg bucket is lowered by a rope in which there is 163 N of tension. What is the acceleration of the bucket? Is i ...
A feather falls through the air more slowly than a brick because of
... Friction causes the ball’s motion to get slower the farther it moves through the air. Because the ball’s velocity is changing as it moves, it can be determined that the forces acting on the ball are unbalanced. ...
... Friction causes the ball’s motion to get slower the farther it moves through the air. Because the ball’s velocity is changing as it moves, it can be determined that the forces acting on the ball are unbalanced. ...
Springs Virtual Lab
... The "Reset" button brings the body of pendulum to its initial position. You can start or stop and continue the simulation with the other two buttons. If you choose the option "Slow Motion", the movement will be five times slower. The spring constant, the mass and the amplitude of the oscillation can ...
... The "Reset" button brings the body of pendulum to its initial position. You can start or stop and continue the simulation with the other two buttons. If you choose the option "Slow Motion", the movement will be five times slower. The spring constant, the mass and the amplitude of the oscillation can ...
force-problems-with-acceleration-2-step
... 5. A 50 kg skater pushed by a friend accelerates 5 m/sec2. How much force did the friend apply? F = ma f= 50 x 5 f= 250 N How fast was she going after 1.2 seconds? 6 m/s 6. A force of 250 N is applied to an object that accelerates at a rate of 5 m/sec2. What is the mass of the object? F = ma 250N=(m ...
... 5. A 50 kg skater pushed by a friend accelerates 5 m/sec2. How much force did the friend apply? F = ma f= 50 x 5 f= 250 N How fast was she going after 1.2 seconds? 6 m/s 6. A force of 250 N is applied to an object that accelerates at a rate of 5 m/sec2. What is the mass of the object? F = ma 250N=(m ...