Chapter 2 - OnCourse
... one block on table, one hanging down connected by string Net Force = Fg - Ft Solve for acceleration and tension Same acceleration (different direction) and same tension throughout system Atwood’s Machine Relationship between mass and acceleration with two masses on a pulley Labs Newton’s 2nd Law, Fr ...
... one block on table, one hanging down connected by string Net Force = Fg - Ft Solve for acceleration and tension Same acceleration (different direction) and same tension throughout system Atwood’s Machine Relationship between mass and acceleration with two masses on a pulley Labs Newton’s 2nd Law, Fr ...
ppt document
... can see that the biceps have to exert a large force to hold up a relatively light weight! What advantage does this give? Note how far the biceps have to contract in order to move the weight! This is the advantage of the elbow setup! In practice, we use clubs and rackets to make this ...
... can see that the biceps have to exert a large force to hold up a relatively light weight! What advantage does this give? Note how far the biceps have to contract in order to move the weight! This is the advantage of the elbow setup! In practice, we use clubs and rackets to make this ...
CST Review - cloudfront.net
... A stationary object that stays stationary and a moving object continues to move in a straight line at constant velocity because of: A) force. B) gravity. C) momentum. D) inertia. ...
... A stationary object that stays stationary and a moving object continues to move in a straight line at constant velocity because of: A) force. B) gravity. C) momentum. D) inertia. ...
shm-intro - Mrs Physics
... 3. When an 80.0 kg person climbs into an 1100 kg car, the car's springs compress vertically by 1.2 cm. What will be the frequency of vibration when the car hits a bump? 1.18 Hz 4. A spring vibrates with a frequency of 2.4 Hz when a weight of 0.60 kg is hung from it. What will its frequency be if onl ...
... 3. When an 80.0 kg person climbs into an 1100 kg car, the car's springs compress vertically by 1.2 cm. What will be the frequency of vibration when the car hits a bump? 1.18 Hz 4. A spring vibrates with a frequency of 2.4 Hz when a weight of 0.60 kg is hung from it. What will its frequency be if onl ...
Lab 1500-5 - Otterbein University
... the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. However, according to Newton, the force merely changes the velocity. It is the acceleration, not the velocity, that is proportional to the force. Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a mu ...
... the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. However, according to Newton, the force merely changes the velocity. It is the acceleration, not the velocity, that is proportional to the force. Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a mu ...
Section 2 Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation
... • The gravitational forces that two masses exert on each other are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. • This is an example of Newton’s third law of motion. • One example is the Earth-moon system, shown on the next slide. • As a result of these forces, the moon and Earth each orbit ...
... • The gravitational forces that two masses exert on each other are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. • This is an example of Newton’s third law of motion. • One example is the Earth-moon system, shown on the next slide. • As a result of these forces, the moon and Earth each orbit ...
Lab3_Friction (donot print)
... of the block. Hint: Do not press the block down upon the horizontal surface, set it down gently. Why? Also, will you do several trials, or is one enough? Finally, to make life easier for you, be sure that your applied force is perfectly horizontal (Why?). Now consider the effect of the weight of the ...
... of the block. Hint: Do not press the block down upon the horizontal surface, set it down gently. Why? Also, will you do several trials, or is one enough? Finally, to make life easier for you, be sure that your applied force is perfectly horizontal (Why?). Now consider the effect of the weight of the ...
Chapter 5: Forces and Motion II
... in the knee are flat and horizontal. 11. •As a skydiver falls faster and faster through the air, does his acceleration increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain your answer. SSM 12. •Why do raindrops fall from the sky at different speeds? Explain your answer. 13. •Why might your car start to s ...
... in the knee are flat and horizontal. 11. •As a skydiver falls faster and faster through the air, does his acceleration increase, decrease, or remain the same? Explain your answer. SSM 12. •Why do raindrops fall from the sky at different speeds? Explain your answer. 13. •Why might your car start to s ...
pp\momentum - Dr. Robert MacKay
... Introduction Newtons 3 laws of motion 1. Law of inertia 2. Net Force = mass x acceleration ...
... Introduction Newtons 3 laws of motion 1. Law of inertia 2. Net Force = mass x acceleration ...
F - Cloudfront.net
... constant speed by an applied force. The applied force is parallel to the ramp, and points towards the top of the ramp. The coefficient of friction between the ramp and the surface is 0.400 and the block is pulled a distance of 5.00 meters up the ramp. What is the work done by each force? What is the ...
... constant speed by an applied force. The applied force is parallel to the ramp, and points towards the top of the ramp. The coefficient of friction between the ramp and the surface is 0.400 and the block is pulled a distance of 5.00 meters up the ramp. What is the work done by each force? What is the ...
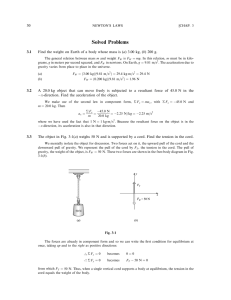
Kinetic Friction Experiment
... 3. Place the wood side of the block against the track and add 500 g of mass on top of the friction block. (What is the mass that will now slide along the track?) The block should be at least 30 cm in front of the motion sensor. 4. Attach a pulley as shown in Figure 2. Place the larger area wood sur ...
... 3. Place the wood side of the block against the track and add 500 g of mass on top of the friction block. (What is the mass that will now slide along the track?) The block should be at least 30 cm in front of the motion sensor. 4. Attach a pulley as shown in Figure 2. Place the larger area wood sur ...