THE MODIFIED ROSCHIN GODINSEARL GENERATORS - ExMF-PS
... and require some theoretical explanation. Unfortunately, the interpretation of the results within the framework of the conventional physical theory cannot explain all the observed phenomena besides the change of the weight” [2]. Based on the new approach in fundamental physics as introduced by The M ...
... and require some theoretical explanation. Unfortunately, the interpretation of the results within the framework of the conventional physical theory cannot explain all the observed phenomena besides the change of the weight” [2]. Based on the new approach in fundamental physics as introduced by The M ...
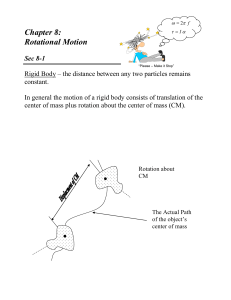
Rolling Motion: • A motion that is a combination of rotational
... • Other components often cancel by symmetry Conservation of Angular Momentum: • If any component of the net external torque on a system is zero, then the component of the angular momentum of the system along that axis is conserved. • If a rotating object can some how changes its moment of inertia by ...
... • Other components often cancel by symmetry Conservation of Angular Momentum: • If any component of the net external torque on a system is zero, then the component of the angular momentum of the system along that axis is conserved. • If a rotating object can some how changes its moment of inertia by ...
Ch.6 Momentum
... 2 Object Momentum Conservation • momentum before = momentum after • (m1v1)initial + (m2v2)initial = (m1v1)final + (m2v2)final • When can we use this equation? • When net force due to all other objects acting on 1 and 2 is zero. • Or, very soon after collision ends ...
... 2 Object Momentum Conservation • momentum before = momentum after • (m1v1)initial + (m2v2)initial = (m1v1)final + (m2v2)final • When can we use this equation? • When net force due to all other objects acting on 1 and 2 is zero. • Or, very soon after collision ends ...
Examine the forces exerted on objects by gravity
... any more because of air resistance, it is said to be at terminal velocity In Earth’s atmosphere, leaves fall slower than rocks In a vacuum, they both fall at the same rate ...
... any more because of air resistance, it is said to be at terminal velocity In Earth’s atmosphere, leaves fall slower than rocks In a vacuum, they both fall at the same rate ...
Newton`s First Law - Swift
... This tells us two things. One is that the speed at which an object falls does not depend on its mass. The second is that if the acceleration due to gravity were different (say, on another planet) you’d weigh a different amount. These two concepts are the basis of the classroom activities. Additional ...
... This tells us two things. One is that the speed at which an object falls does not depend on its mass. The second is that if the acceleration due to gravity were different (say, on another planet) you’d weigh a different amount. These two concepts are the basis of the classroom activities. Additional ...
Basic Physics and Collision Detection
... move, and D is constant • Assume uniform acceleration • Position of falling object at time t: • x(t) = x0 • y(t) = y0 + 1/2 * 9.8 m/s2 * t2 • Incrementally, y += gravity (normalized to frame rate) ...
... move, and D is constant • Assume uniform acceleration • Position of falling object at time t: • x(t) = x0 • y(t) = y0 + 1/2 * 9.8 m/s2 * t2 • Incrementally, y += gravity (normalized to frame rate) ...
2.3 Extra practice for quiz
... b. Determine mathematically the magnitude and direction of the external net force on Sam. ...
... b. Determine mathematically the magnitude and direction of the external net force on Sam. ...
Astronomy Day Two
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncomp resse d) de com press or are nee ded to s ee this picture. ...
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncomp resse d) de com press or are nee ded to s ee this picture. ...
Work and Energy
... Work and Energy 22. Now select the portion of the graph corresponding to the first 20 cm of stretch (twice the stretch). Find the work done to stretch the spring 20 cm. Record the value in the data table. 23. Select the portion of the graph corresponding to the maximum stretch you achieved. Find th ...
... Work and Energy 22. Now select the portion of the graph corresponding to the first 20 cm of stretch (twice the stretch). Find the work done to stretch the spring 20 cm. Record the value in the data table. 23. Select the portion of the graph corresponding to the maximum stretch you achieved. Find th ...
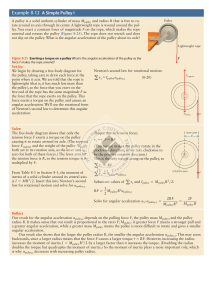
Rotational Dynamics
... • The angular acceleration this torque produces depends on the mass of the rotating object and upon the distribution of its mass with respect to the axis of rotation. • If the mass remains fixed in position, torque and angular acceleration are directly proportional. • If the mass is closer to the ...
... • The angular acceleration this torque produces depends on the mass of the rotating object and upon the distribution of its mass with respect to the axis of rotation. • If the mass remains fixed in position, torque and angular acceleration are directly proportional. • If the mass is closer to the ...