Kinematics
... SOH: Sine of = Opposite side divided by Hypotenuse. CAH: Cosine of = Adjacent side divided by Hypotenuse. TOA: Tangent of = Opposite side divided by Adjacent side. This will be especially useful for dealing with vectors that point in more than one direction. We can use these definitions to exp ...
... SOH: Sine of = Opposite side divided by Hypotenuse. CAH: Cosine of = Adjacent side divided by Hypotenuse. TOA: Tangent of = Opposite side divided by Adjacent side. This will be especially useful for dealing with vectors that point in more than one direction. We can use these definitions to exp ...
AP Physics – Applying Forces
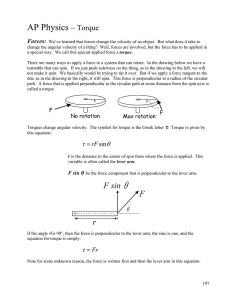
... We’ve learned that forces change the velocity of an object. But what does it take to change the angular velocity of a thing? Well, forces are involved, but the force has to be applied in a special way. We call this special applied force a torque. There are many ways to apply a force to a system that ...
... We’ve learned that forces change the velocity of an object. But what does it take to change the angular velocity of a thing? Well, forces are involved, but the force has to be applied in a special way. We call this special applied force a torque. There are many ways to apply a force to a system that ...
Elastic Potential Energy
... it neutral position. It is now released. Neglecting the mass of the spring and assuming that the mass is sliding on a frictionless surface, how fast will the mass move as it passes the neutral position of the spring? (4) A 5.0 g pellet is placed in the barrel of a toy gun and is propelled by a sprin ...
... it neutral position. It is now released. Neglecting the mass of the spring and assuming that the mass is sliding on a frictionless surface, how fast will the mass move as it passes the neutral position of the spring? (4) A 5.0 g pellet is placed in the barrel of a toy gun and is propelled by a sprin ...
Basic_MD
... correct quantum treatment. Much more important than absolute accuracy of the trajectories is adherence of the whole system to conservation of energy and momentum. Failure in this regard implies failure to sample the correct statistical mechanical ensemble. Small fluctuations in energy conservation c ...
... correct quantum treatment. Much more important than absolute accuracy of the trajectories is adherence of the whole system to conservation of energy and momentum. Failure in this regard implies failure to sample the correct statistical mechanical ensemble. Small fluctuations in energy conservation c ...
Item #
... Then one of your group member says “Both the truck and the car exerts a force on the other vehicle but the truck exerts a larger force because the truck has more mass is going to do more damage to the car and the car will be pushed back.” How do you think about the students’ reasoning? “Force is cal ...
... Then one of your group member says “Both the truck and the car exerts a force on the other vehicle but the truck exerts a larger force because the truck has more mass is going to do more damage to the car and the car will be pushed back.” How do you think about the students’ reasoning? “Force is cal ...
Force Motion Pasco Lab
... Newton's Second Law – Constant Force (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor) PURPOSE The purpose of this laboratory activity is to investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. THEORY Newton described the relationship between acceleration, force, and mass as follows: The acceleration of ...
... Newton's Second Law – Constant Force (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor) PURPOSE The purpose of this laboratory activity is to investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. THEORY Newton described the relationship between acceleration, force, and mass as follows: The acceleration of ...
PPT
... If we look at the projection onto the x axis of an object moving in a circle of radius A at a constant speed vmax, we find that the x component of its velocity varies as: ...
... If we look at the projection onto the x axis of an object moving in a circle of radius A at a constant speed vmax, we find that the x component of its velocity varies as: ...
Getting mathematical - Teaching Advanced Physics
... x = A sin 2ft or x = A sin t f is the frequency of the oscillation, and is related to the period T by f = 1/T. The amplitude of the oscillation is A. Velocity: v = 2f A cos 2ft = A cos t Acceleration: a = - (2f)2 A sin 2ft = -2 A sin t Depending on your students’ mathematical knowledge, y ...
... x = A sin 2ft or x = A sin t f is the frequency of the oscillation, and is related to the period T by f = 1/T. The amplitude of the oscillation is A. Velocity: v = 2f A cos 2ft = A cos t Acceleration: a = - (2f)2 A sin 2ft = -2 A sin t Depending on your students’ mathematical knowledge, y ...
Circular Motion Lab
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
AP Physics - Circular Motion Lab
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
A 1 - Andes Physics Tutor
... 4. Seatbelts provide two main advantages in a car accident: (i) they keep you from being thrown from the car, and (ii) they reduce the force that acts on you during the collision to survivable levels. The second benefit can be illustrated by comparing the net force exerted on the driver of a car in ...
... 4. Seatbelts provide two main advantages in a car accident: (i) they keep you from being thrown from the car, and (ii) they reduce the force that acts on you during the collision to survivable levels. The second benefit can be illustrated by comparing the net force exerted on the driver of a car in ...
CTEnergyAnsFa06
... point as before, would the work done by gravity be the .. A) same, or B) different. Answer: the same! Any journey can be thought of a series of small vertical or horizontal displacements. During any horizontal segment, the work done by gravity is zero. All upward vertical segments are cancelled by c ...
... point as before, would the work done by gravity be the .. A) same, or B) different. Answer: the same! Any journey can be thought of a series of small vertical or horizontal displacements. During any horizontal segment, the work done by gravity is zero. All upward vertical segments are cancelled by c ...